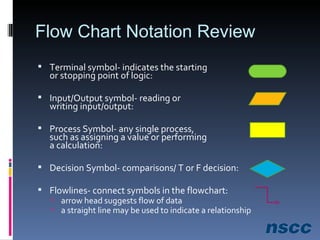
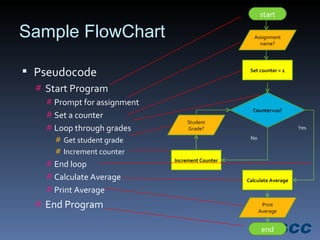
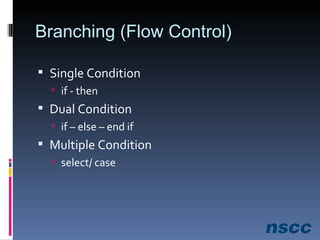
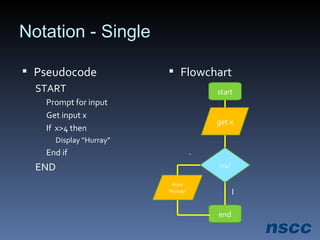
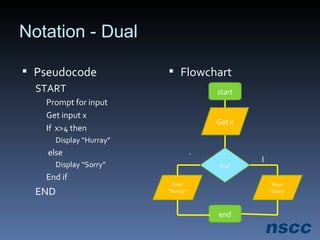
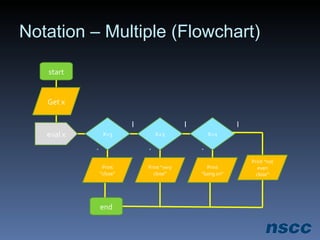
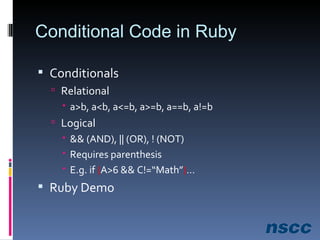
The document outlines a lesson plan focused on conditional logic, including pseudocode and flowchart basics, which involves making decisions based on conditions. It explains the structure of pseudocode, provides examples of flowchart symbols, and details how to implement conditional operators in code using Ruby. Additionally, it discusses project work requirements and evaluation criteria for the students' assignments.