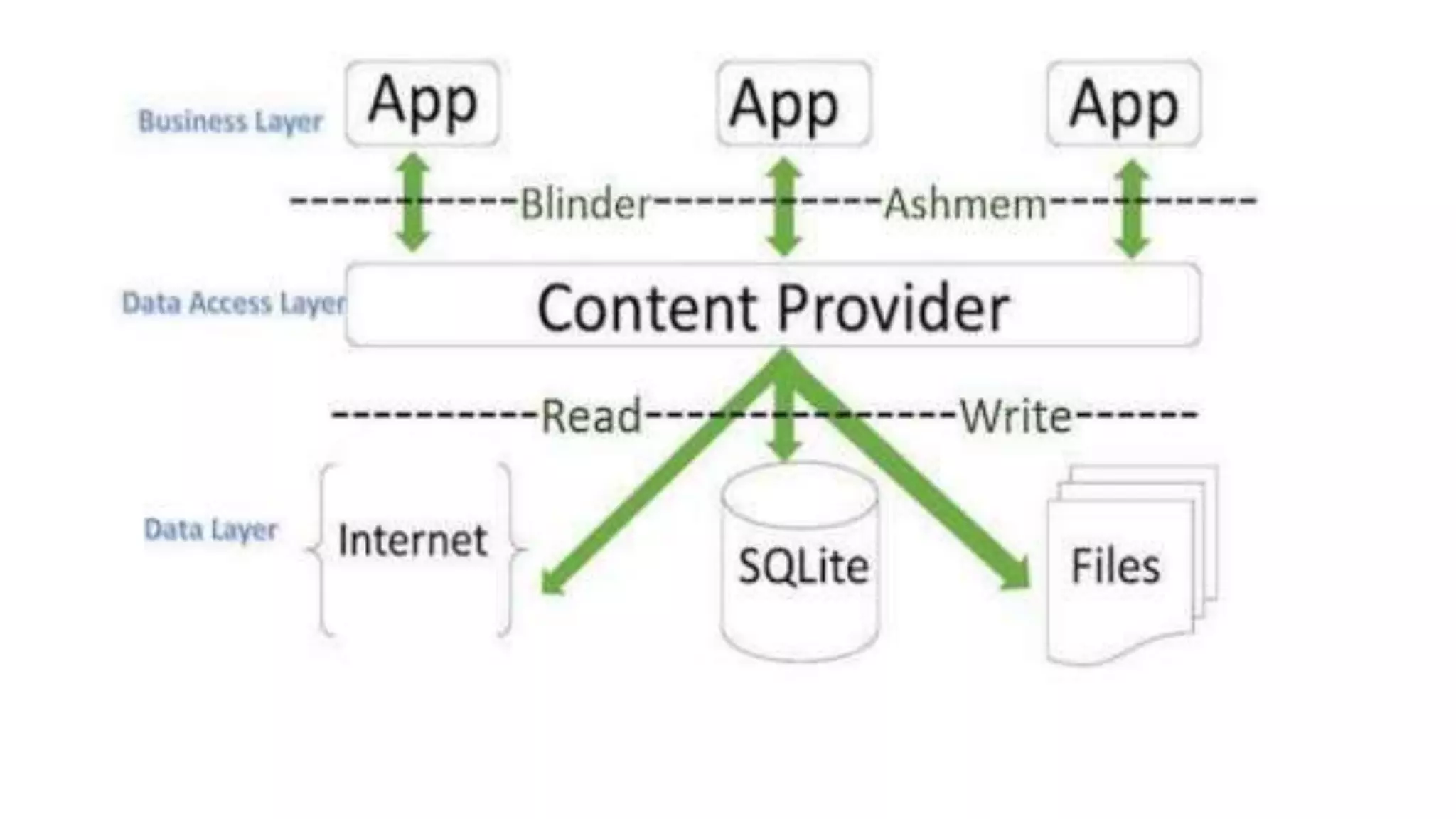
