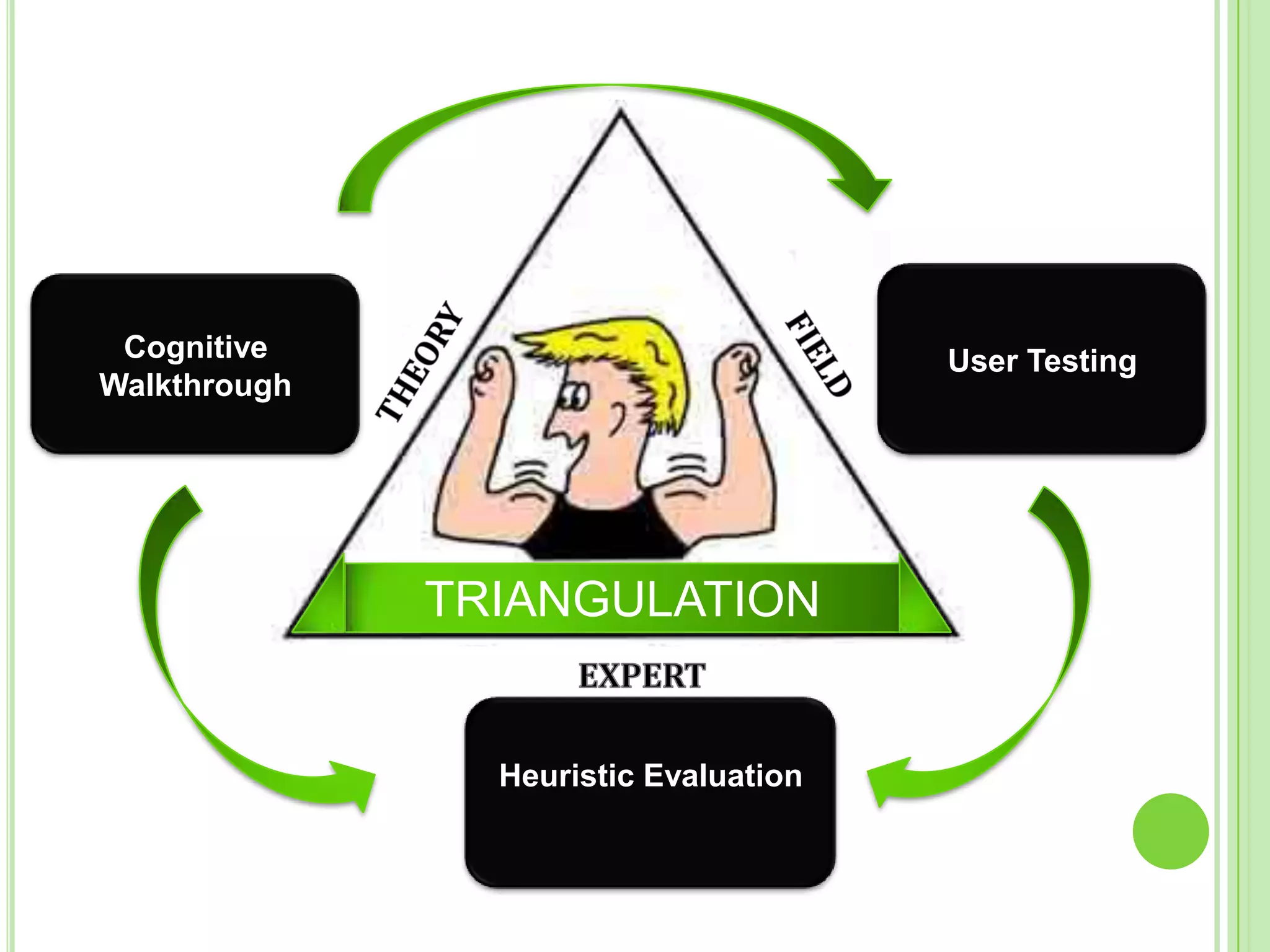
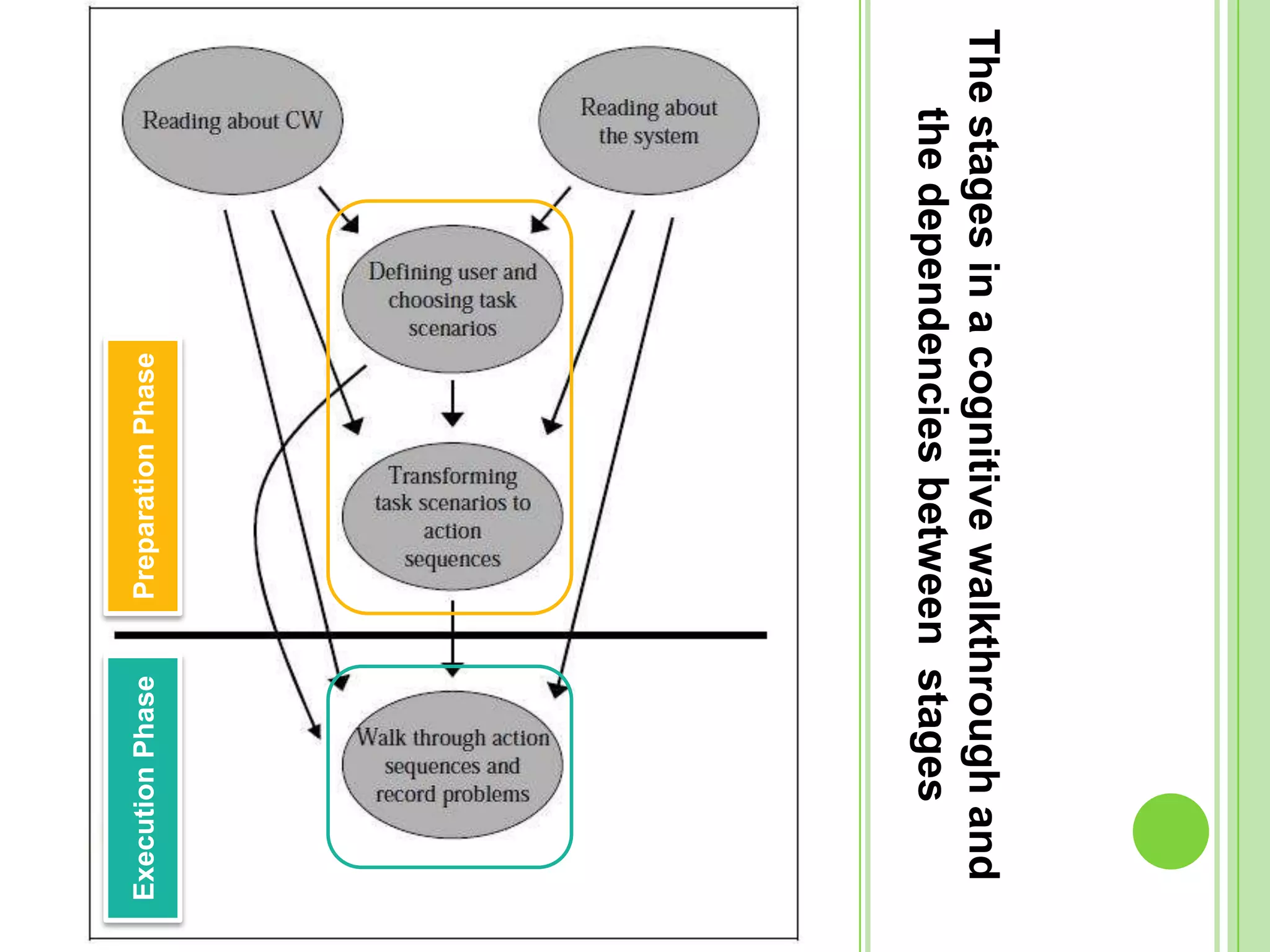
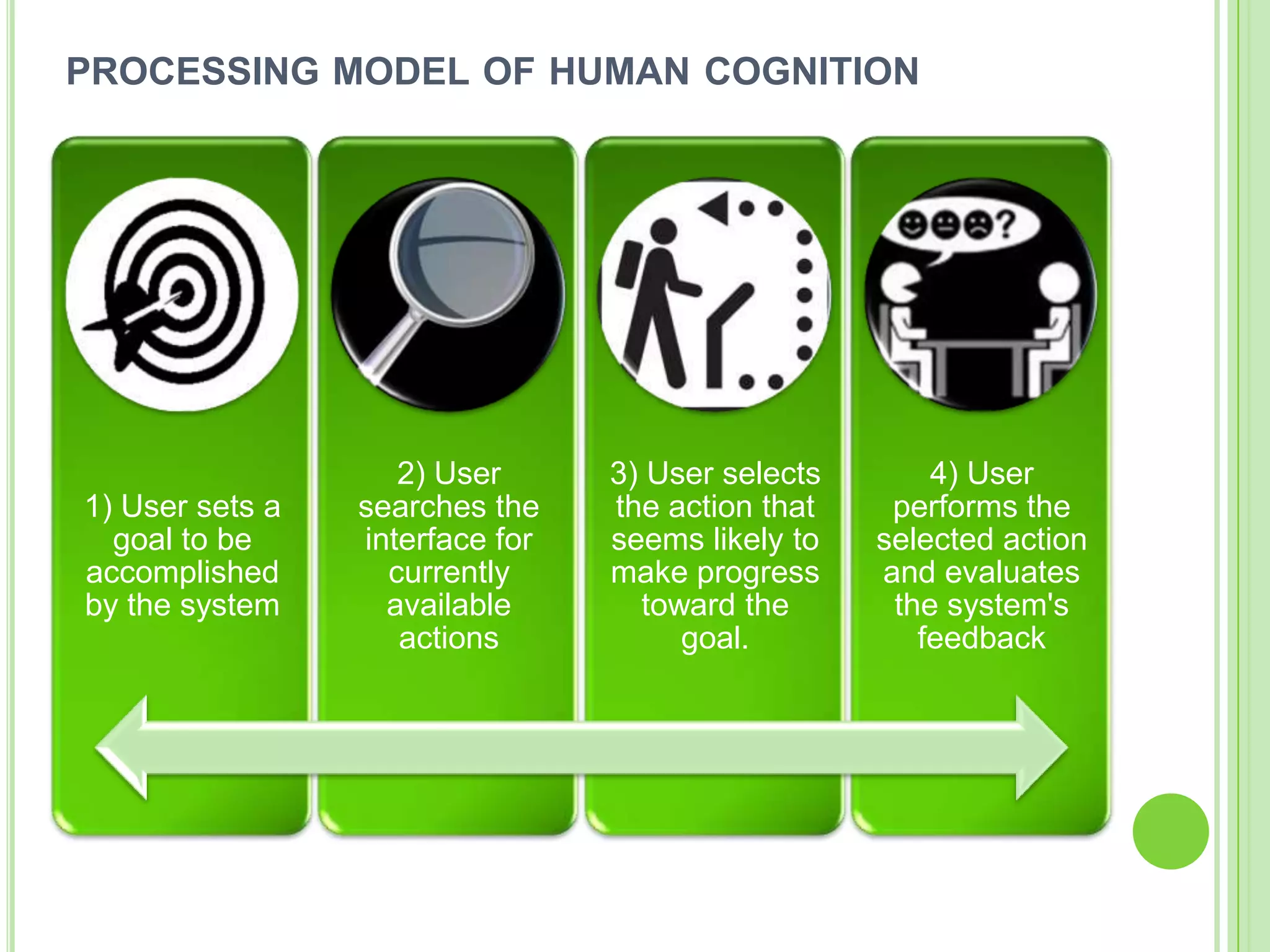
