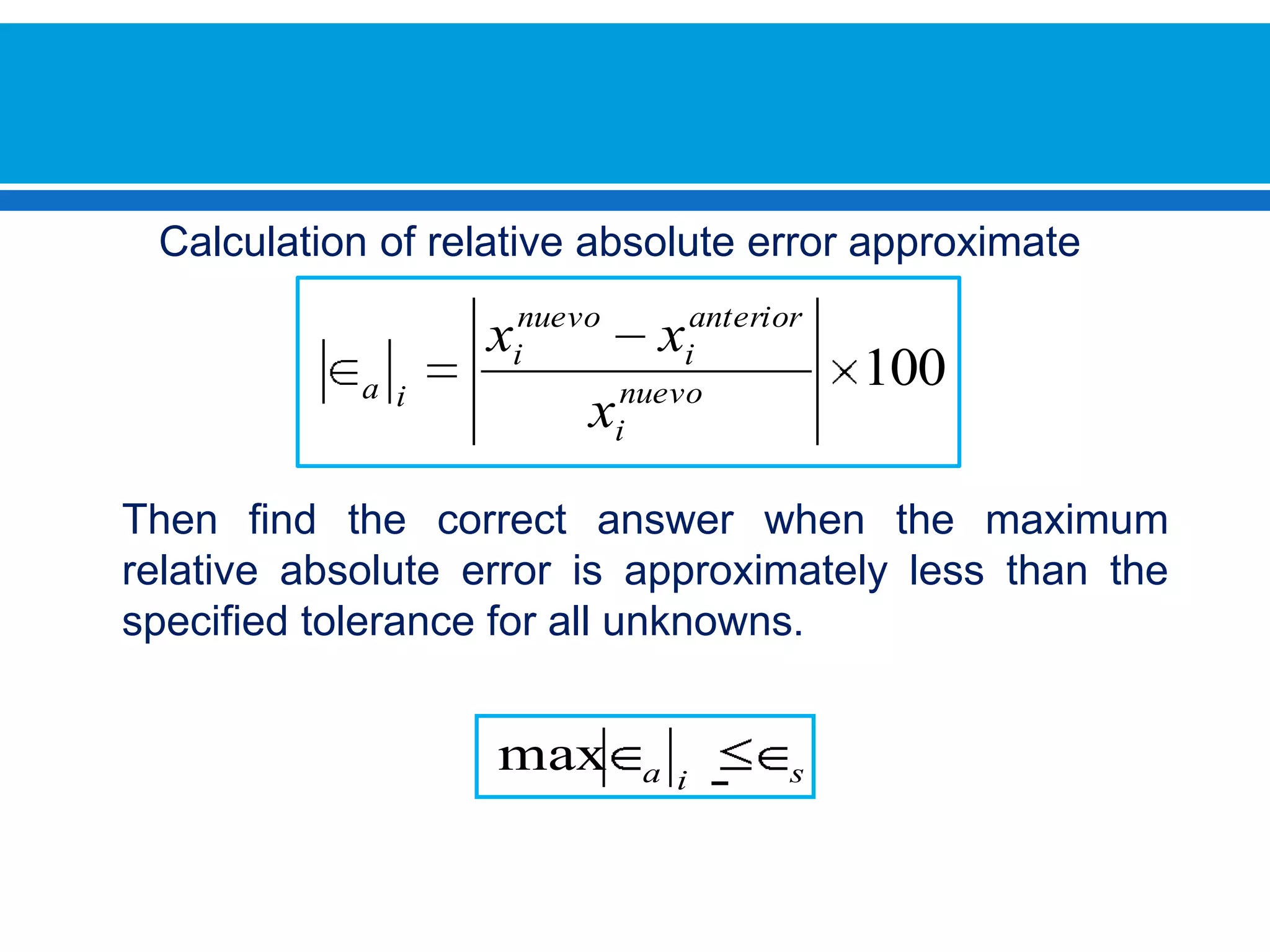
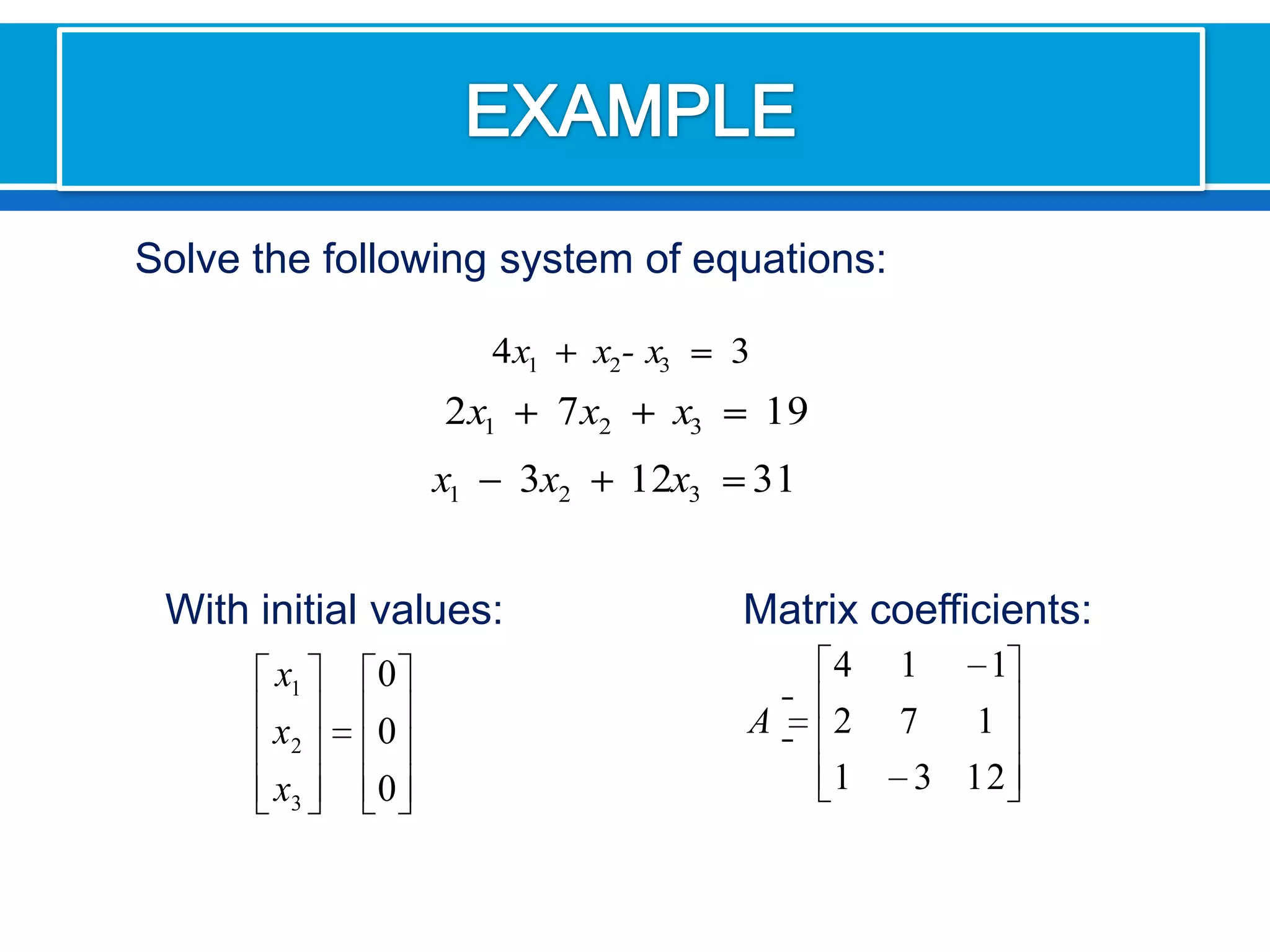
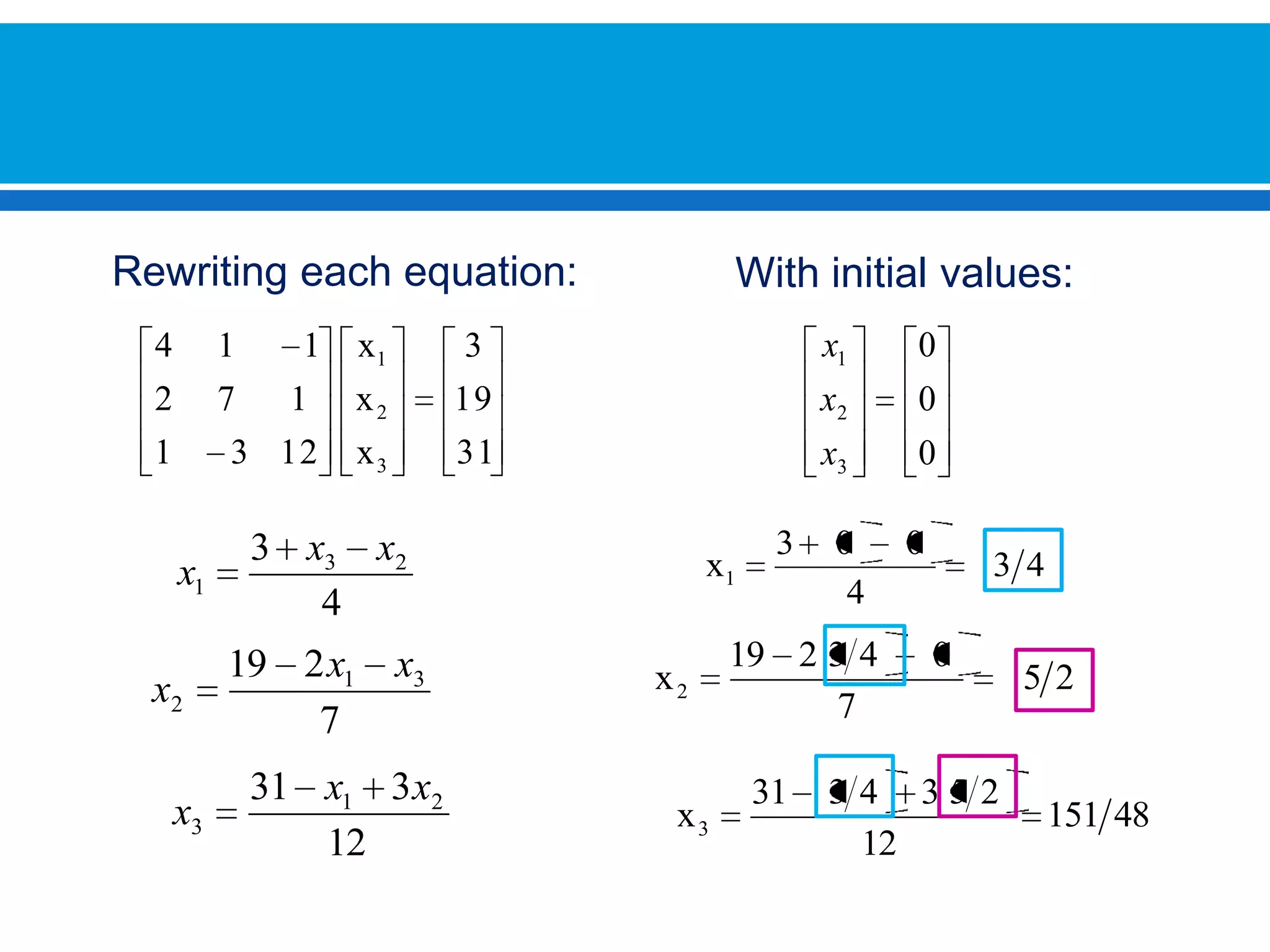
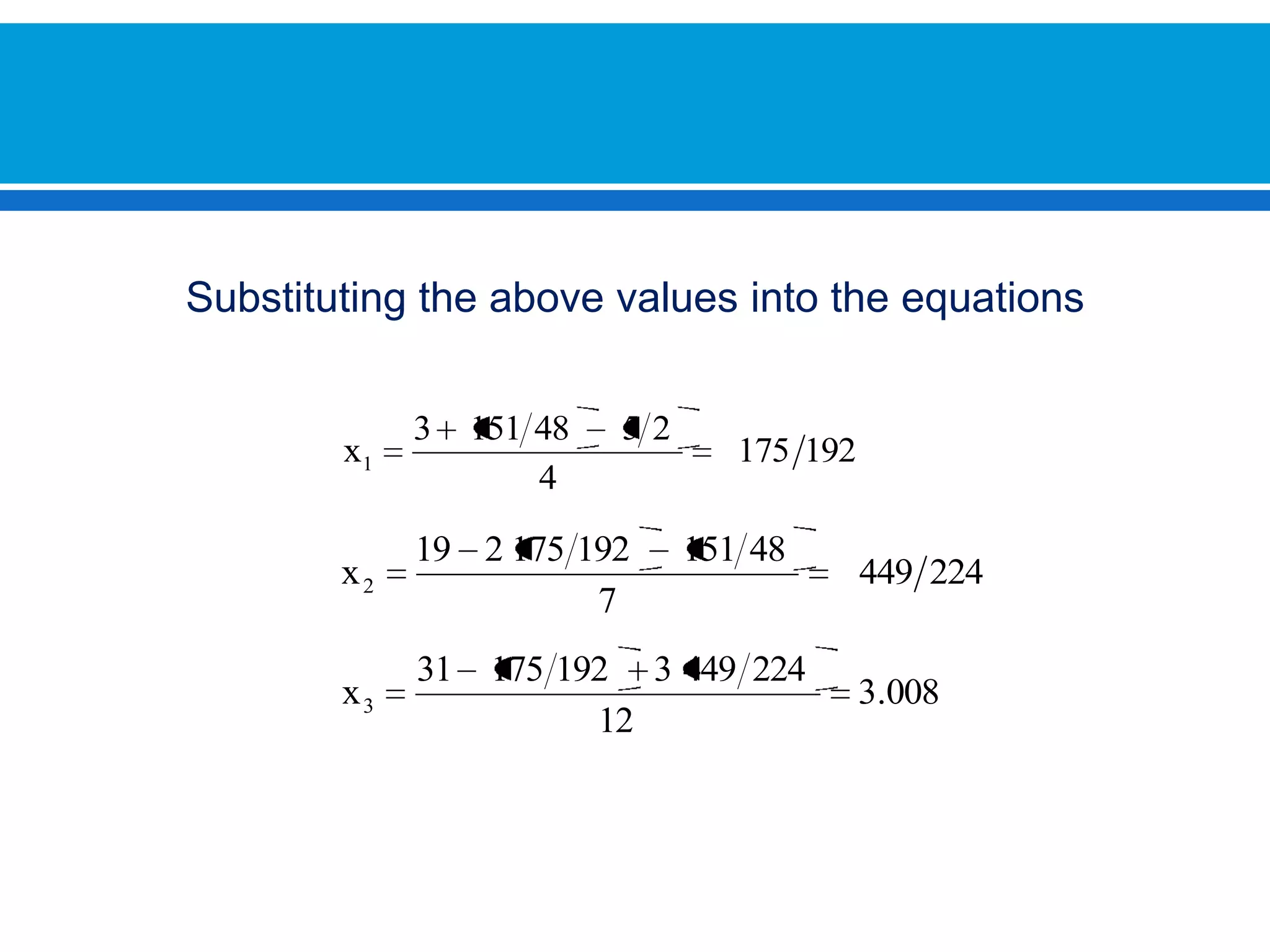
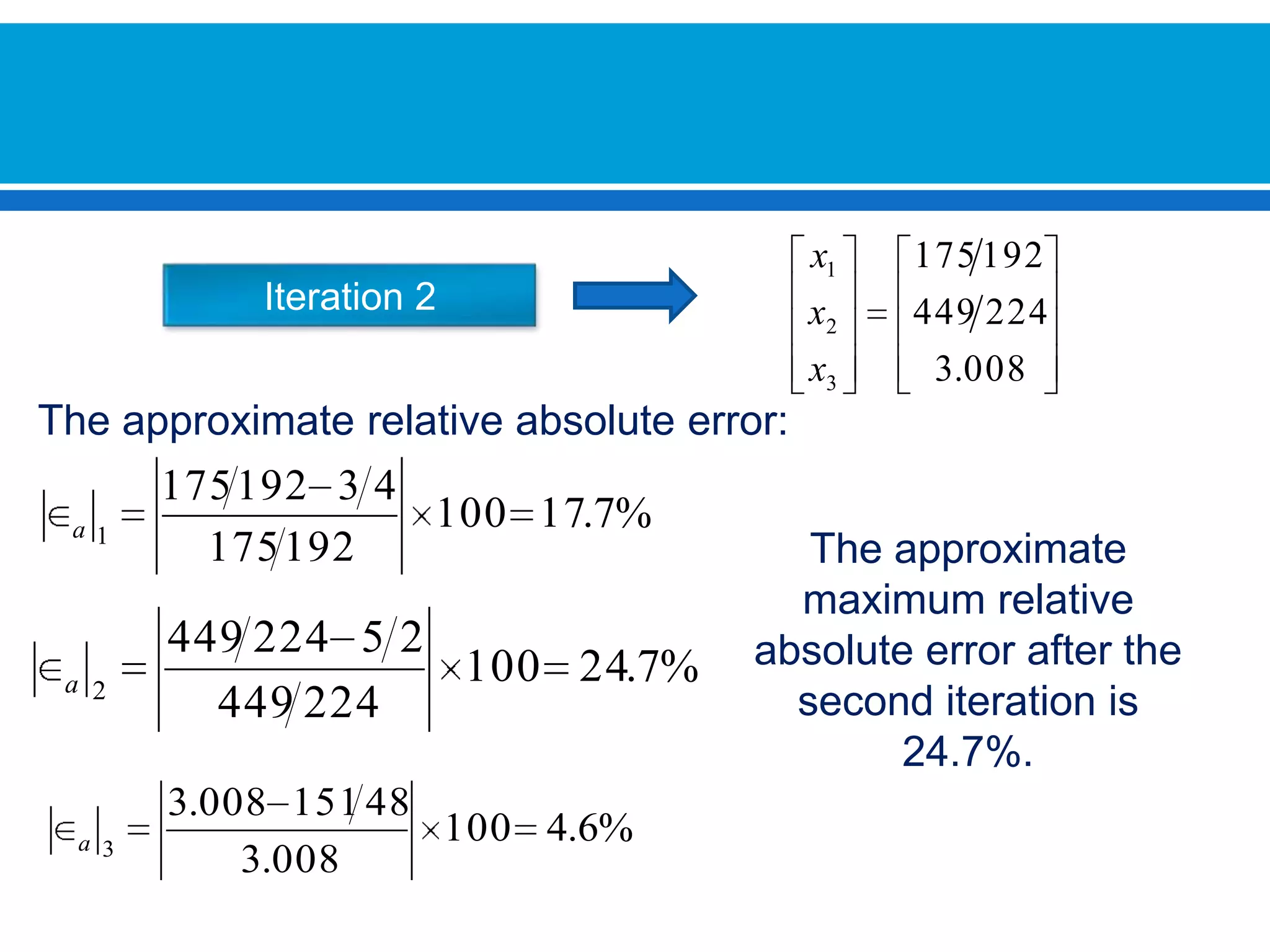
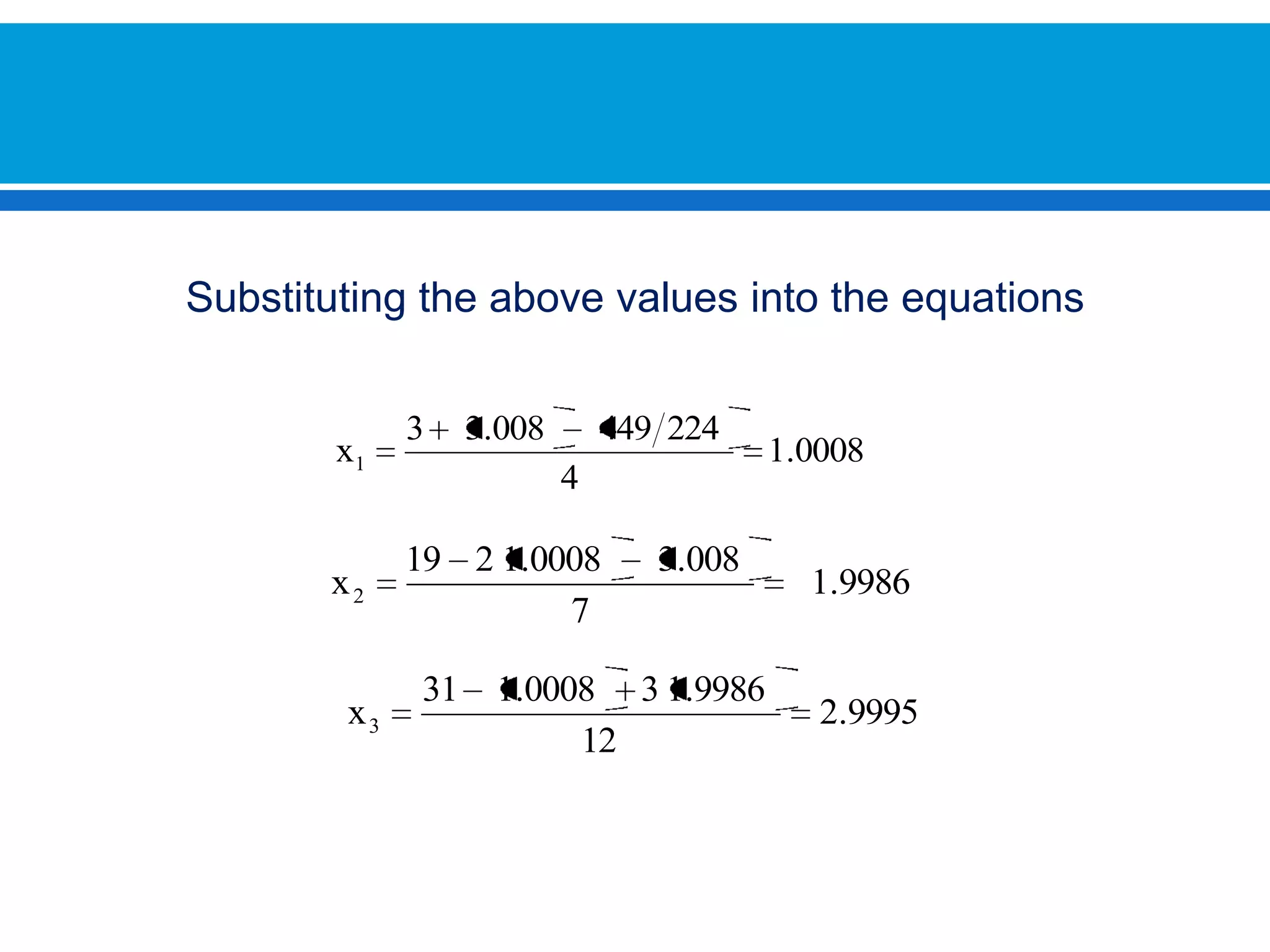
