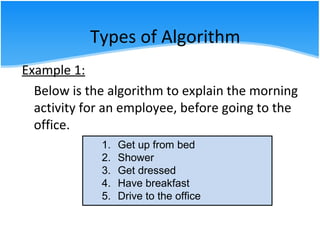
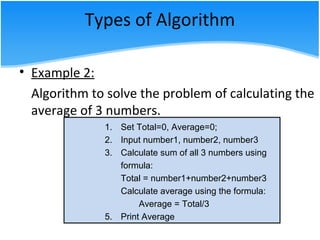
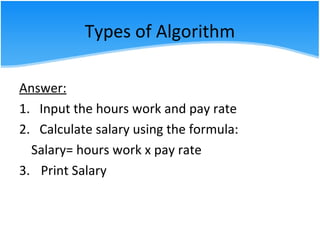
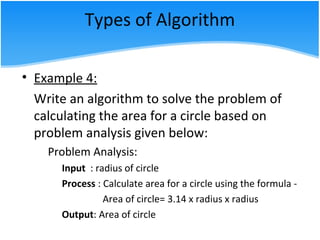
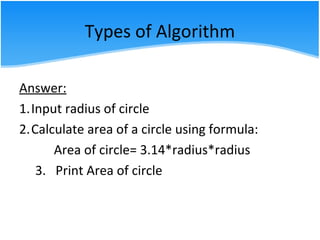
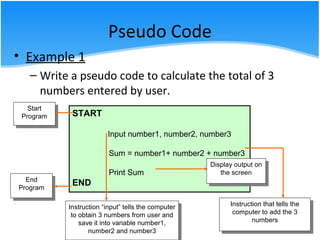
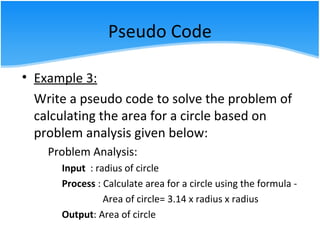
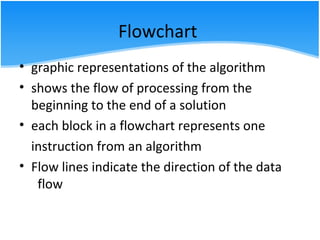
The document outlines various algorithm types and their application in problem-solving through step-by-step instructions. It includes examples of algorithms, pseudo code, and flowcharts, illustrating how to calculate a salary, the area of a circle, and discounts on items. Additionally, it describes the differences between pseudo code and flowcharts, emphasizing their roles in programming.