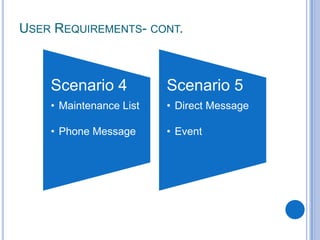
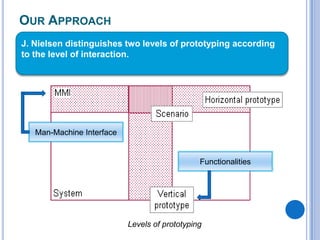
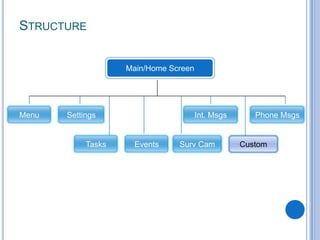
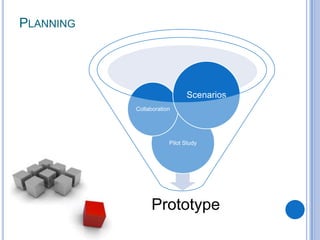
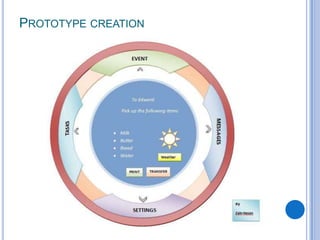
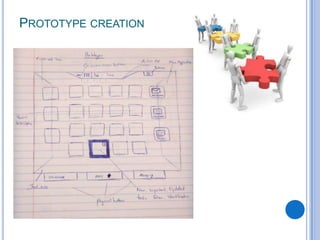
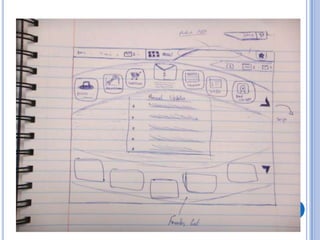
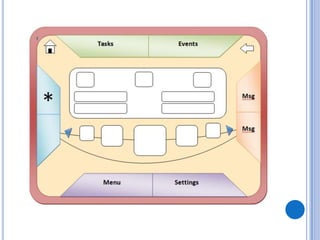
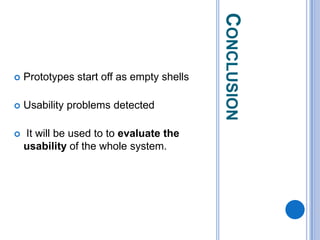
This document discusses the design and prototype 1 of a home automation system called Home-Mess. It introduces prototyping and its benefits, including allowing users to visualize possibilities and identify failures. The objectives are defined as identifying user requirements, developing a supportive design solution, and designing a low-fidelity prototype. User requirements and a two-level prototyping approach are described. The presentation concludes by outlining next steps of evaluation, data analysis, user testing, and new designs.