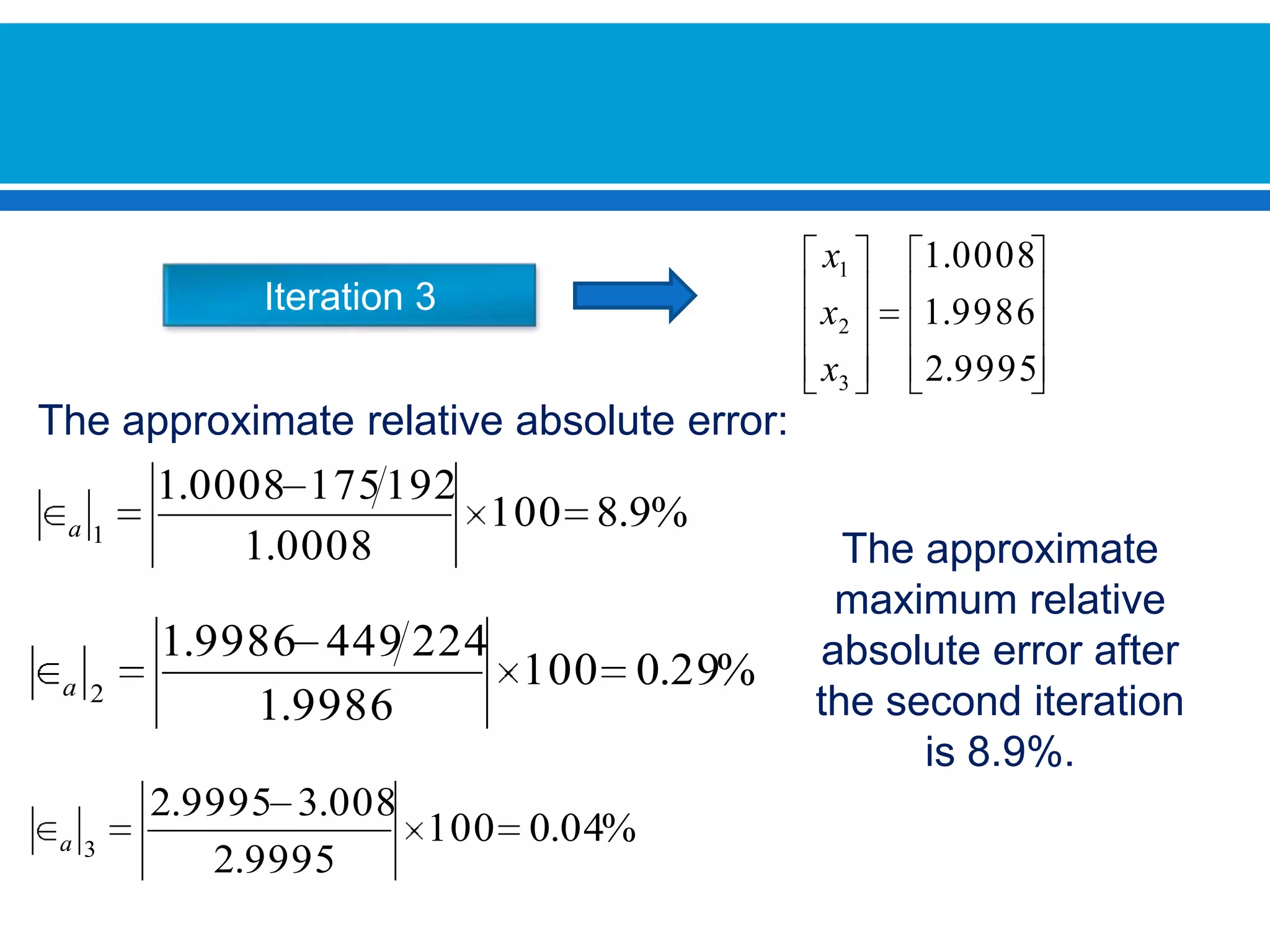
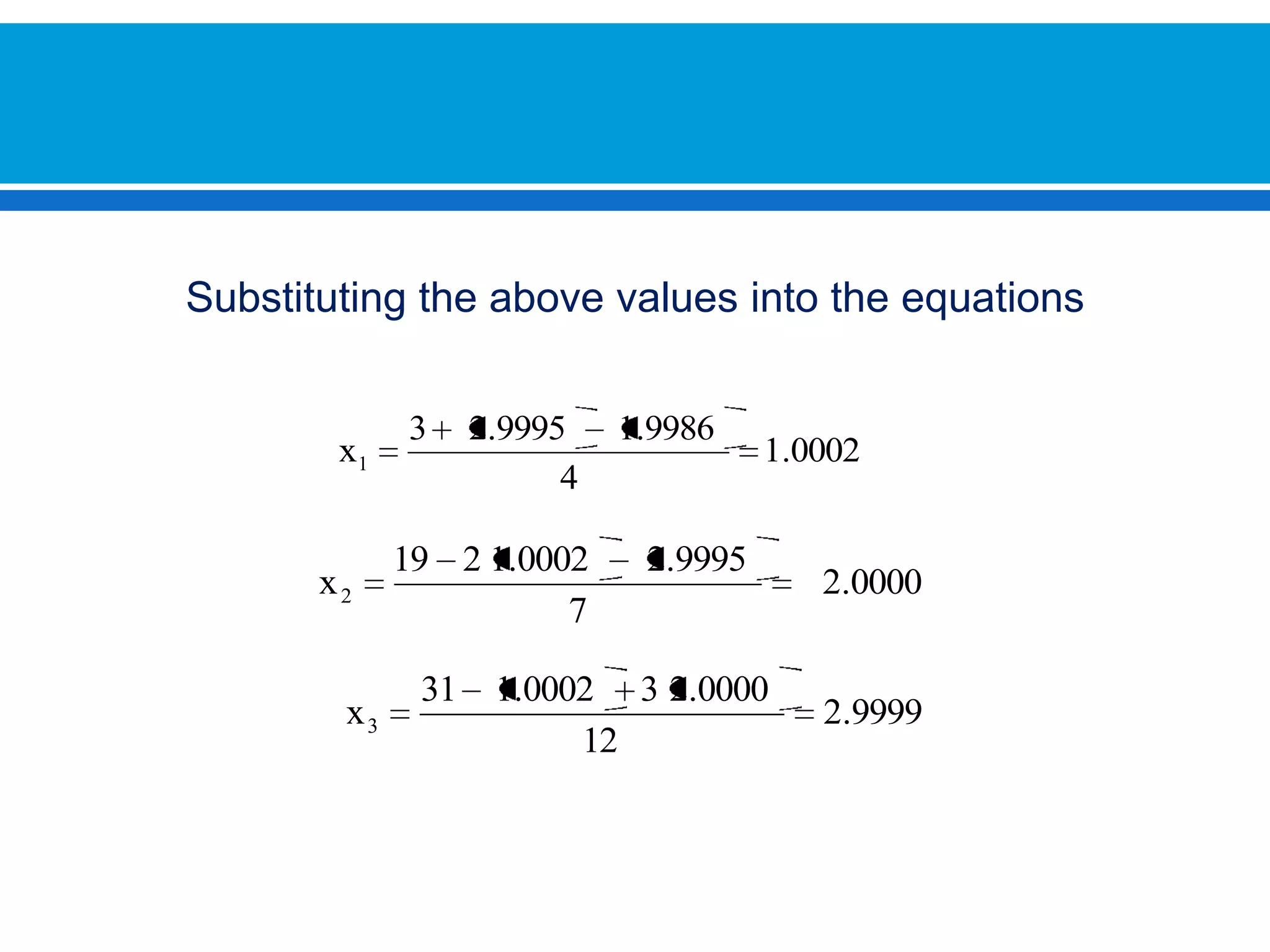
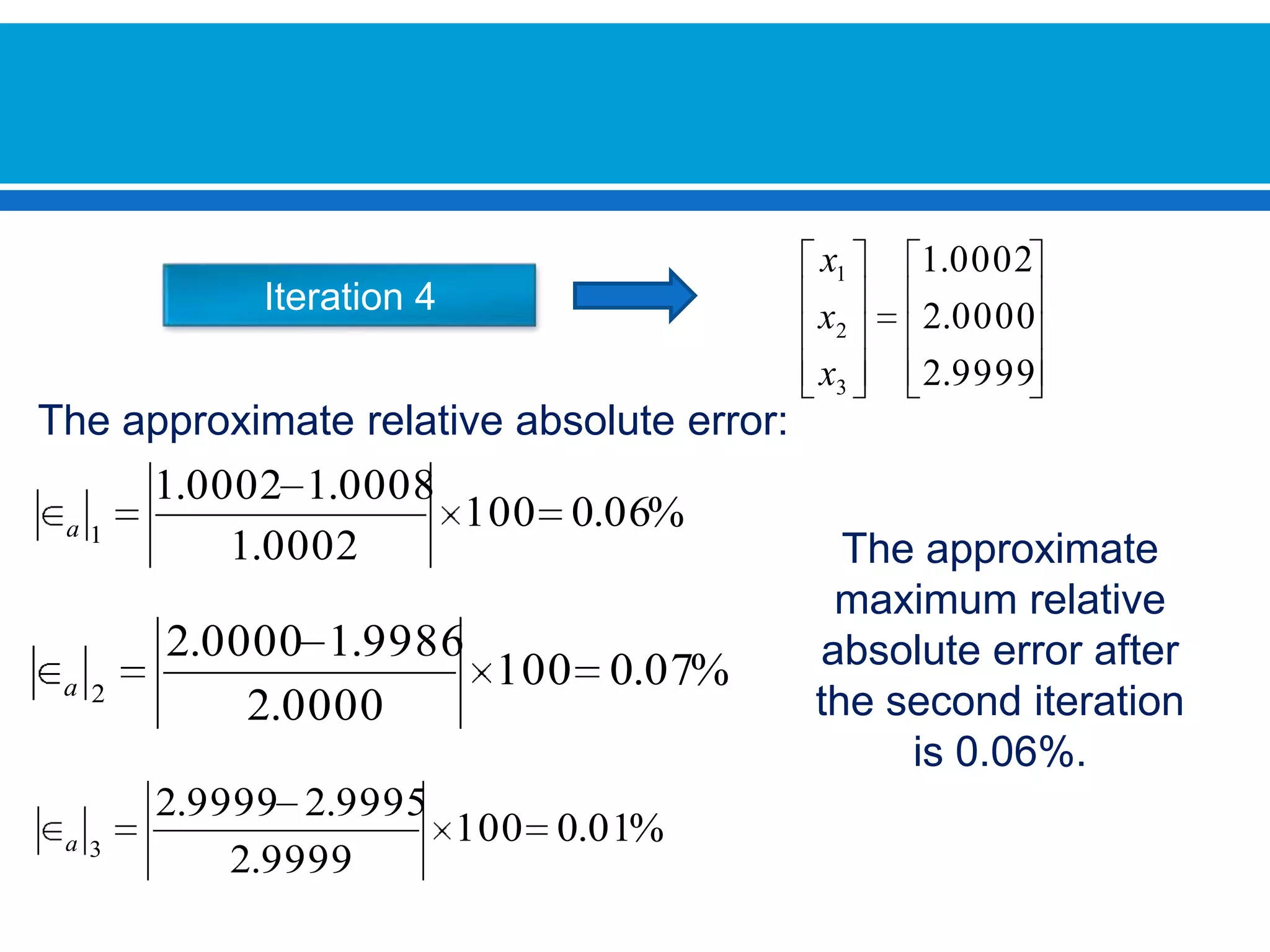
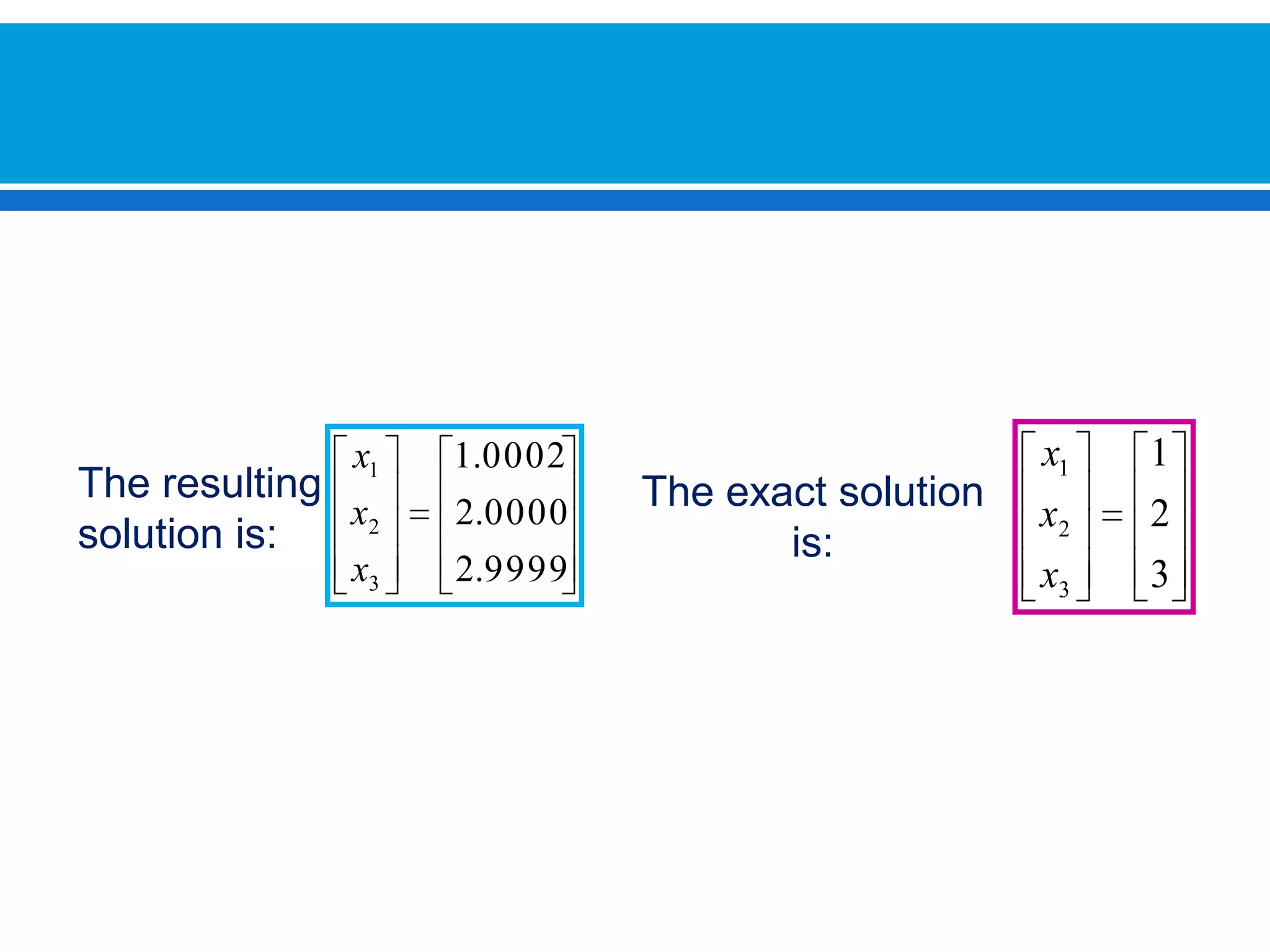
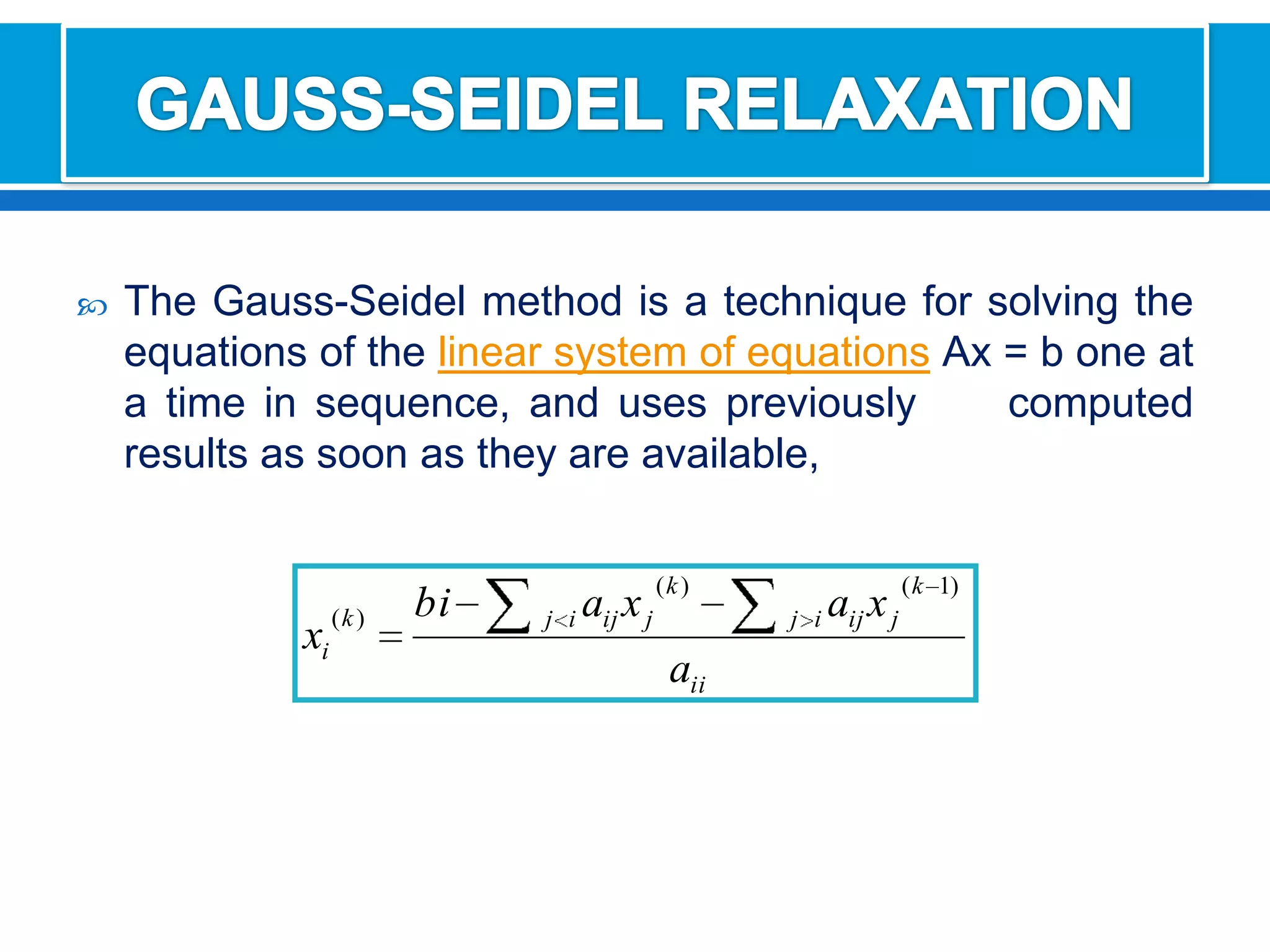
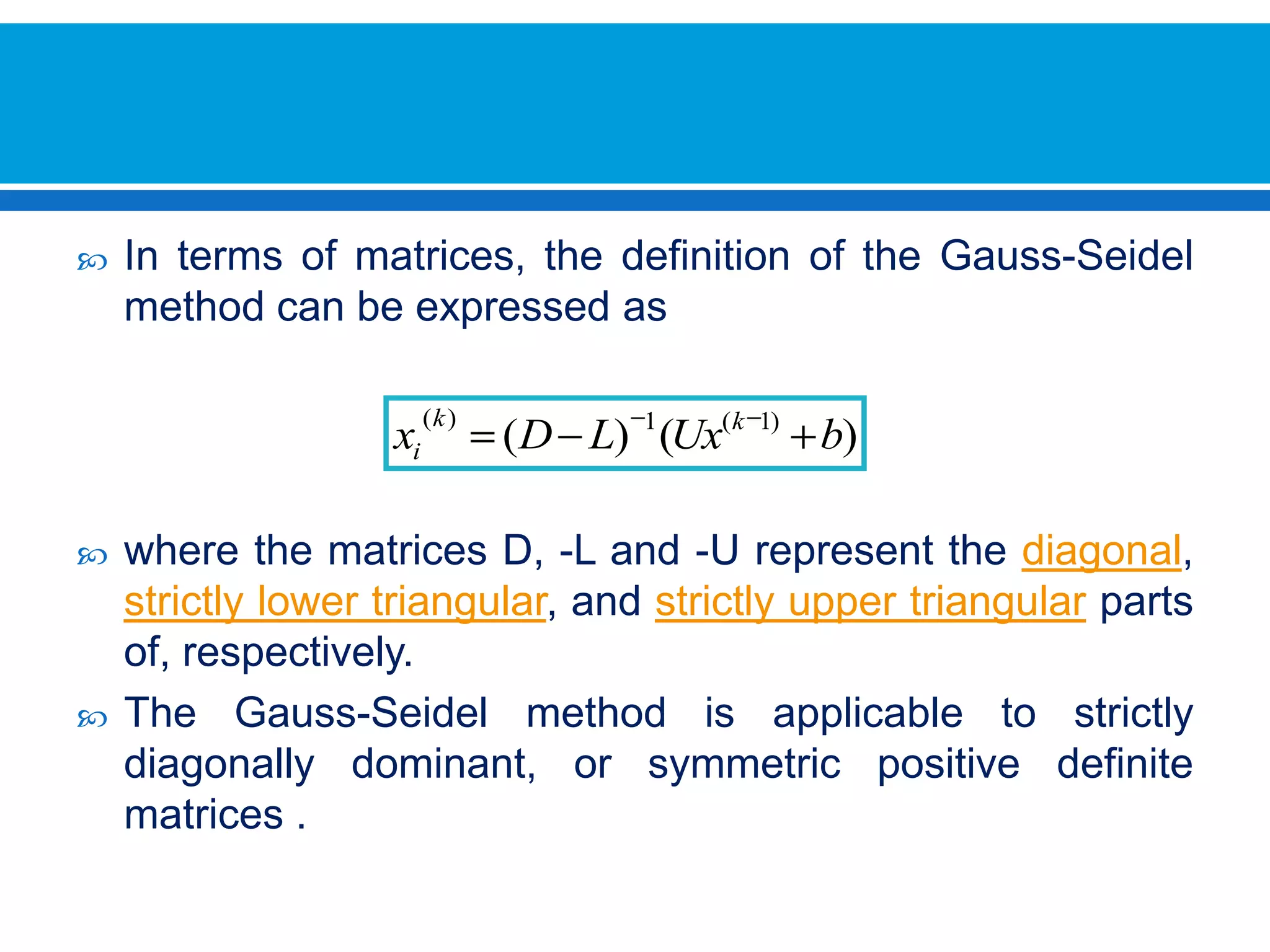
