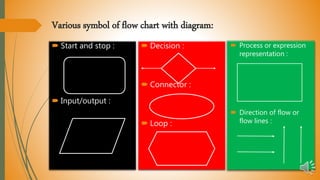
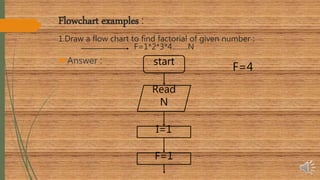
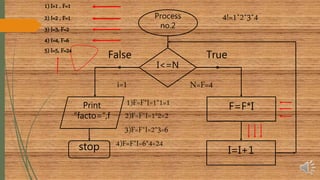
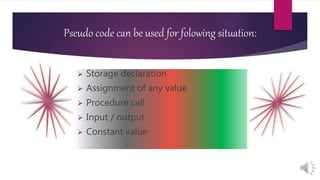
The document explains flowcharts and algorithms, defining flowcharts as graphical representations used for problem-solving in programming, and algorithms as finite sequences of steps for systematic problem-solving. It includes examples of flowcharts for calculating factorials and reversing numbers, highlighting their usefulness in understanding logic and sequence before coding. Additionally, it introduces pseudocode as a simplified language to express algorithms in a structured form.