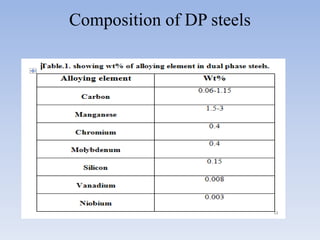
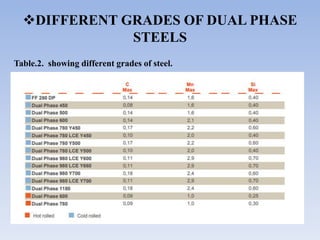
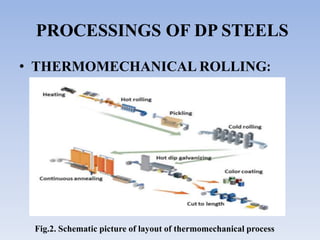
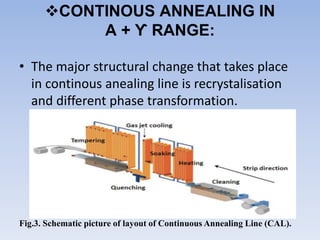
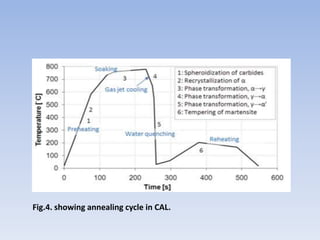
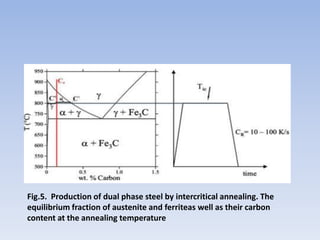
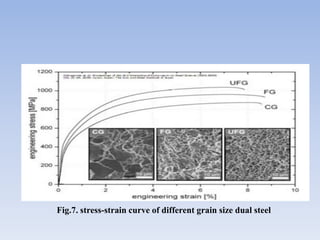
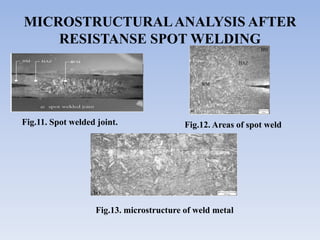
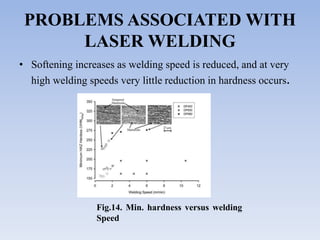
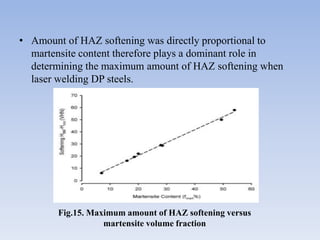
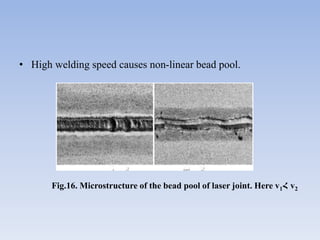
This document discusses dual phase steel and types of welding performed on it. It begins with an introduction to dual phase steel, describing its microstructure and mechanical properties. It then discusses different processing methods for dual phase steel, including thermomechanical rolling and continuous annealing. The document focuses on two main types of welding for dual phase steel: resistance spot welding and laser welding. It describes the microstructure and issues that can occur with each welding process, such as softening in the heat affected zone, and provides guidelines to improve weld quality.