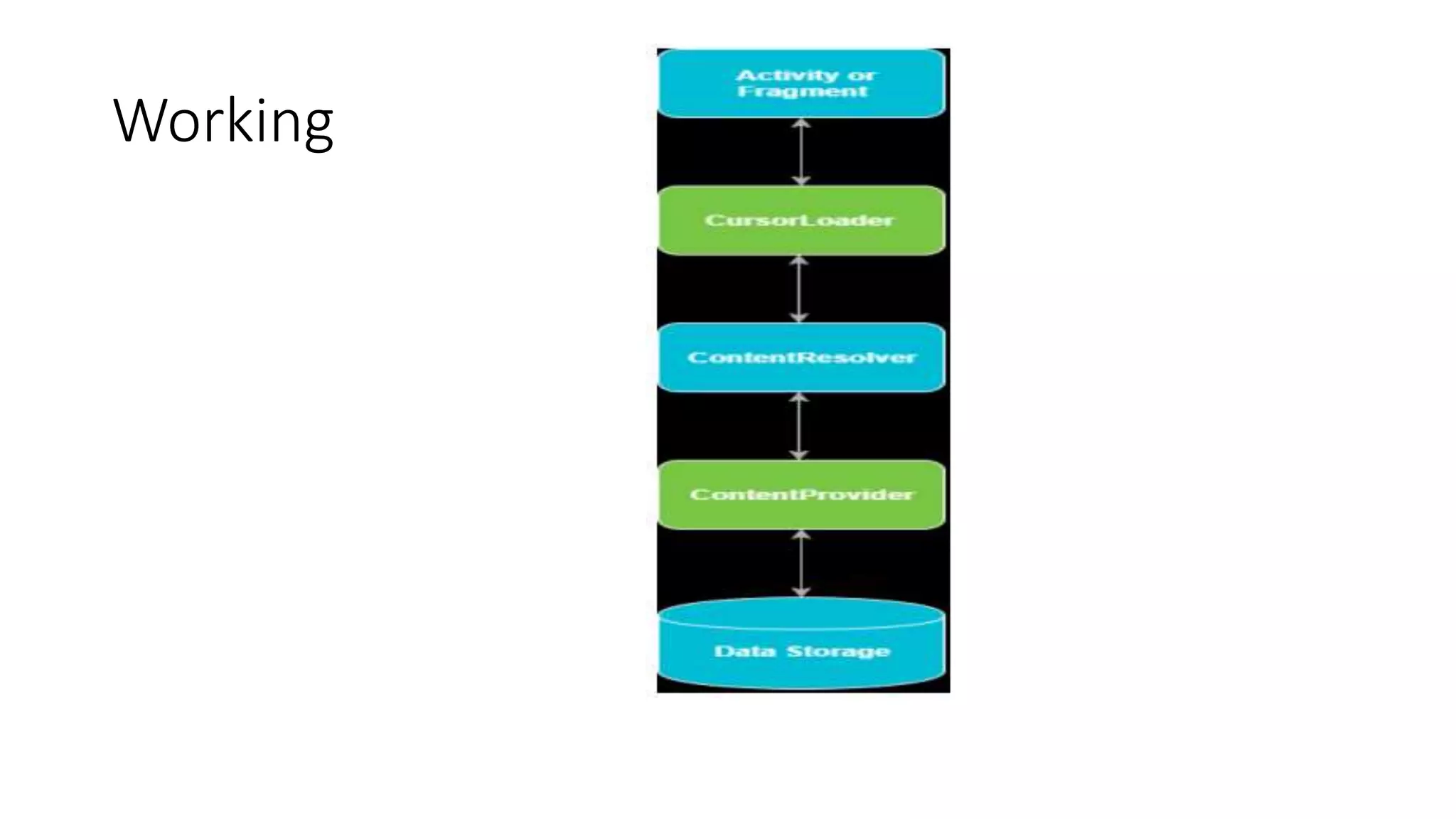
