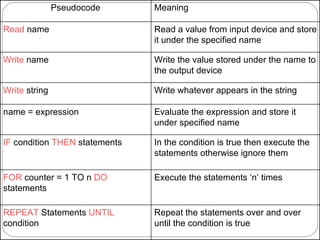
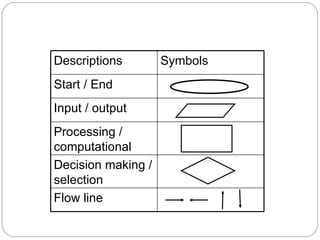
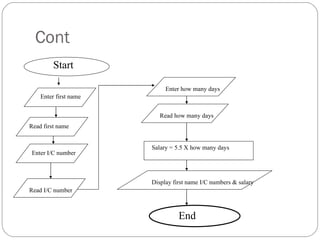
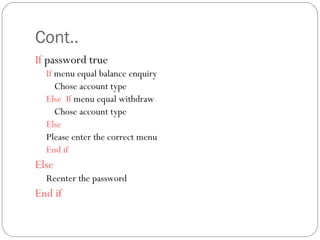
This document provides an overview of programming concepts and control structures. It discusses pseudocode and flowcharts as tools for designing algorithms to solve problems. Different control structures are introduced, including sequence, selection, and repetition structures. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts such as getting user input, making decisions, and repeating steps. The key learning goals are to understand how to design algorithms using control structures and represent them using pseudocode and flowcharts.