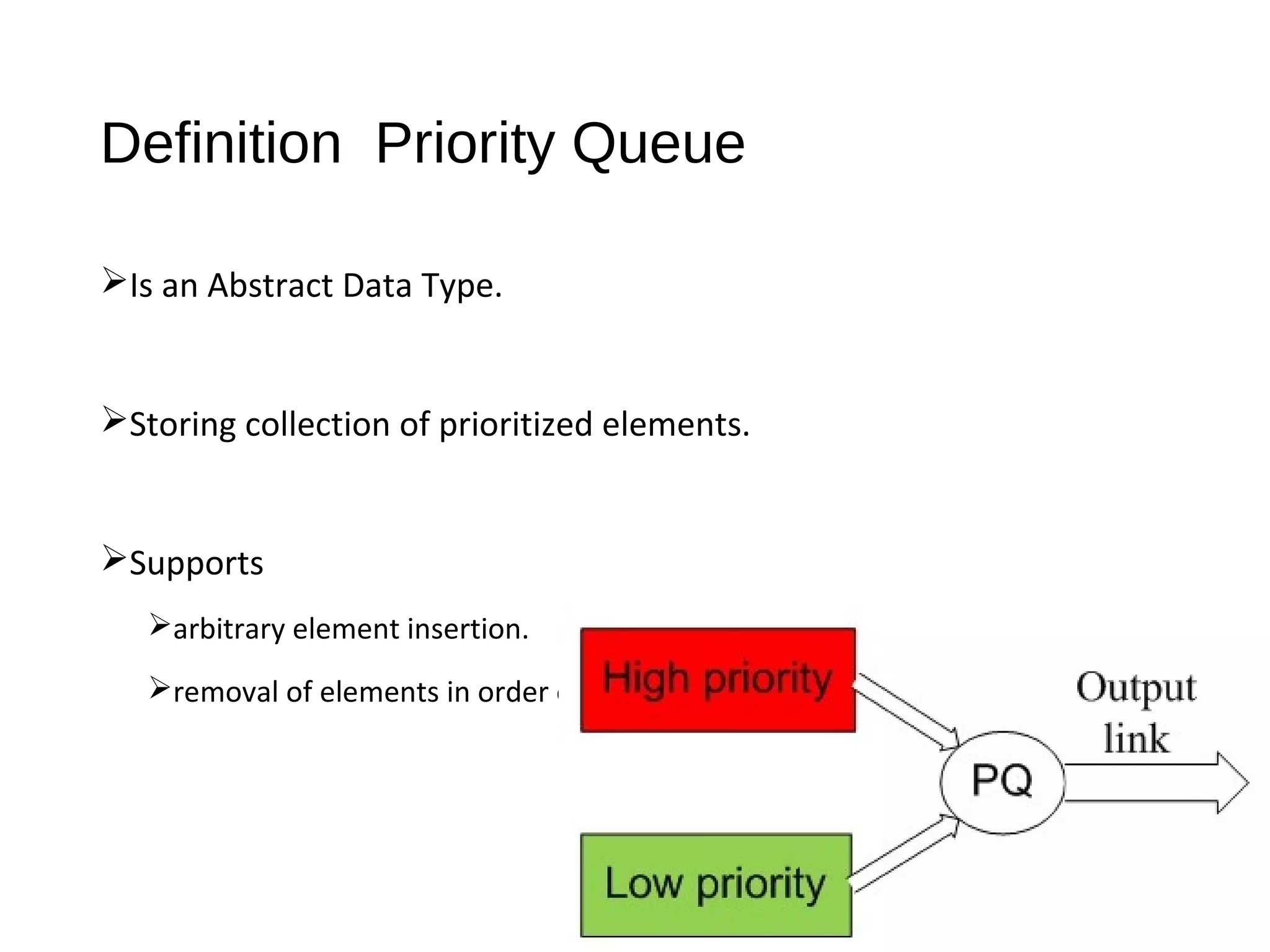
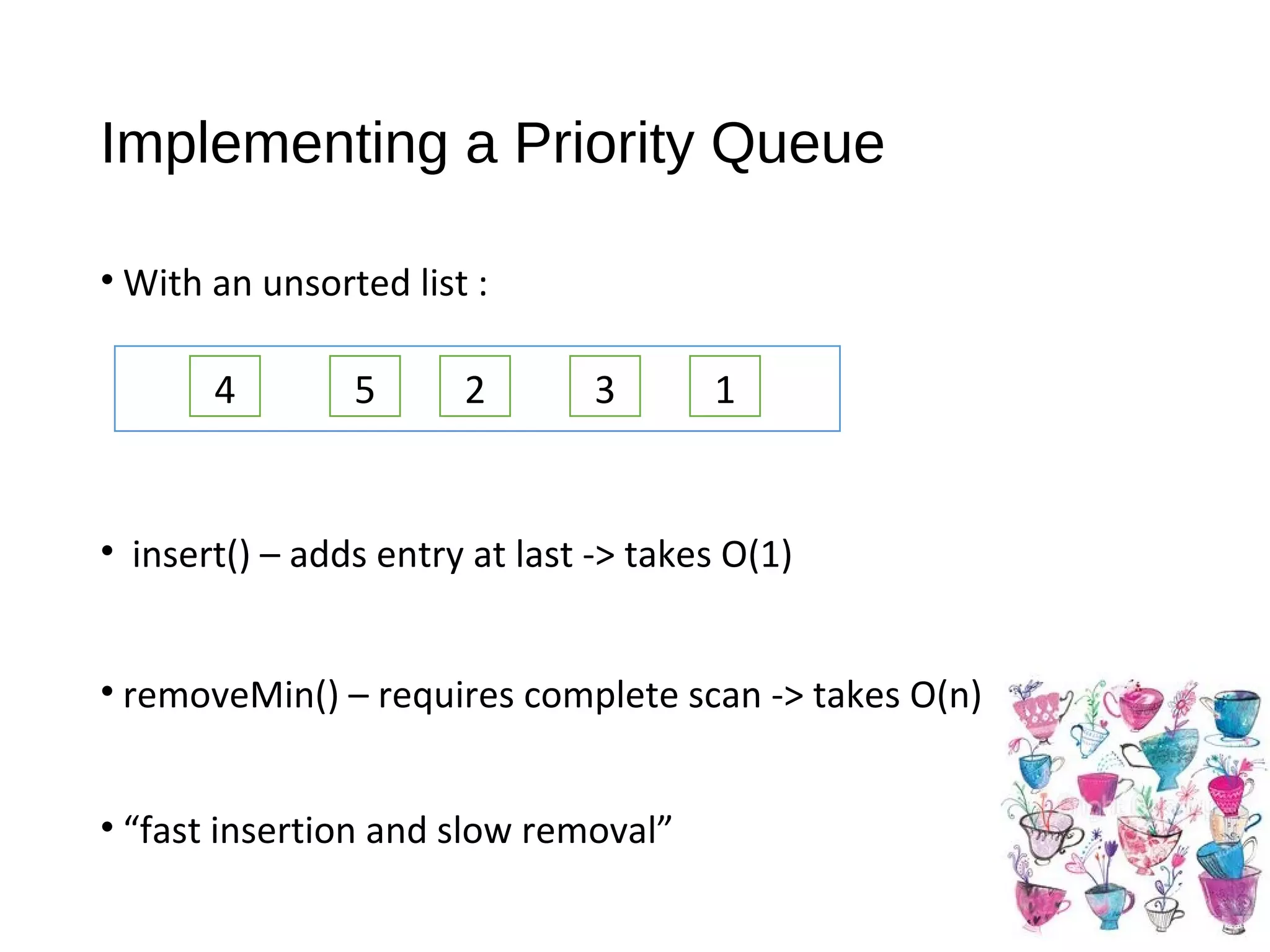
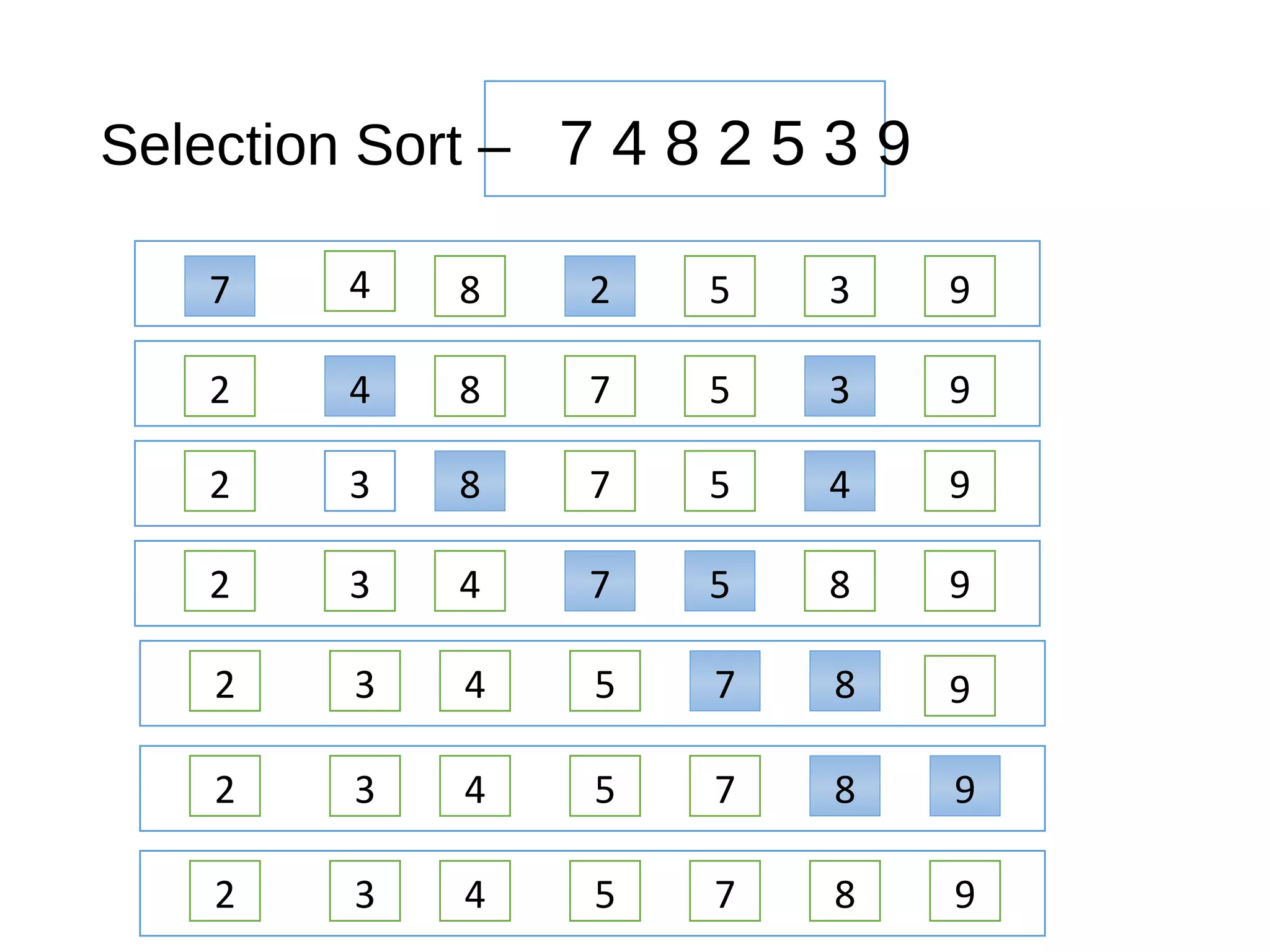
The document discusses priority queues as an abstract data type used for storing prioritized elements, where utility determines the importance of each asset. It outlines key operations and methods for managing priority queues, highlights their applications, and explains sorting methods involving priority queues. Additionally, it compares performance metrics for operations with unsorted and sorted lists.