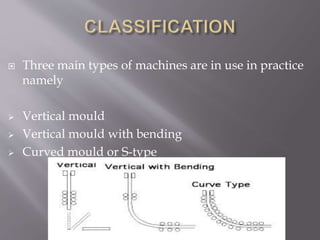
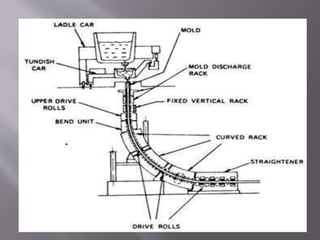
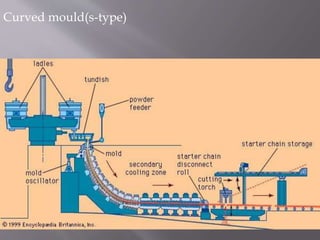
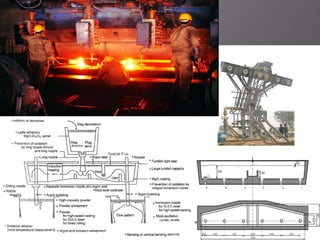
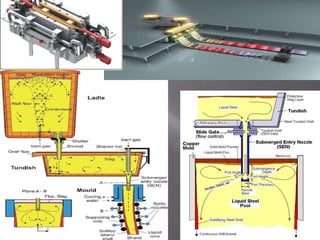
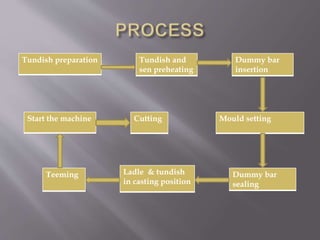
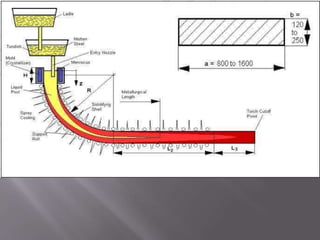
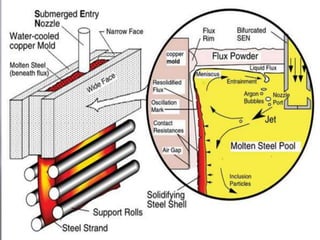
This document discusses the process of continuous casting of steel. It begins with an introduction and overview of the process. It then describes the three main types of continuous casting machines - vertical mould, vertical mould with bending, and curved mould. It provides details on the equipment, materials, process steps, defects, and modern developments of continuous casting. Some advantages are improved yield, quality, productivity and cost efficiency compared to ingot casting. Disadvantages include the need for a large facility and efficient cooling.