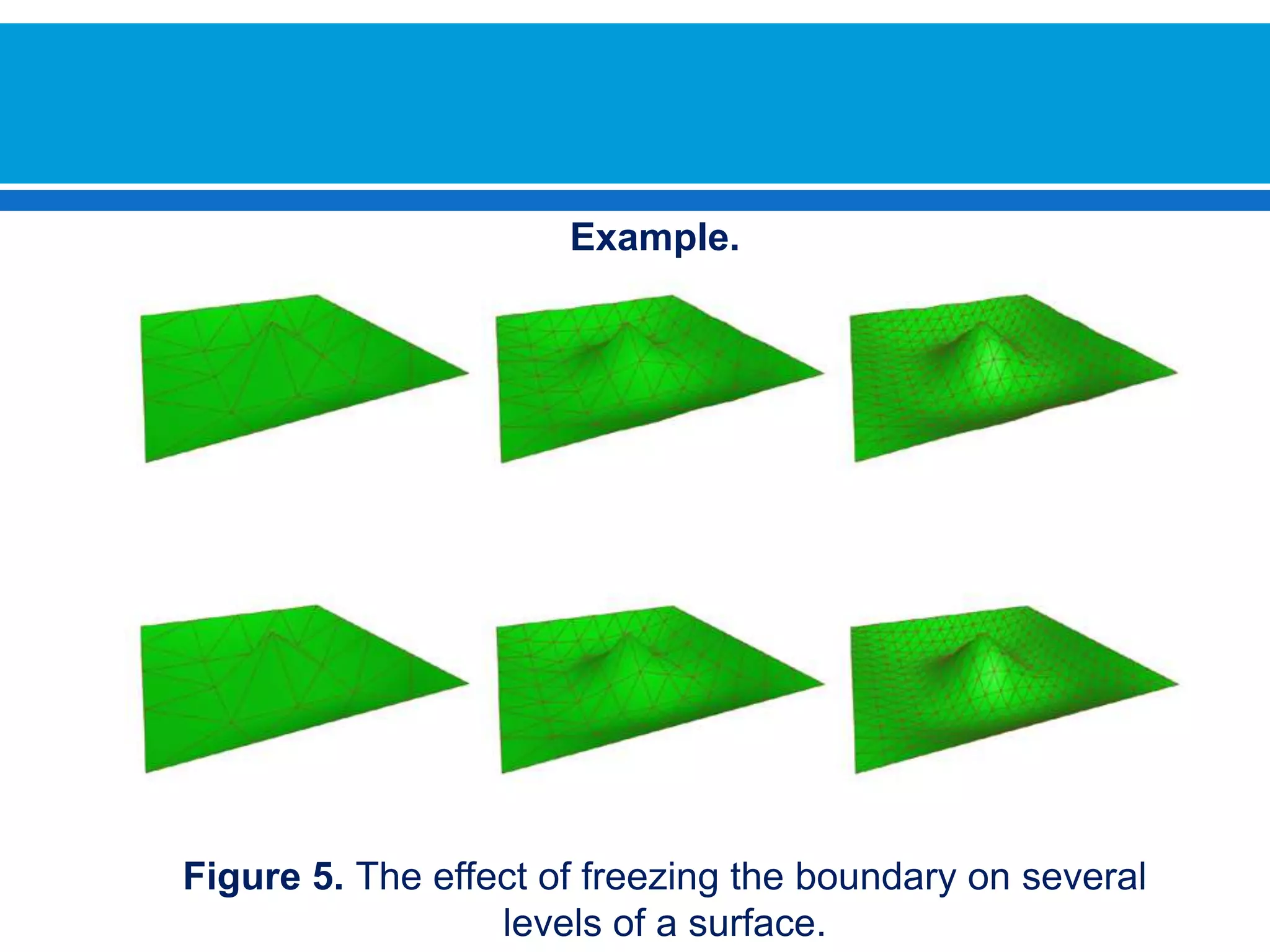
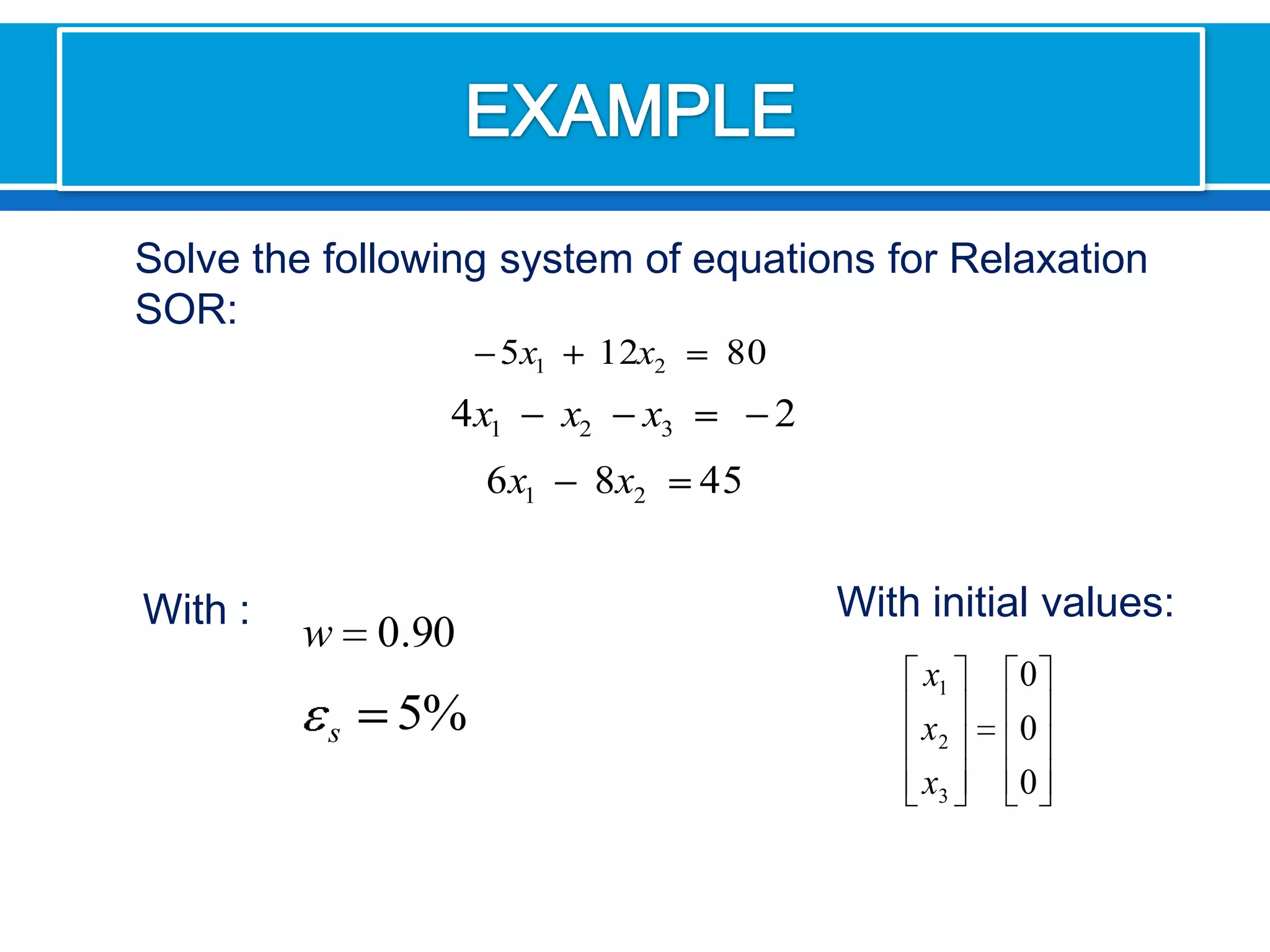
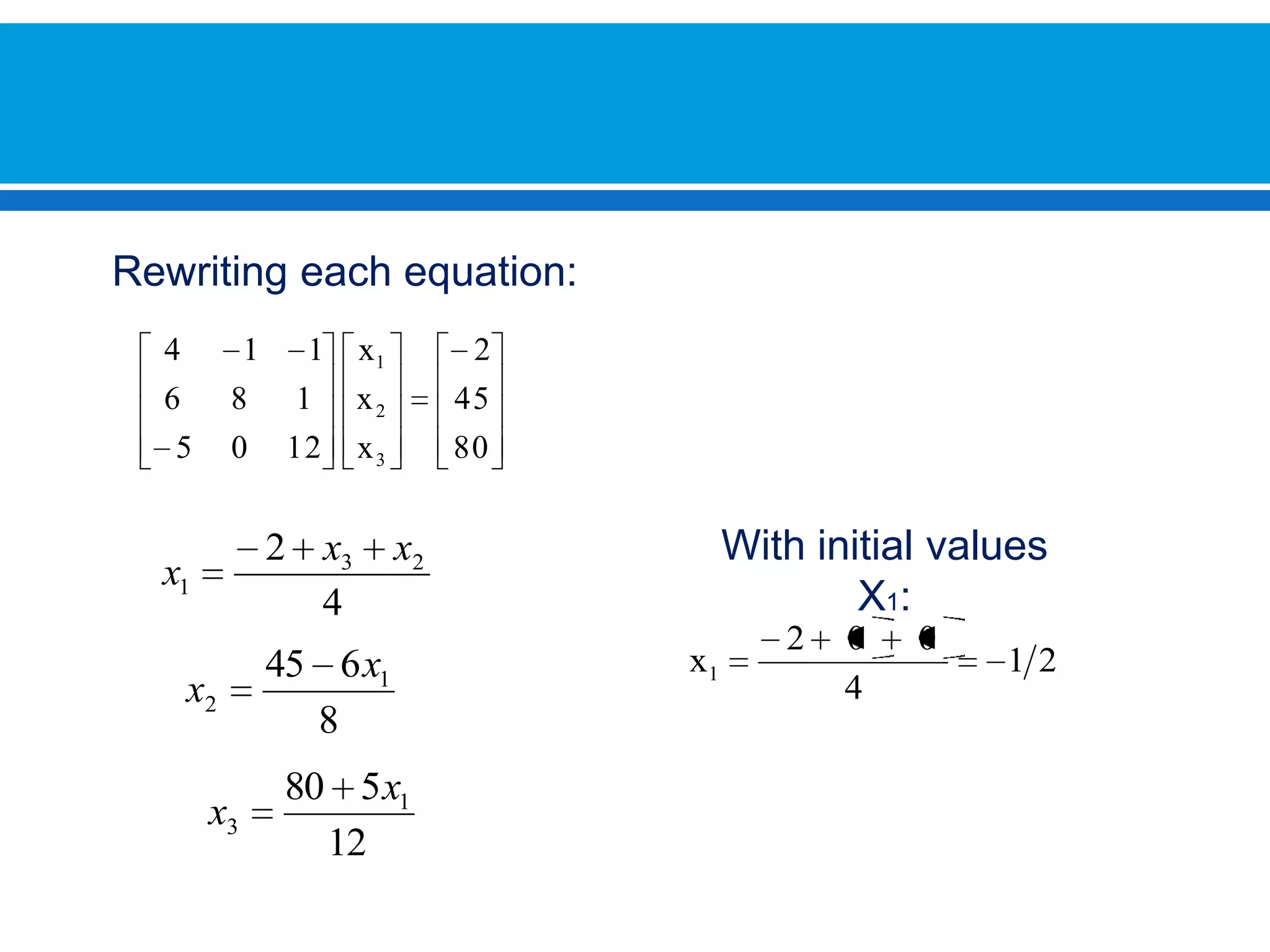
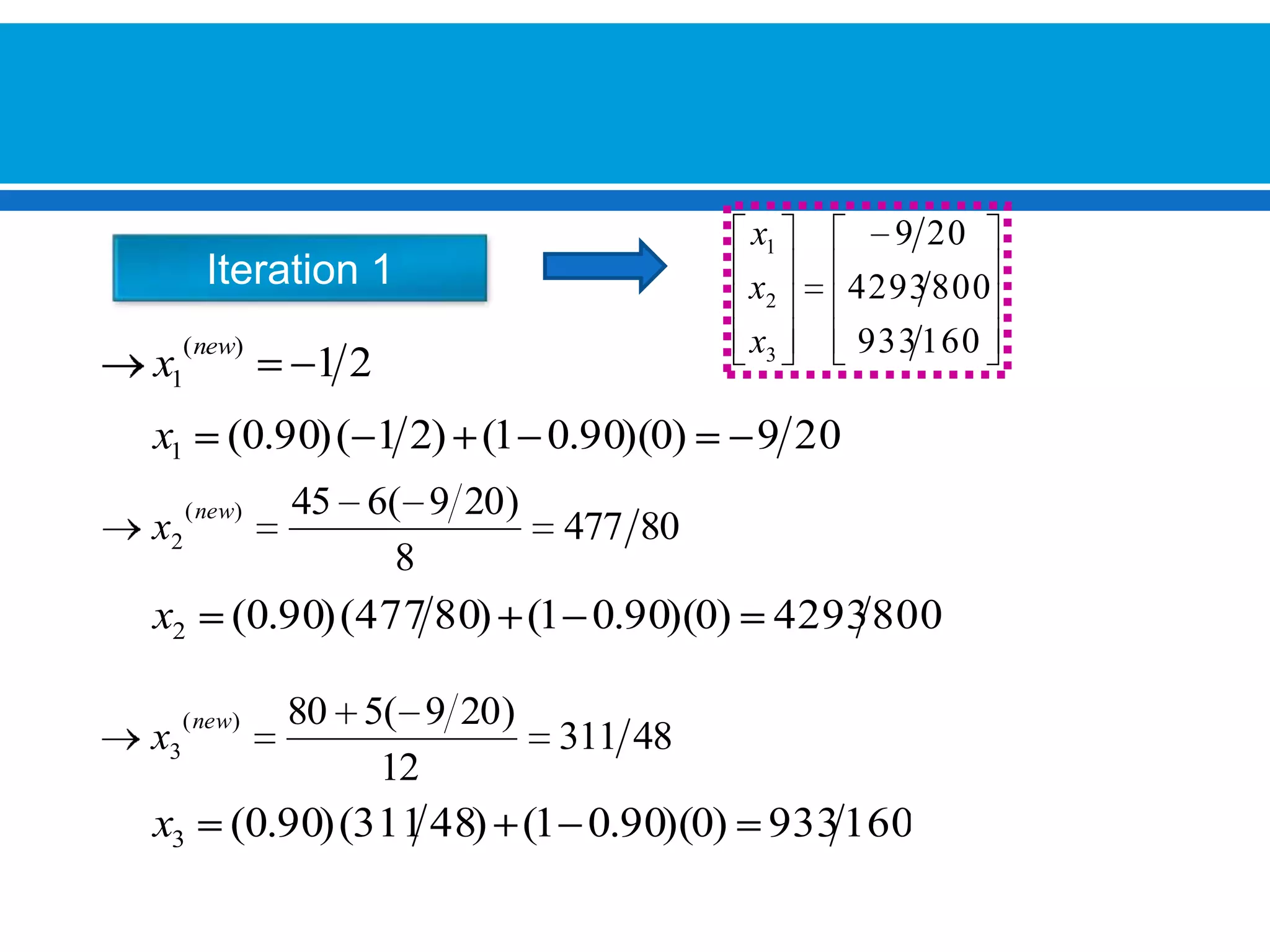
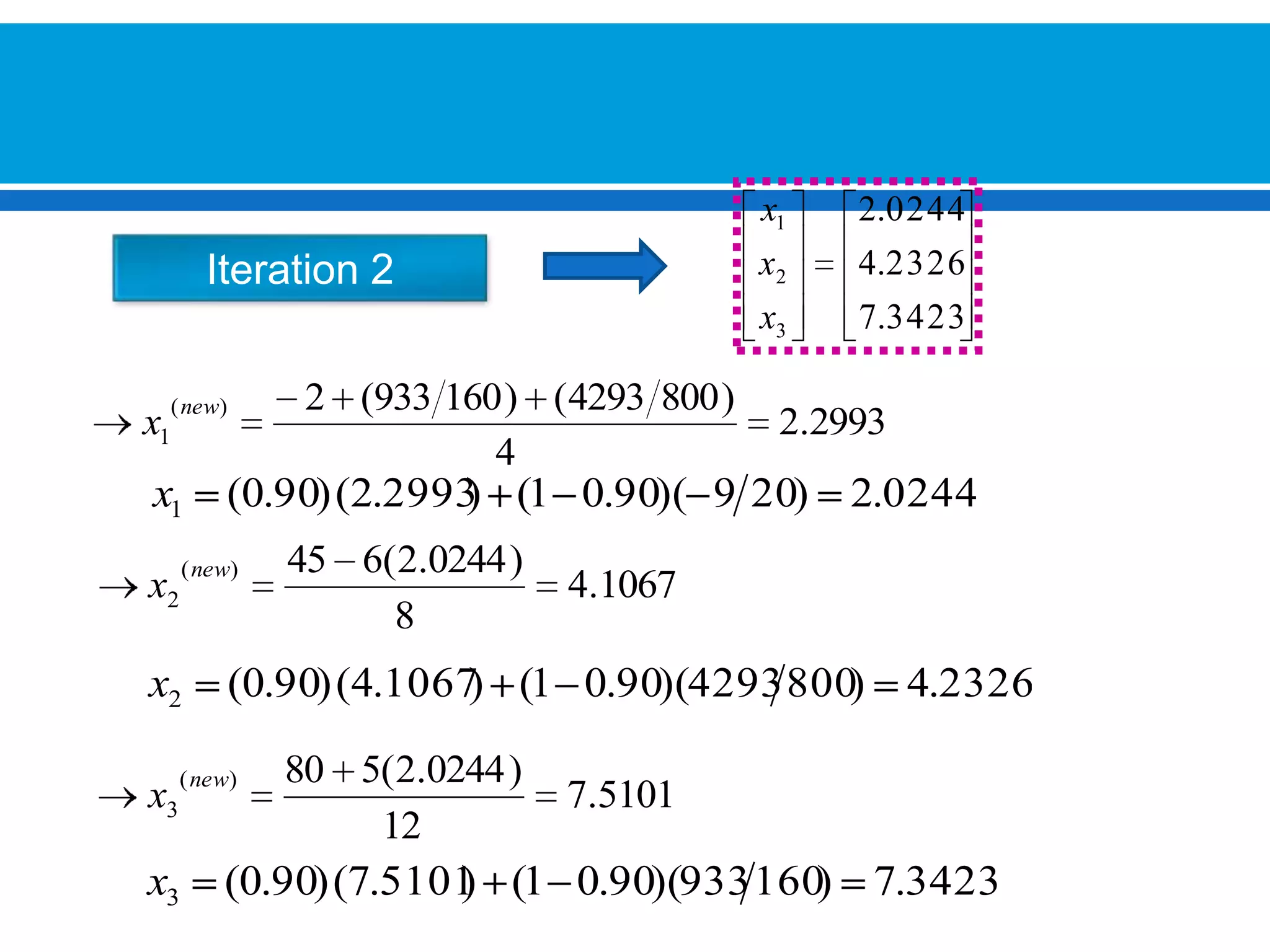
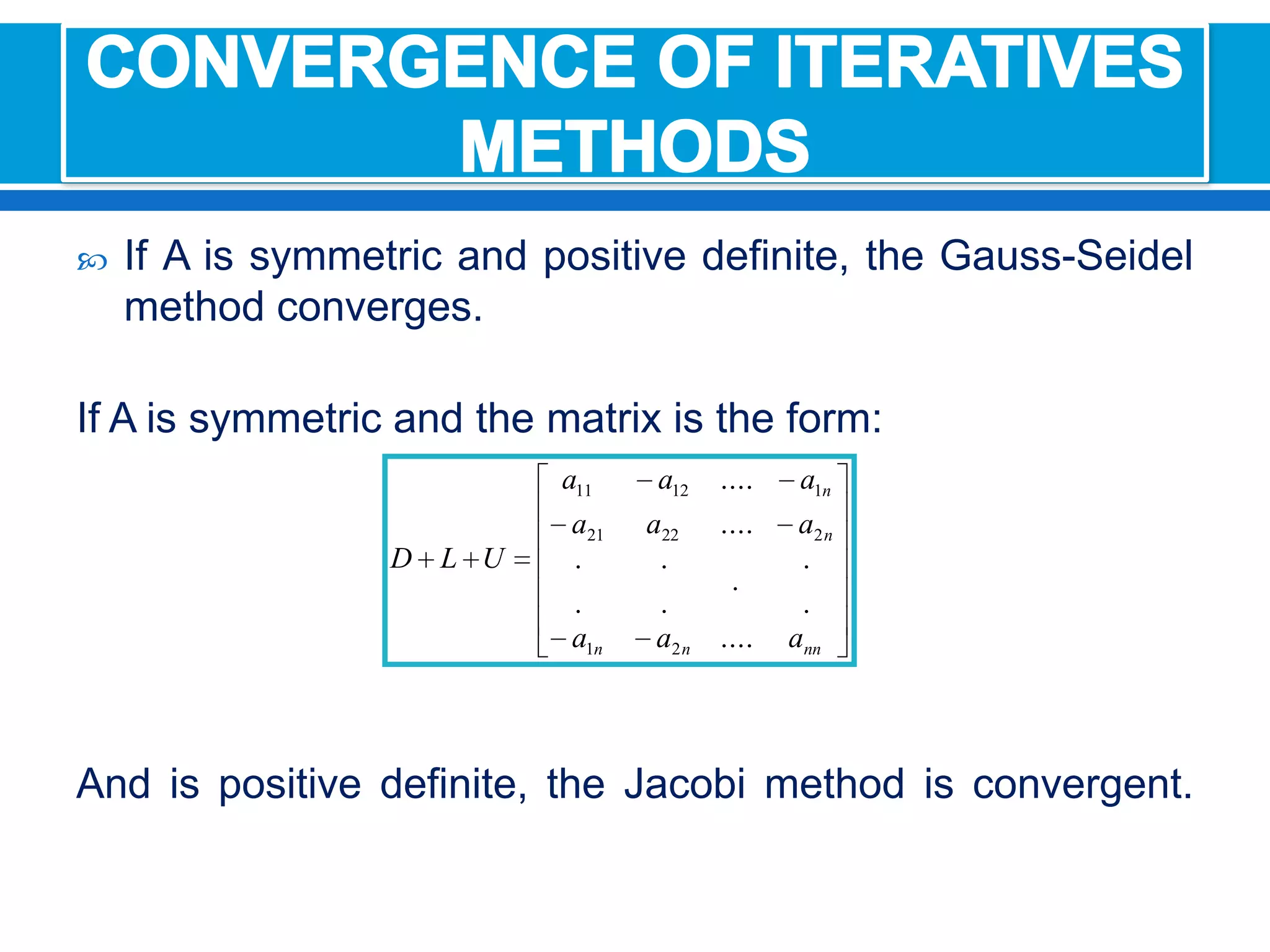