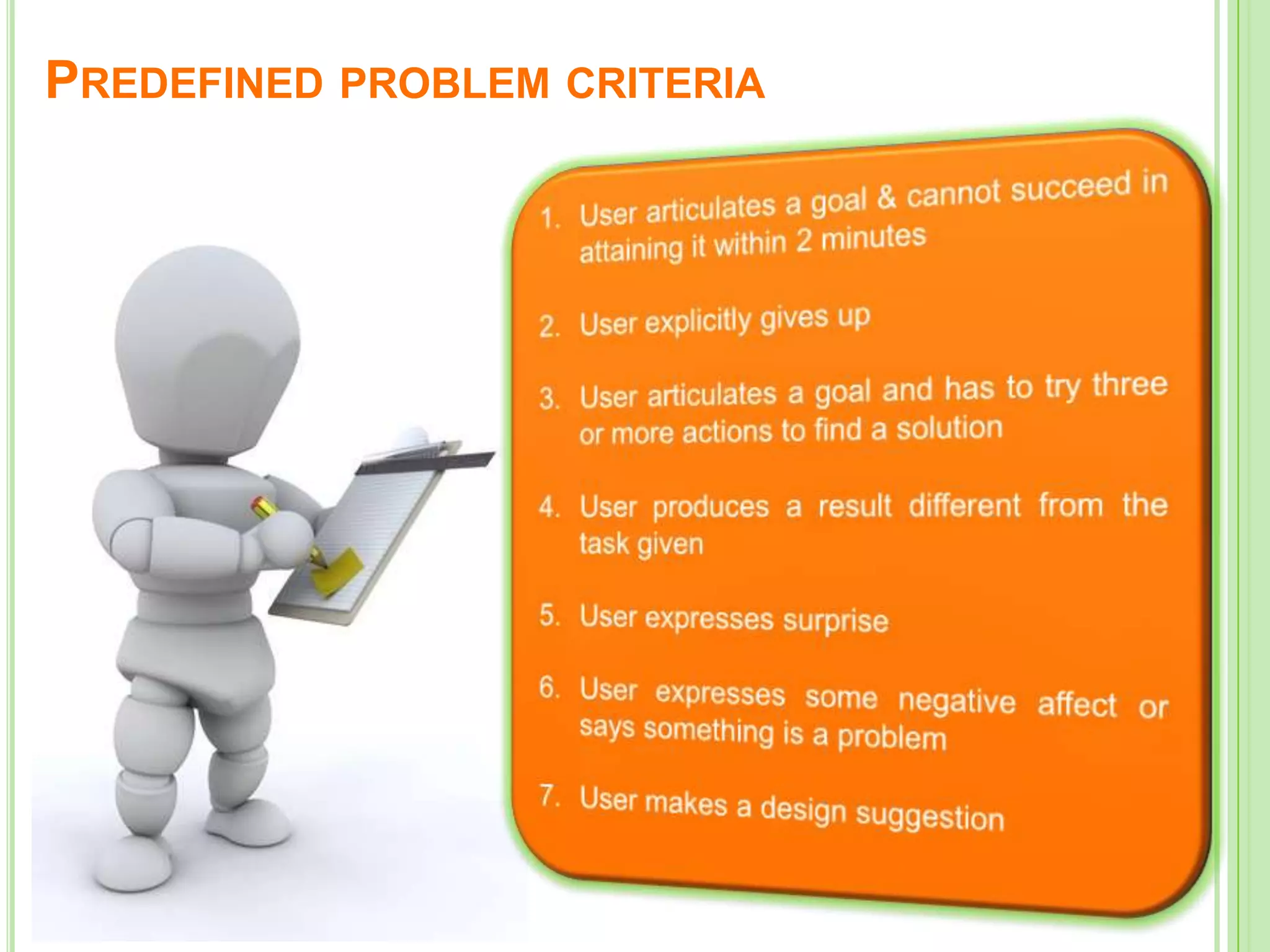
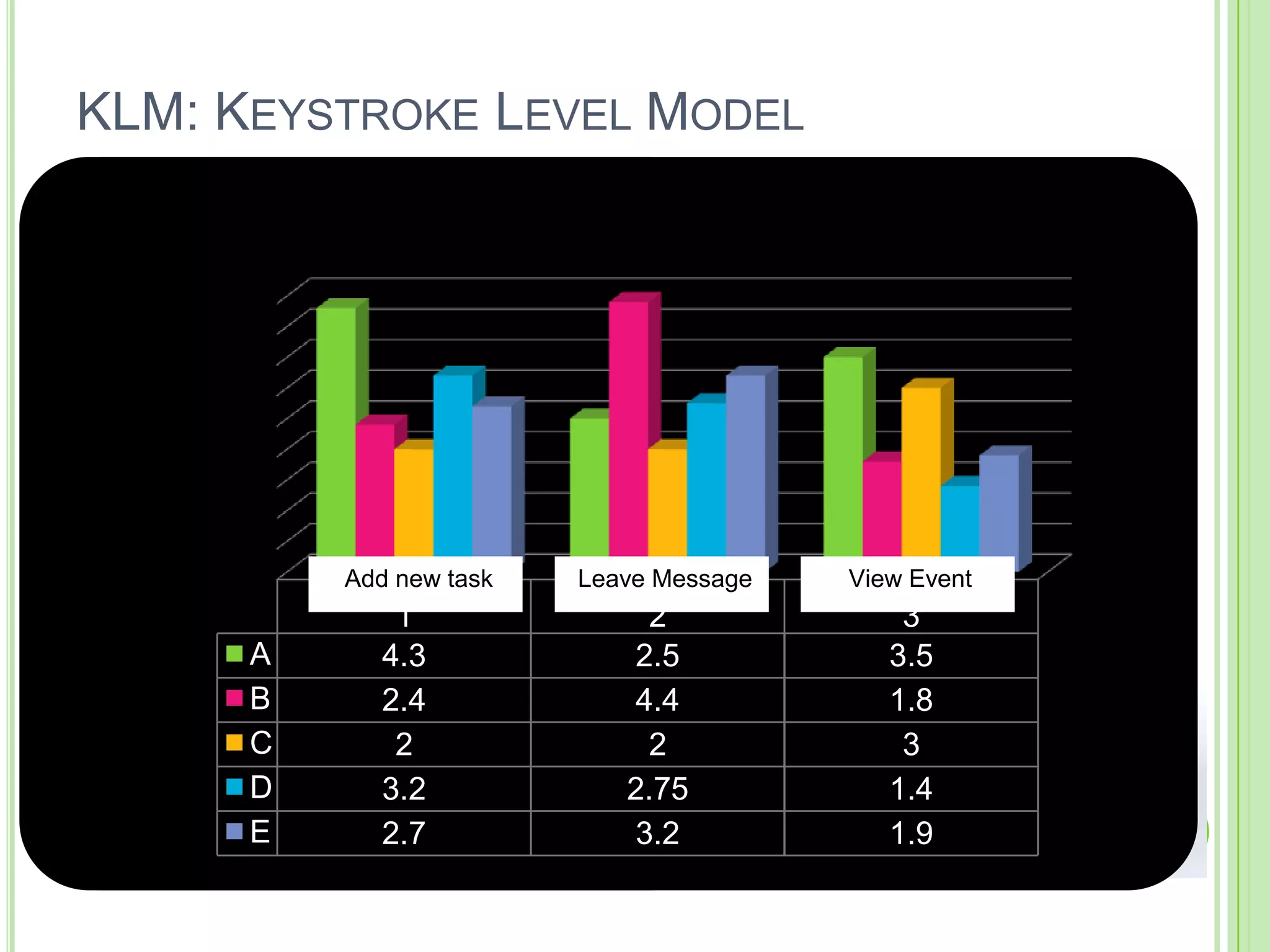
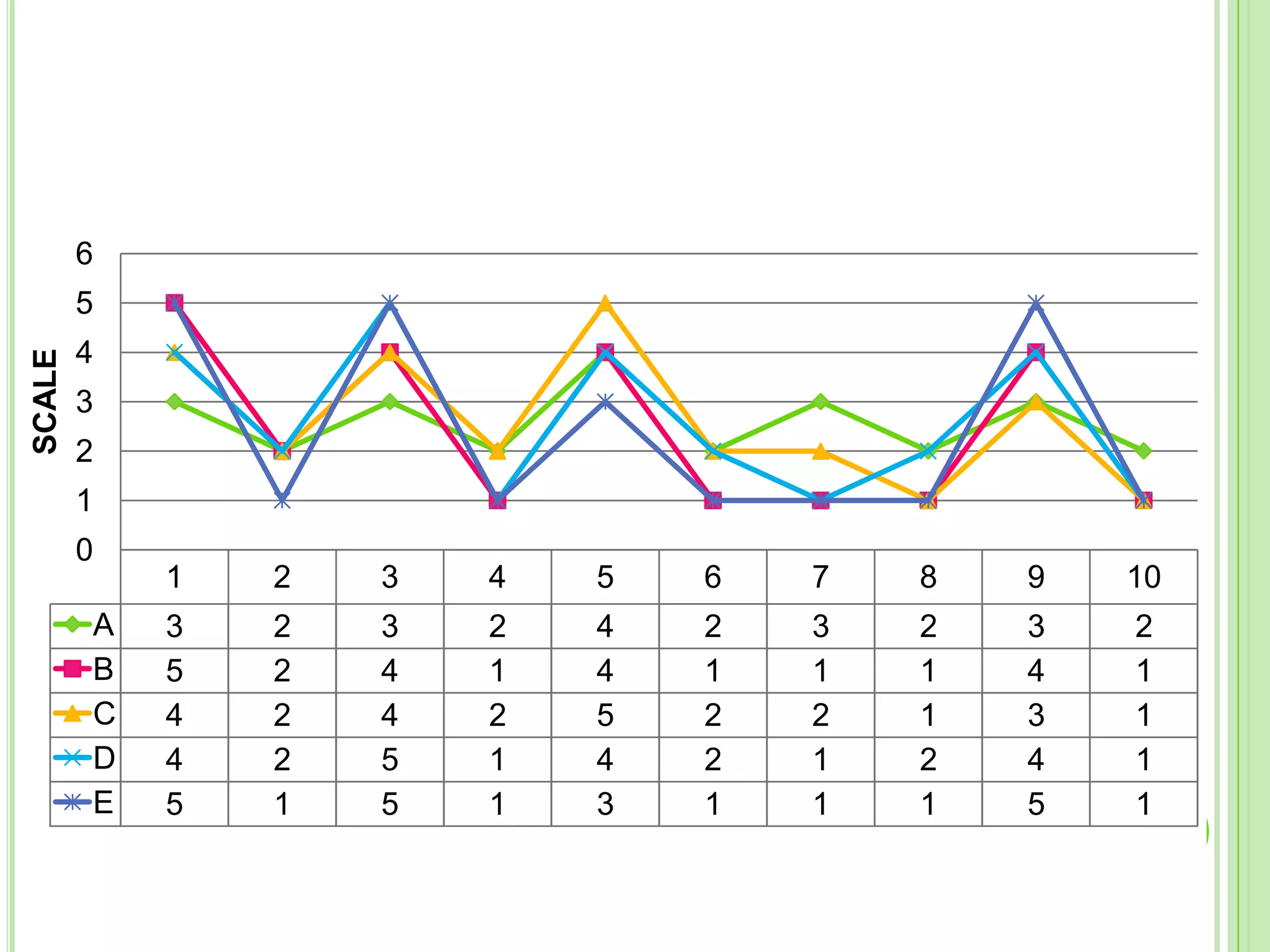
