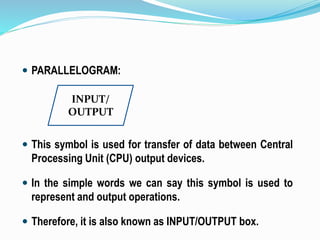
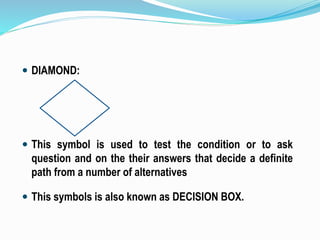
The document discusses the problem-solving process in computing, detailing stages like problem definition, algorithm development, and flowchart creation. It highlights the importance of these stages in accurately solving problems while providing examples of algorithms and flowcharts for various tasks. The document also defines common symbols used in flowcharts and their respective functions.