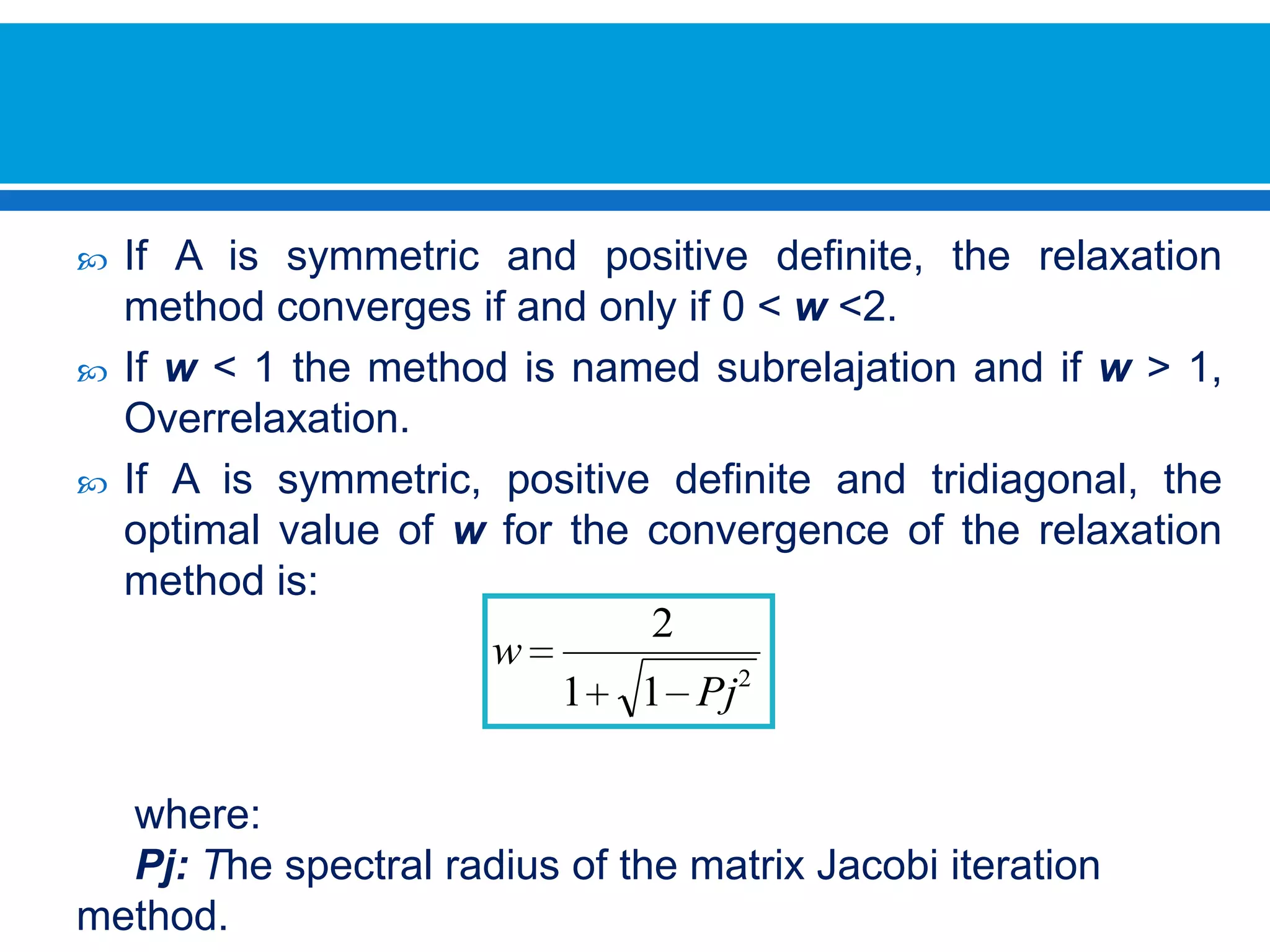
The document discusses iterative methods for solving systems of linear equations, including the Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel, and Gauss-Seidel relaxation methods. The Jacobi method works by