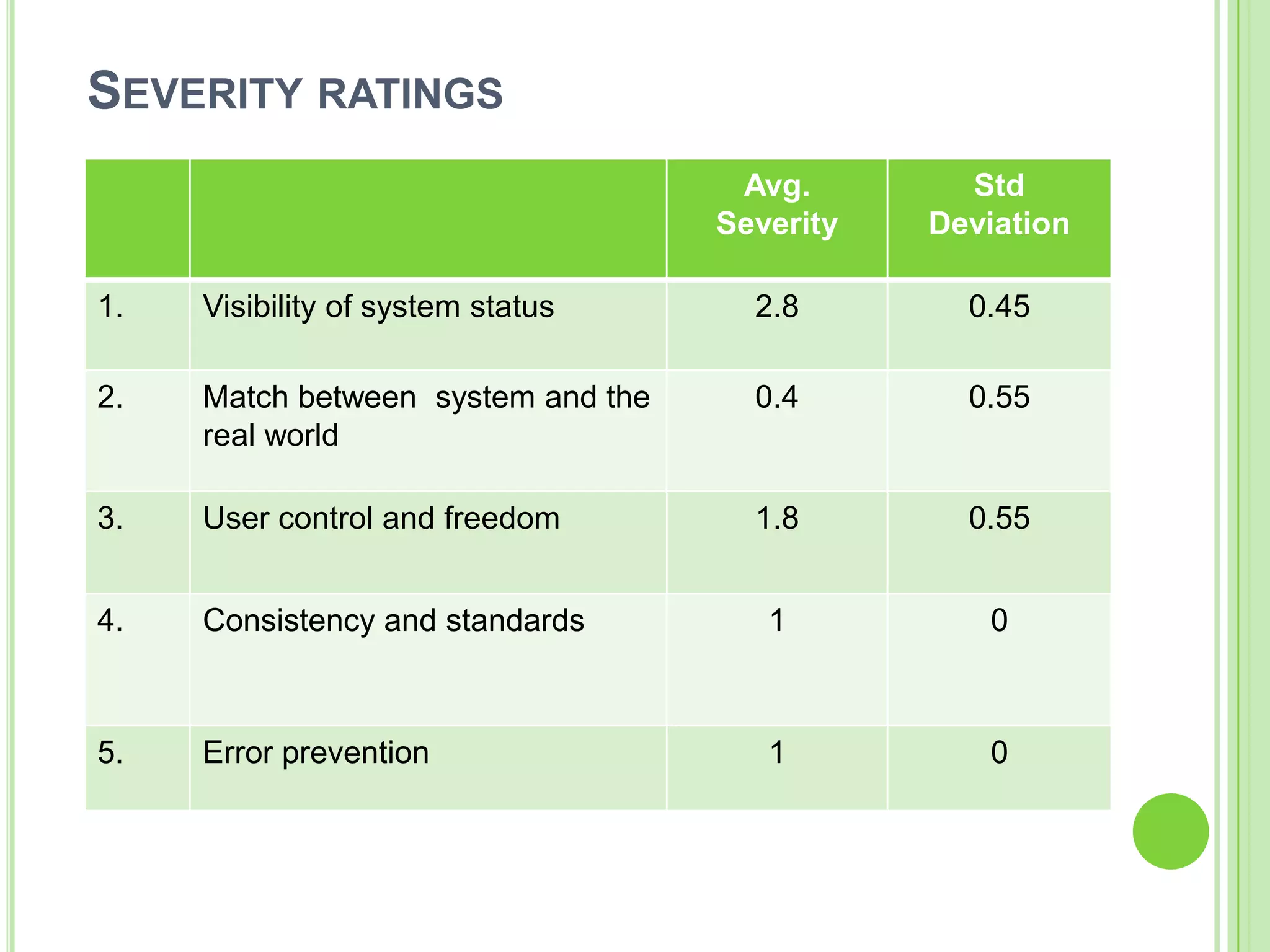
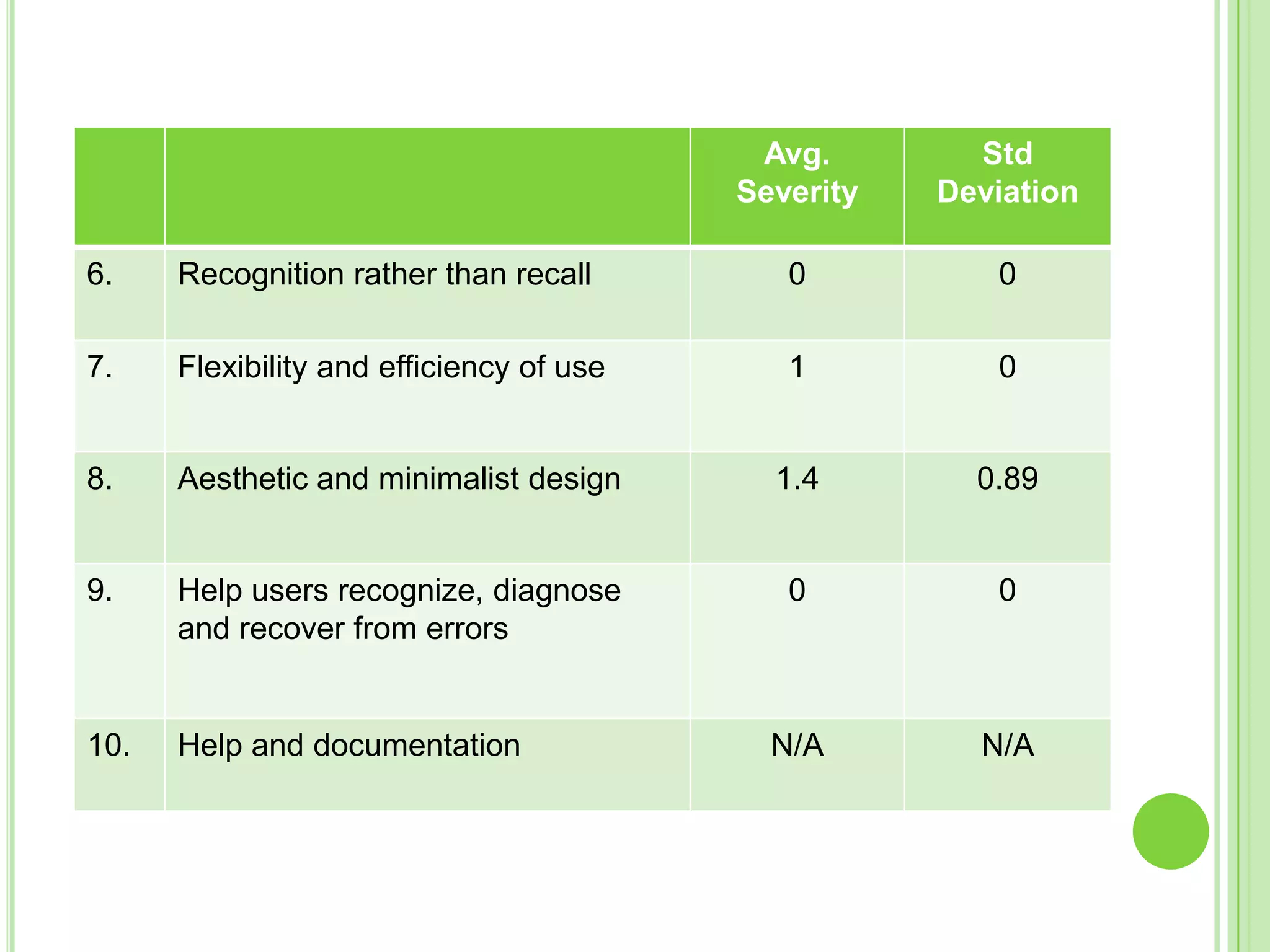
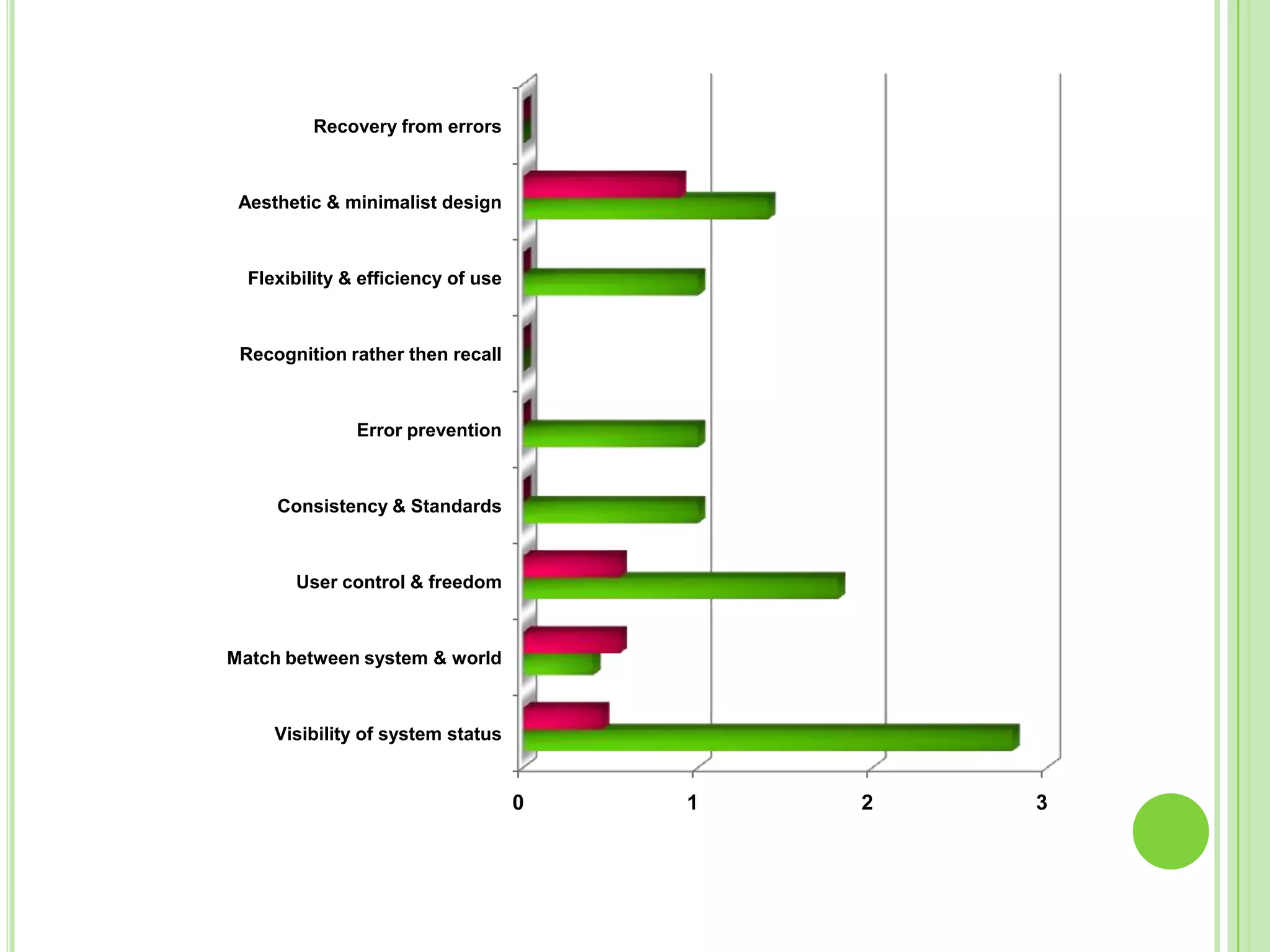