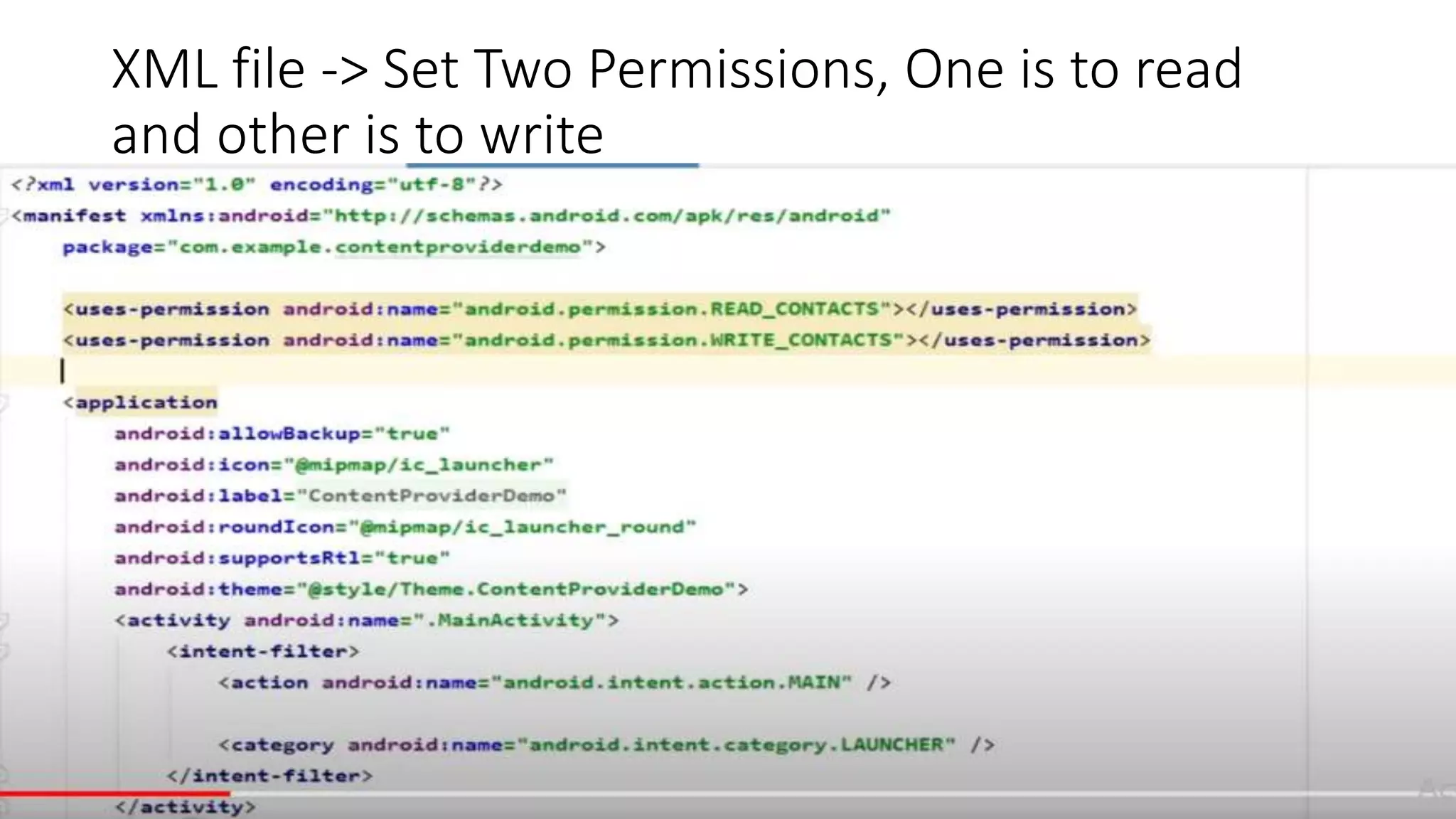
