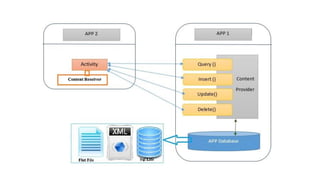
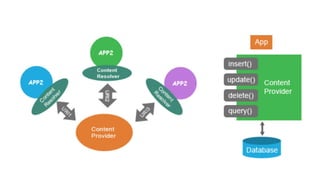
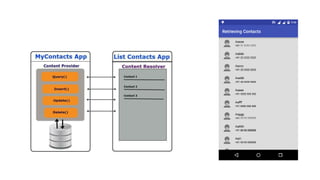
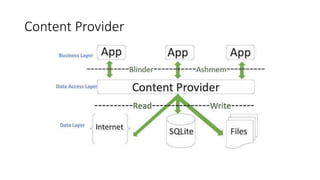
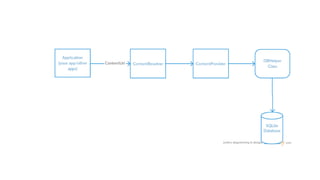
The document discusses Content Providers and Content Resolvers in Android. Content Providers allow access to application data from other applications through a common interface, while enforcing security. Content Resolvers provide a global instance to query Content Providers and resolve requests by directing them to the proper Content Provider based on authority. Content Providers abstract the underlying data source and define security permissions, and Content Resolvers handle CRUD operations on behalf of applications.