rewriting the system in a form where the diagonal entries are isolated and computing successive approximations. The Gauss-Seidel method similarly computes approximations but uses the most recent values available at each step. Relaxation improves the Gauss-Seidel method's convergence by taking a weighted average of the current and previous iterations' results. Examples demonstrate applying the different methods to compute solutions.


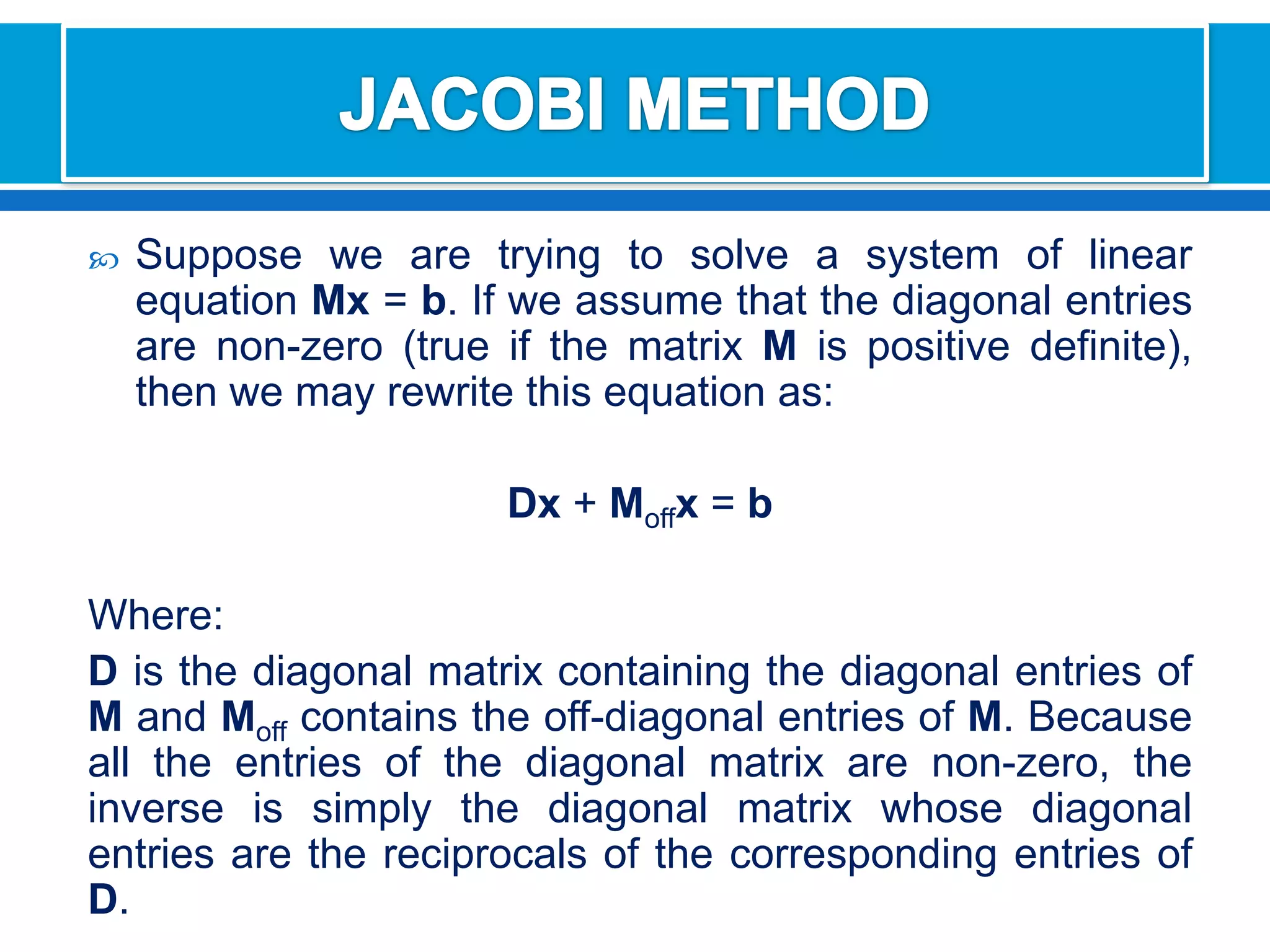

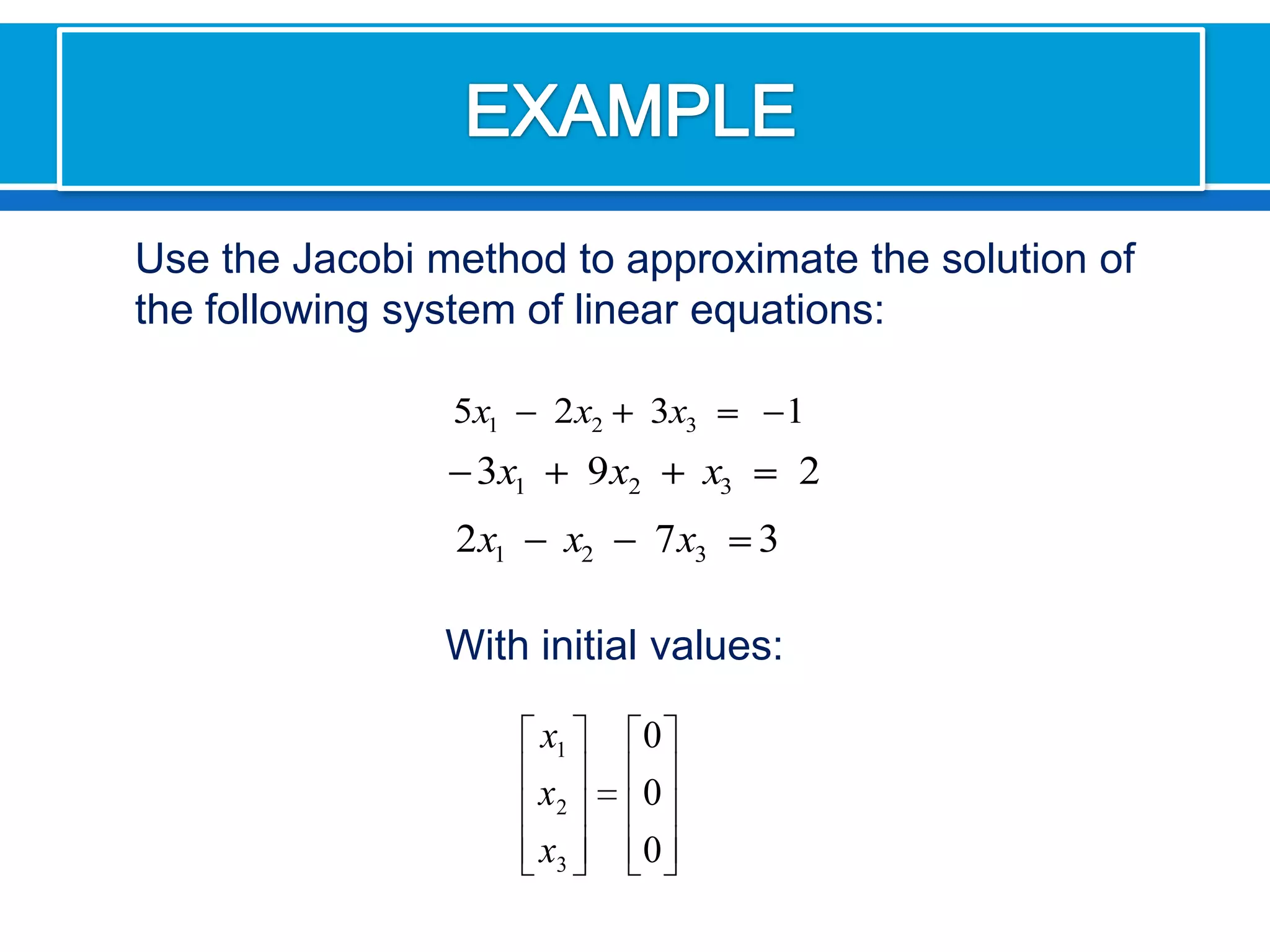