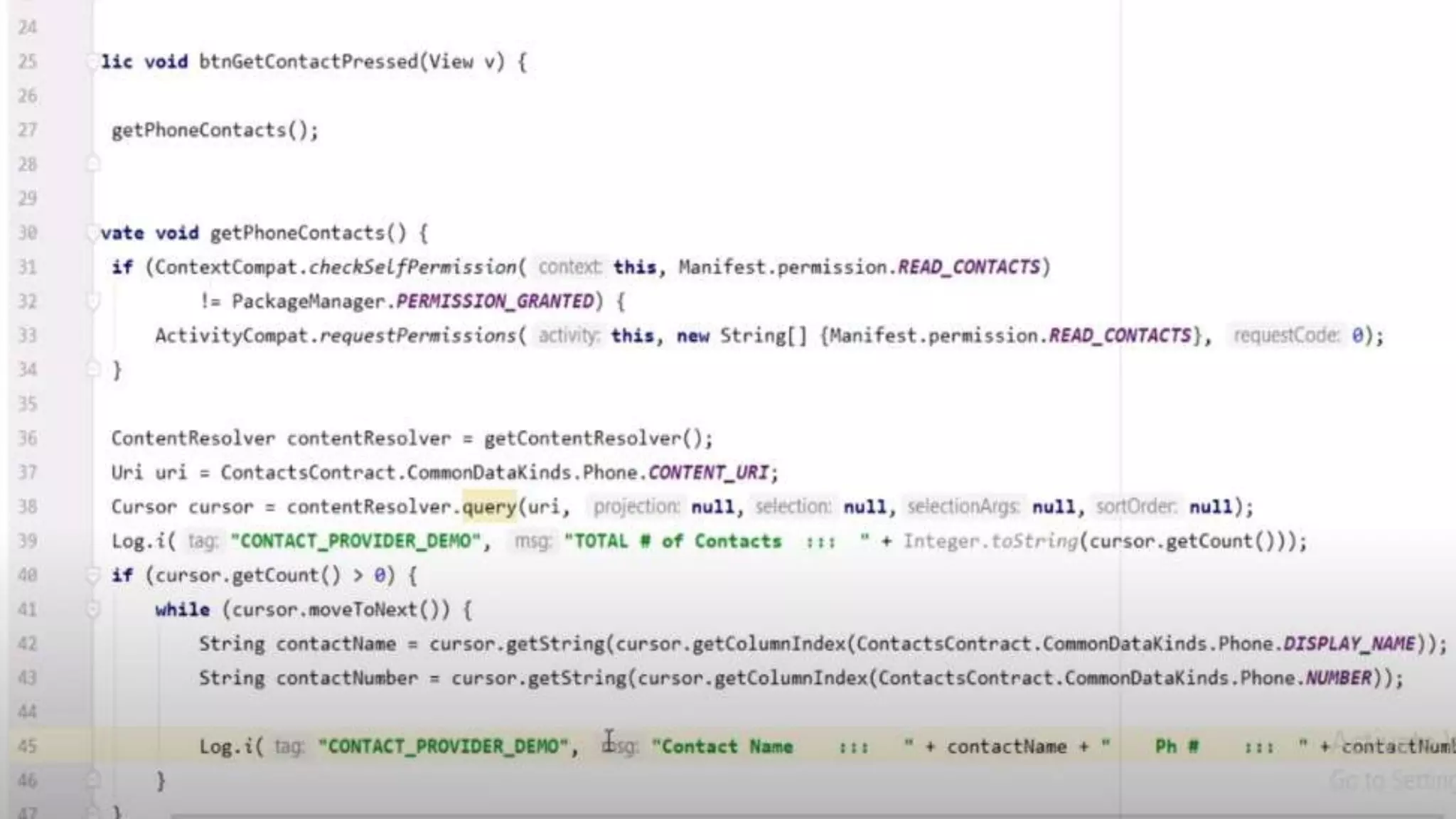
