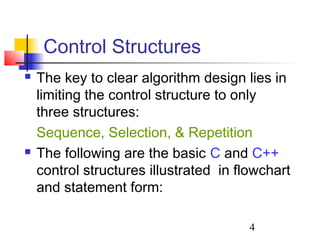
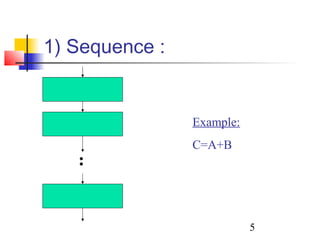
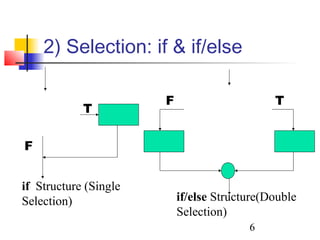
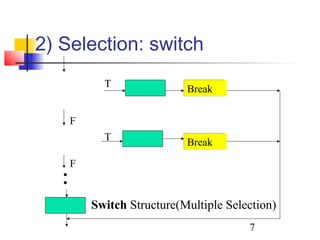
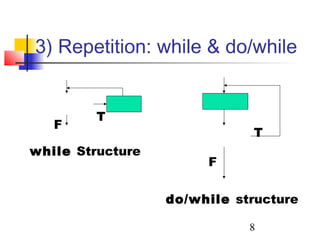
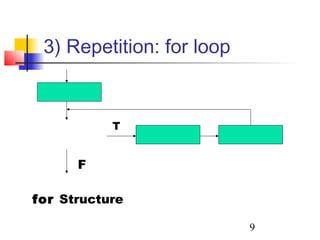
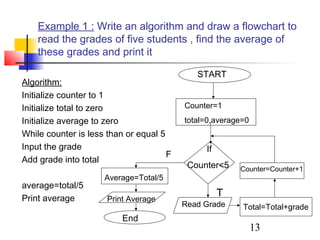
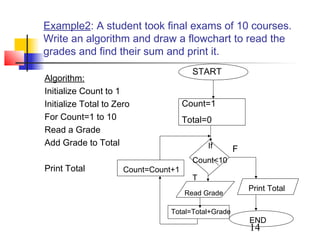
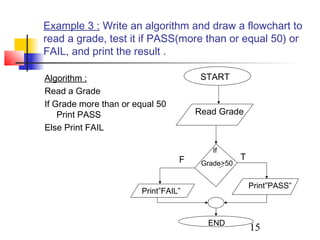
This document discusses algorithms and flowcharts. It defines an algorithm as an unambiguous set of executable steps to solve a problem. The key control structures for algorithms are sequence, selection, and repetition. It provides examples of algorithms using pseudocode and flowcharts to read grades, calculate averages, and determine if a grade passes or fails.