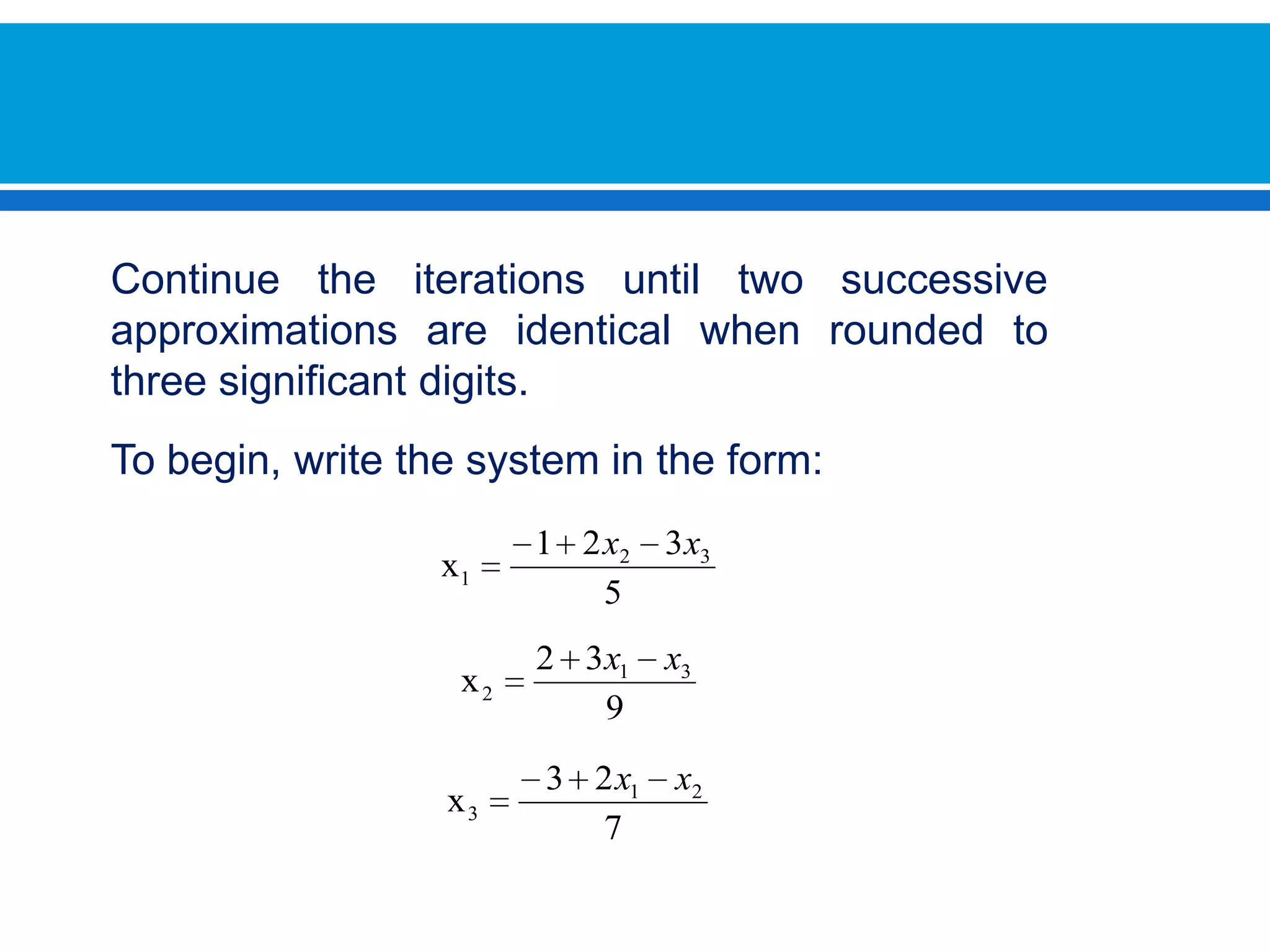

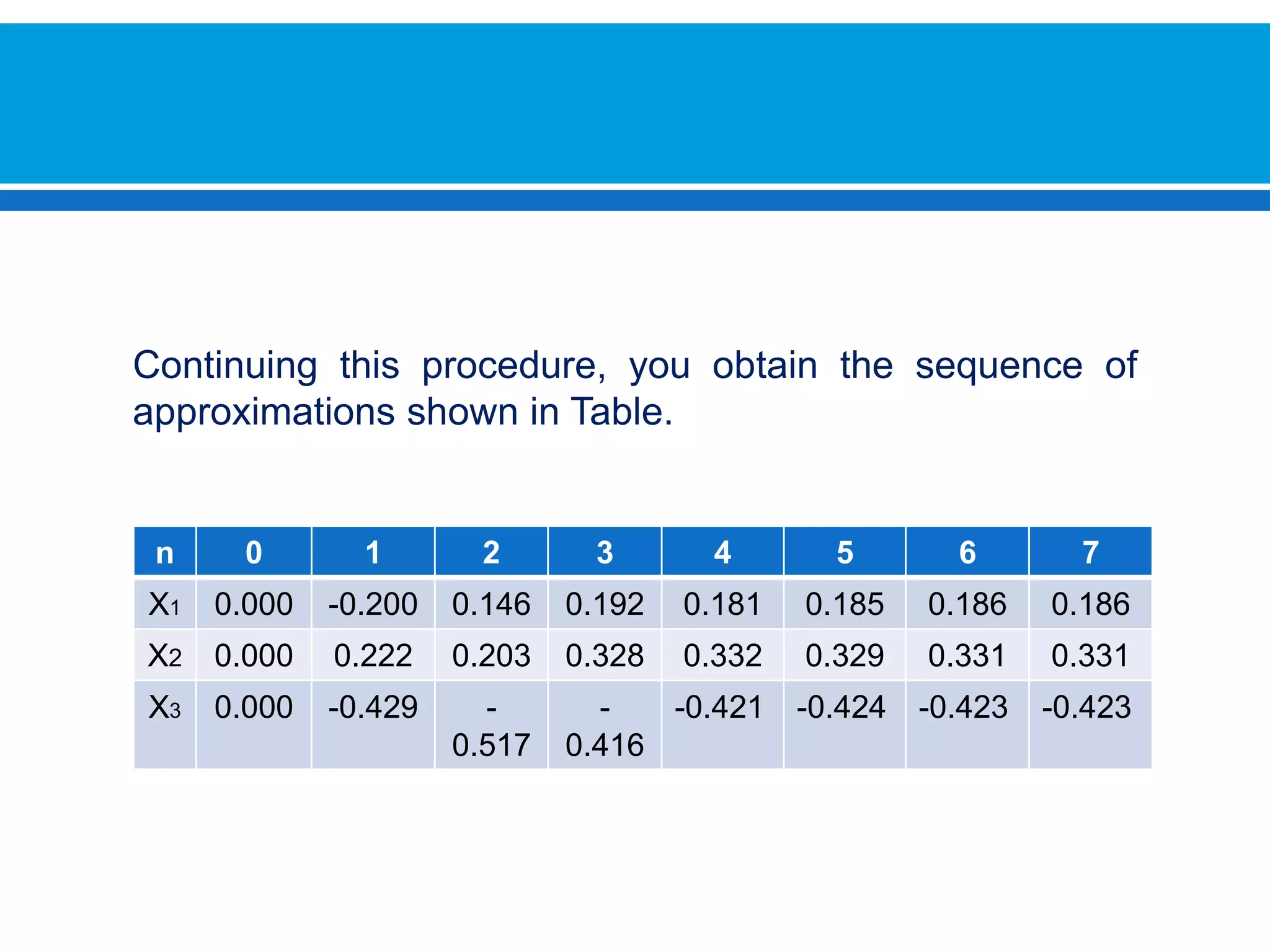
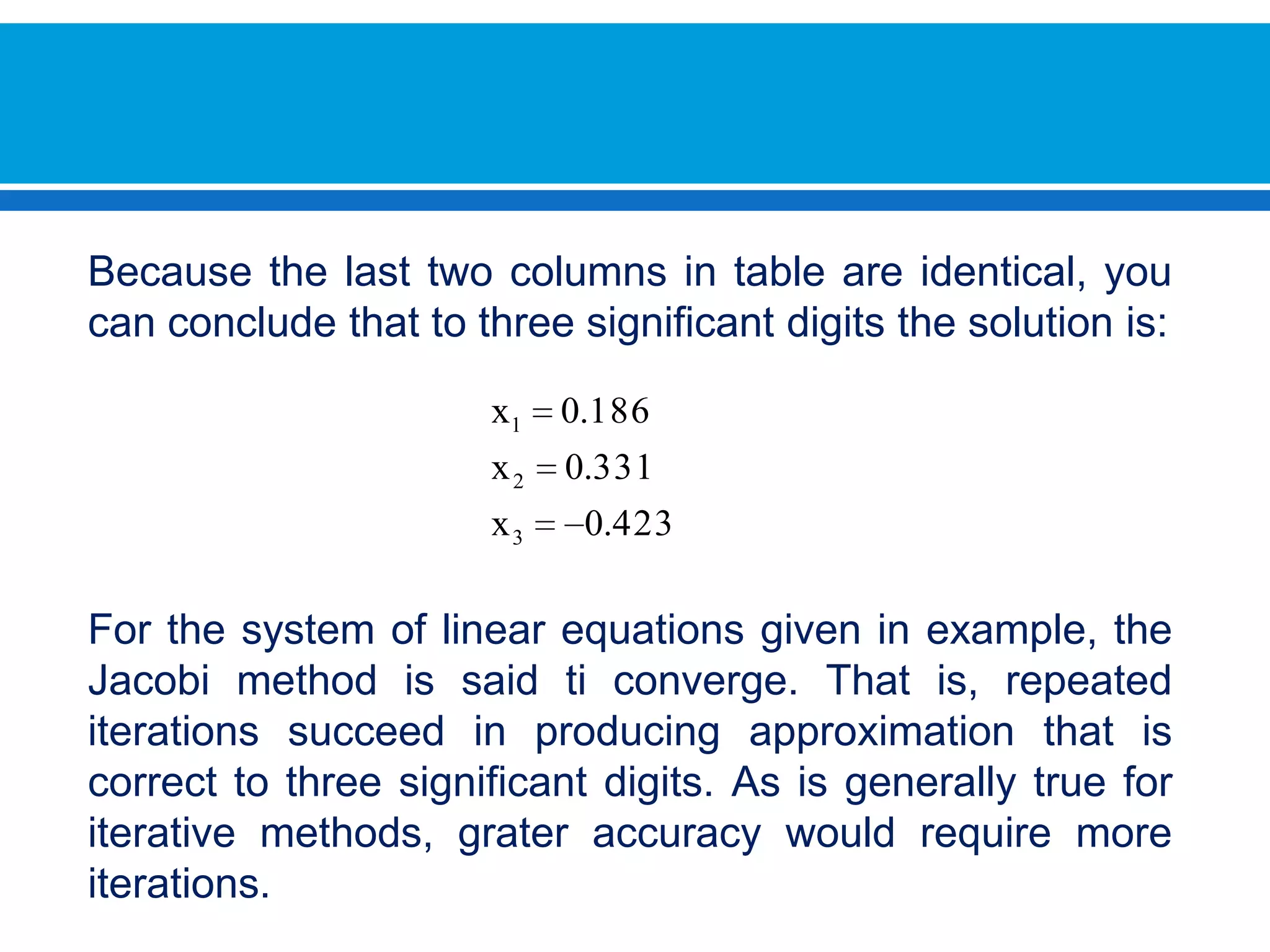

![First solve for the unknowns in order.Then we assume an initial value for [X(0)]We must remember that I always use the most recent value xi. This means that calculated values apply for the calculations are in the current iteration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interactivos-100726191952-phpapp01/75/Interactives-Methods-12-2048.jpg)