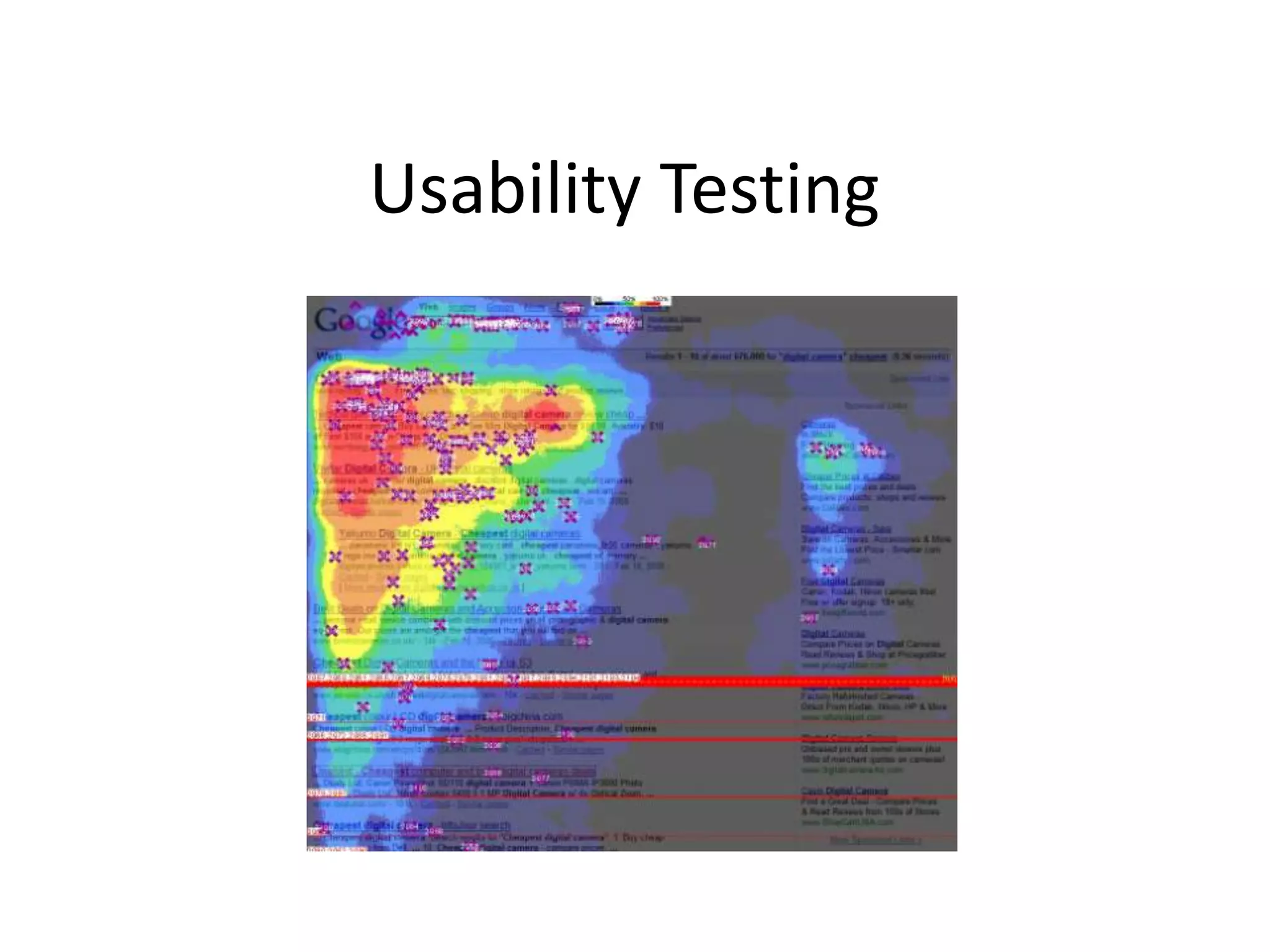
Usability testing is important to ensure websites are easy to use. It identifies functionality issues and shows how users navigate a site. There are different types of usability tests conducted at various stages of development. Exploratory tests examine early design concepts, assessment tests evaluate tasks and problems, and validation tests confirm issues are fixed. Usability principles include using simple navigation and language, providing help, and designing for user needs. Testing benefits include a real user perspective and seeing decision processes.