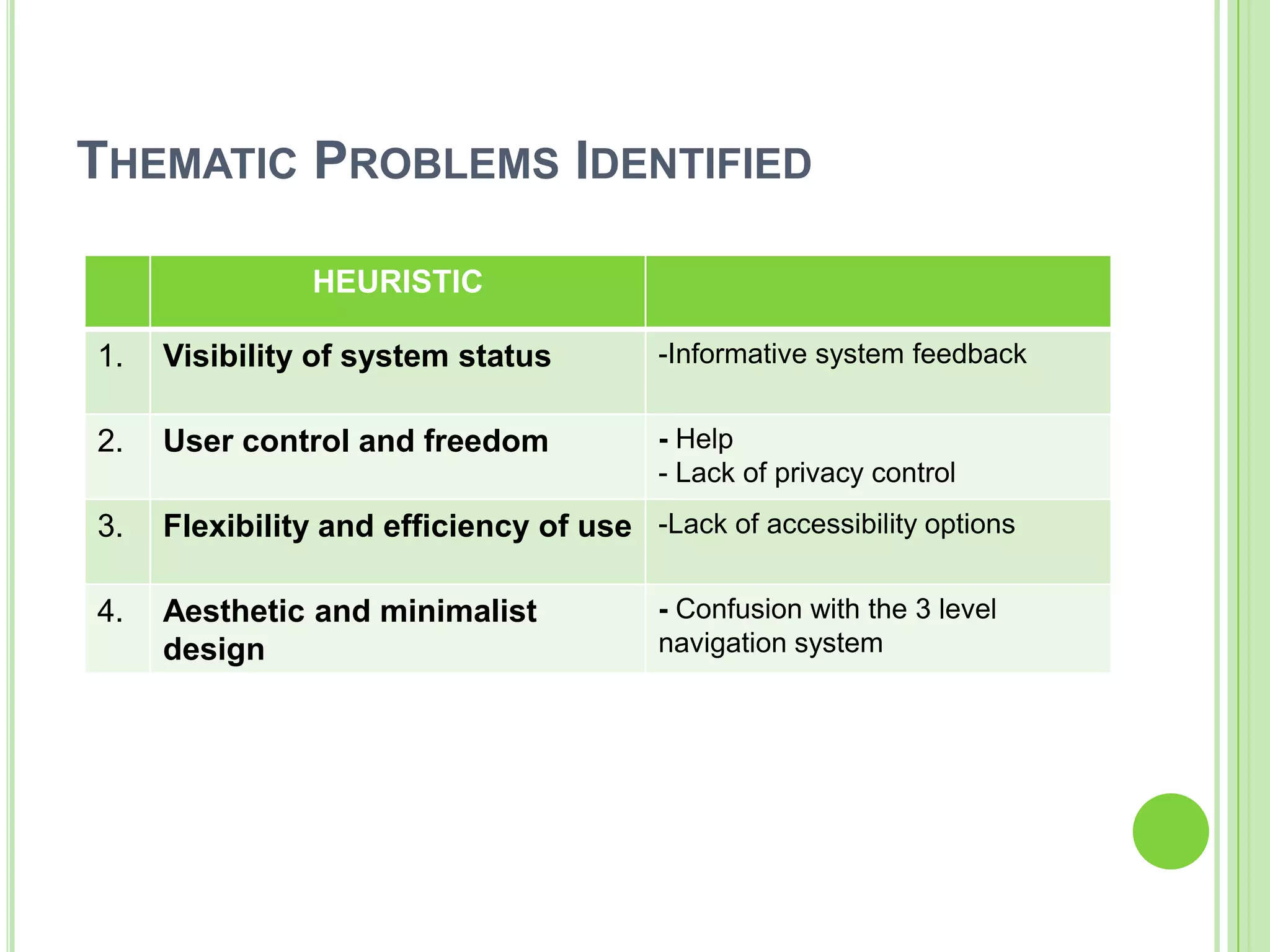
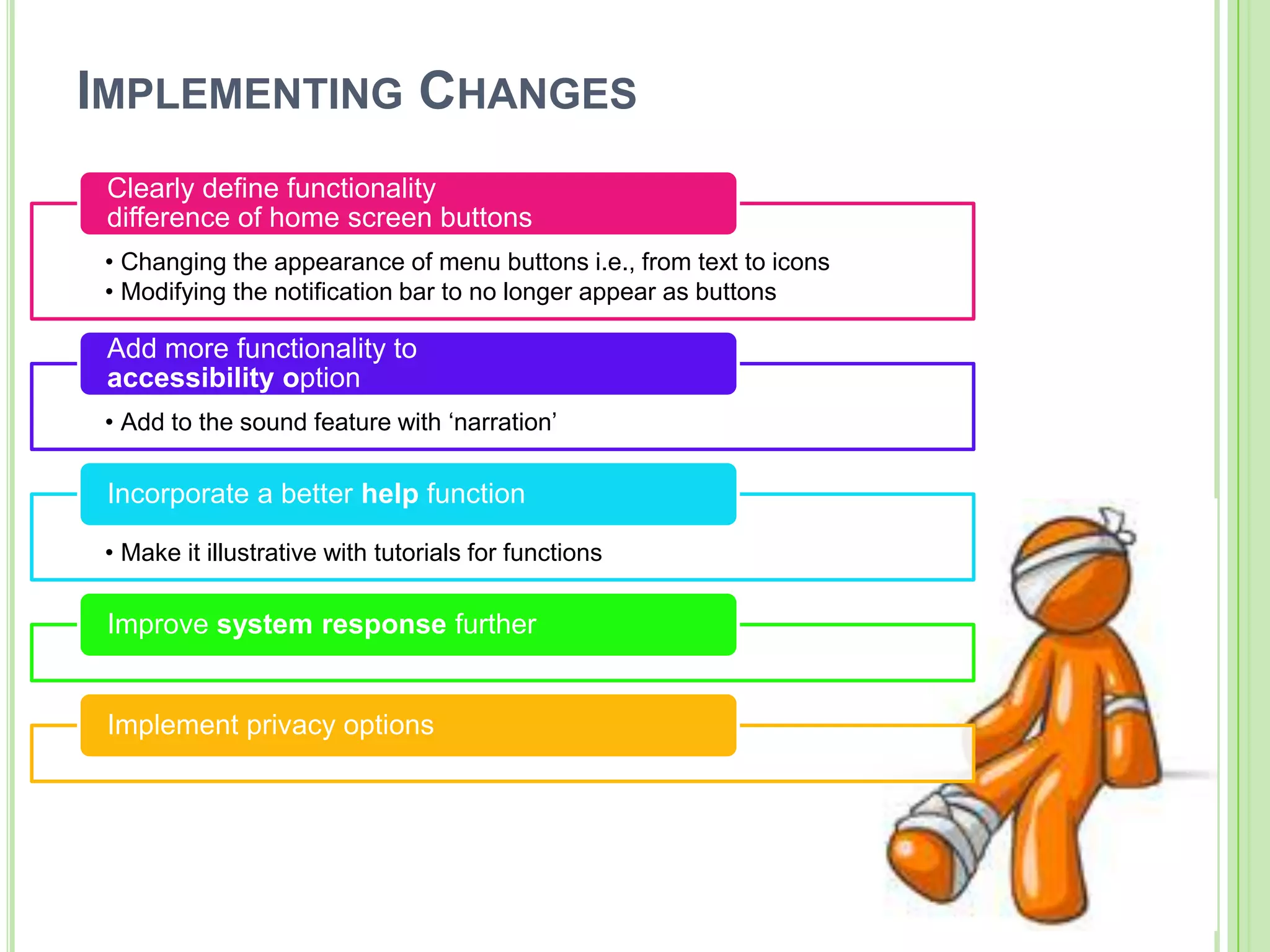
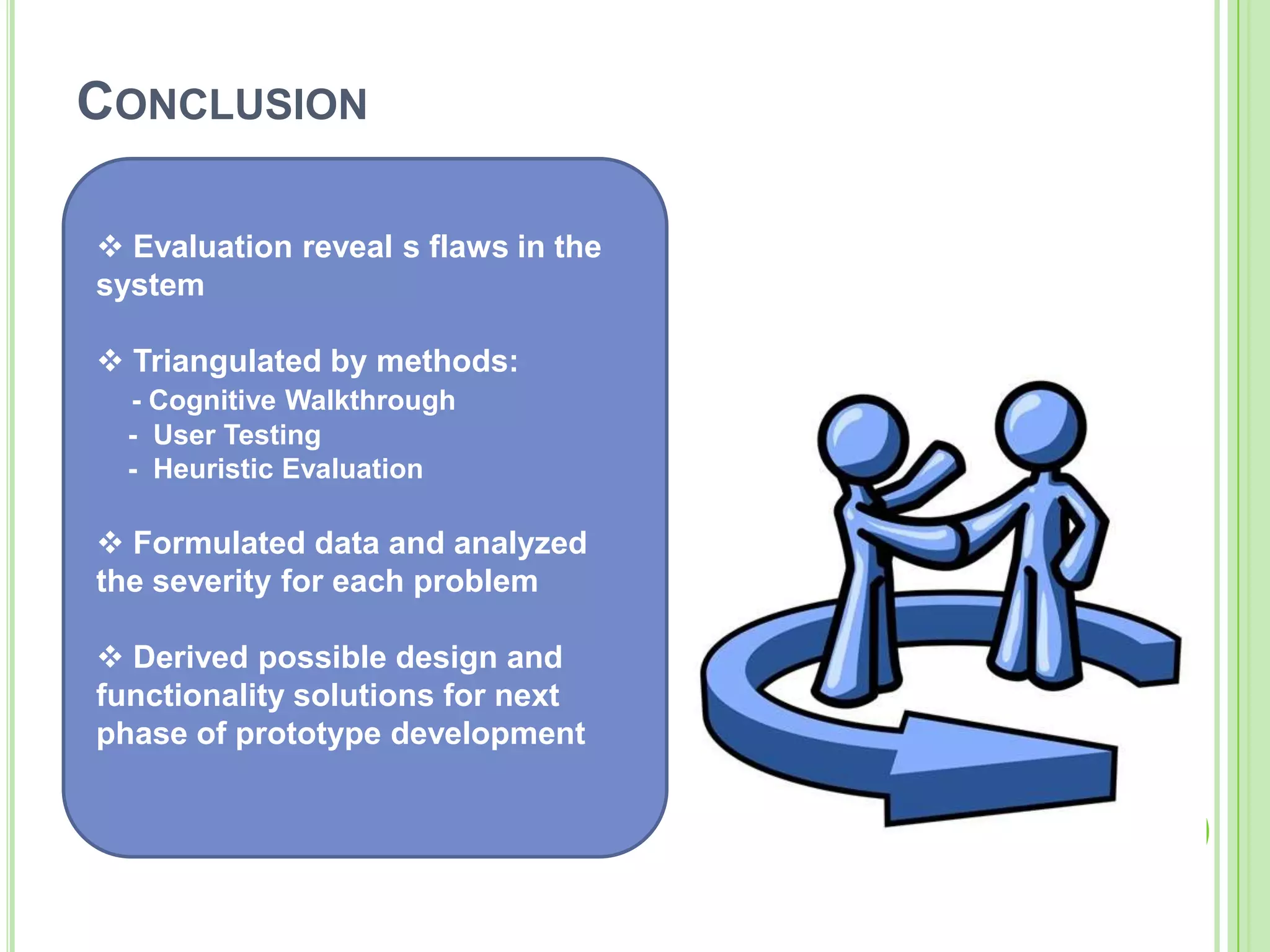
The document outlines a systematic approach to testing a prototype system, focusing on early detection of design and construction flaws to improve usability. It details a multi-faceted evaluation strategy that includes cognitive walkthroughs, user testing, and heuristic evaluations to understand user interactions and identify usability problems. The outcomes from these evaluations aim to inform design improvements for the next phase of prototype development.