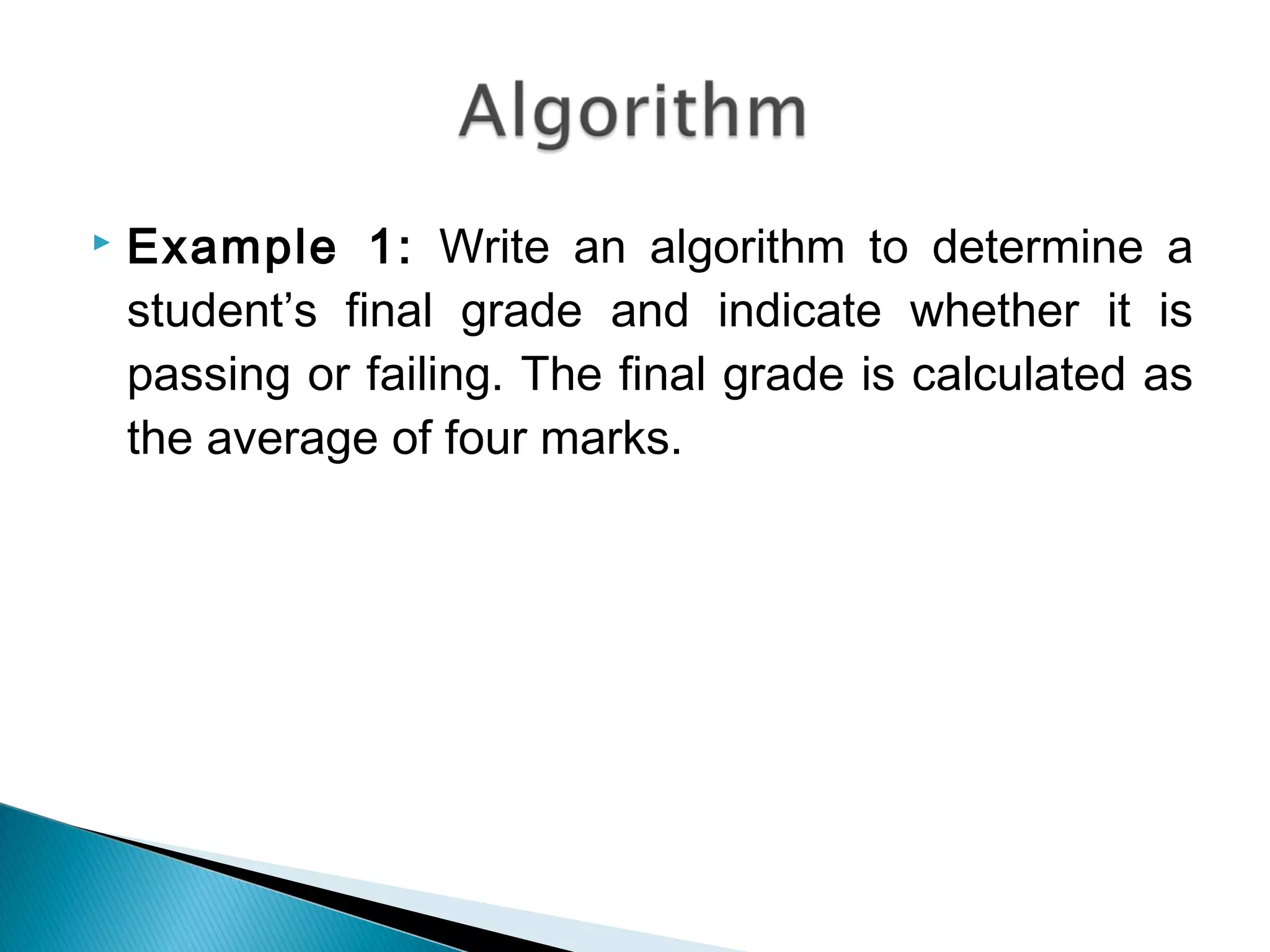
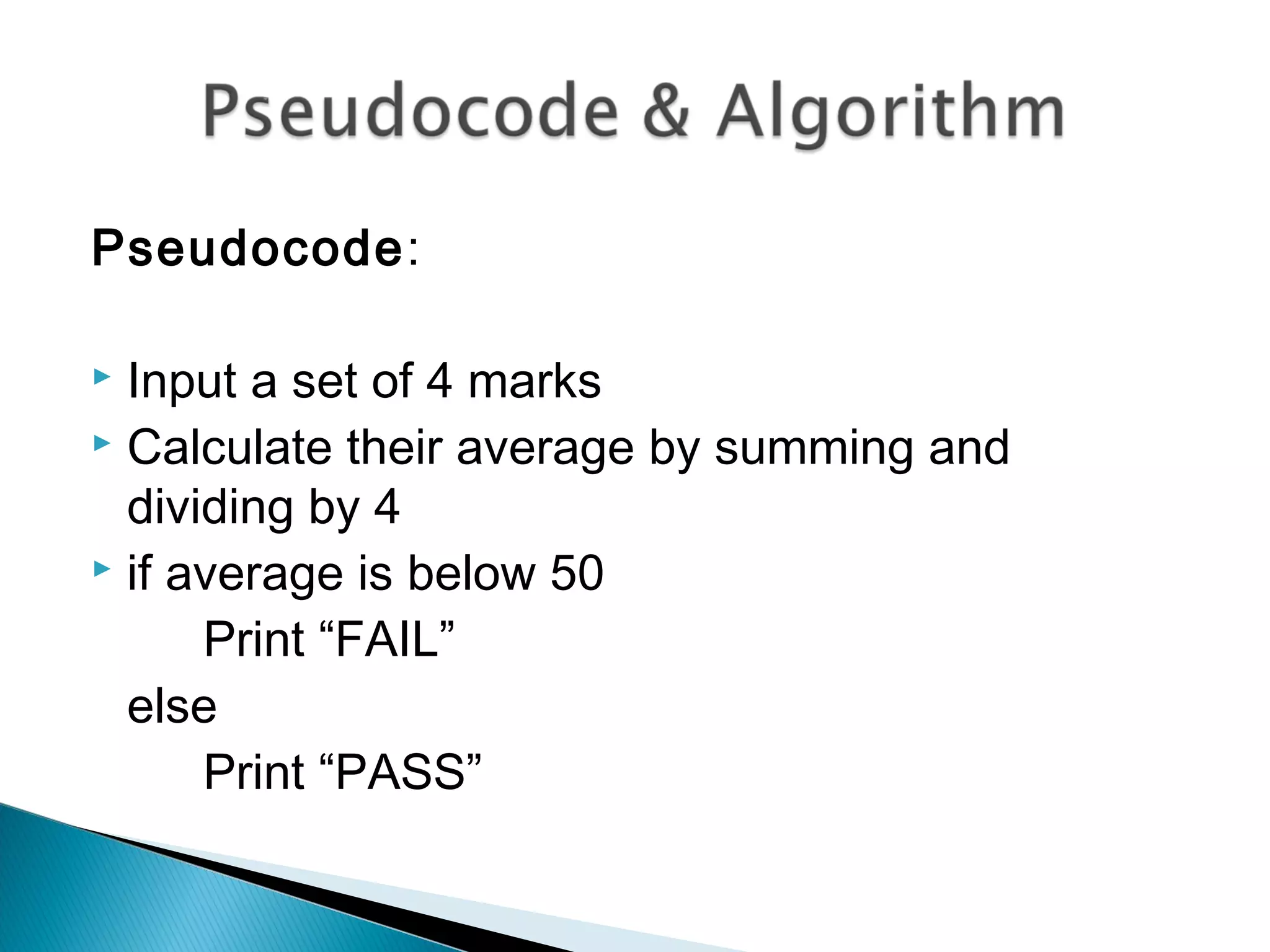
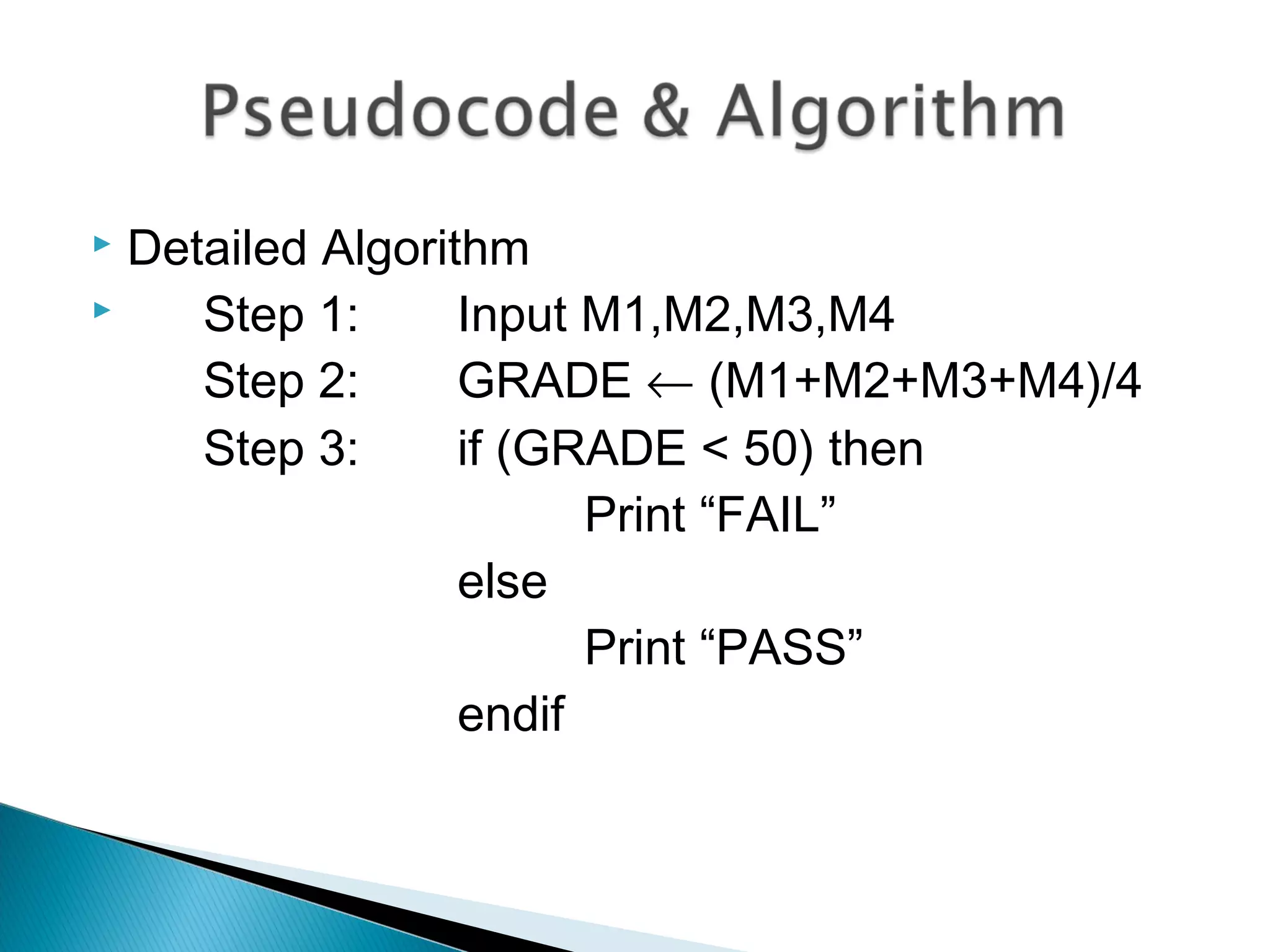
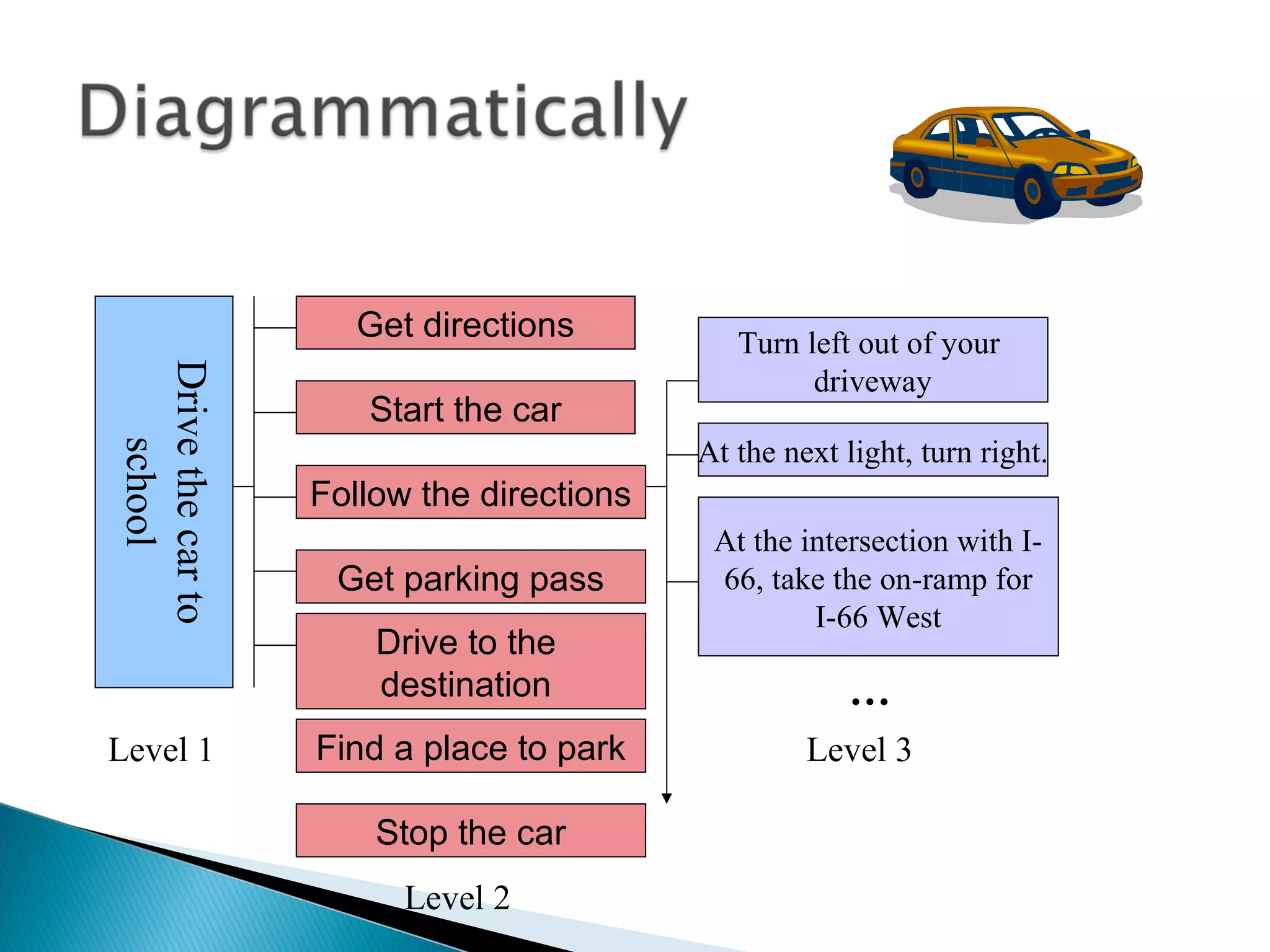
This document discusses algorithms and how to create good algorithms. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure to solve a problem. It lists properties of good algorithms as being simple, complete, correct, with appropriate abstraction and precision. The document provides examples of algorithms using pseudocode and discusses different types of algorithms like sequence, decision, and repetition. It also outlines the steps to create an algorithm as analyzing the problem, designing a solution, implementing the program, testing it, and validating it works under all circumstances.