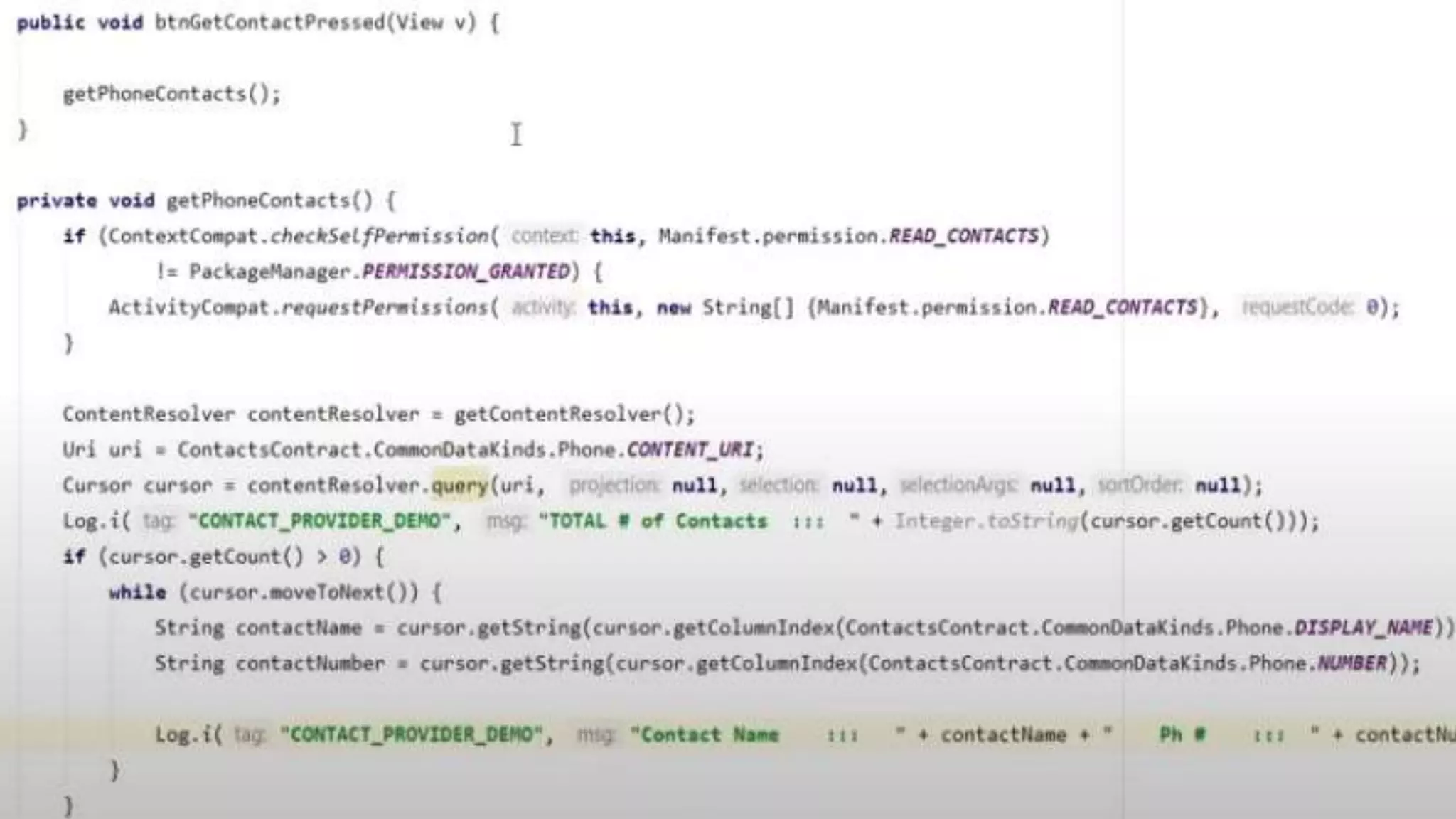
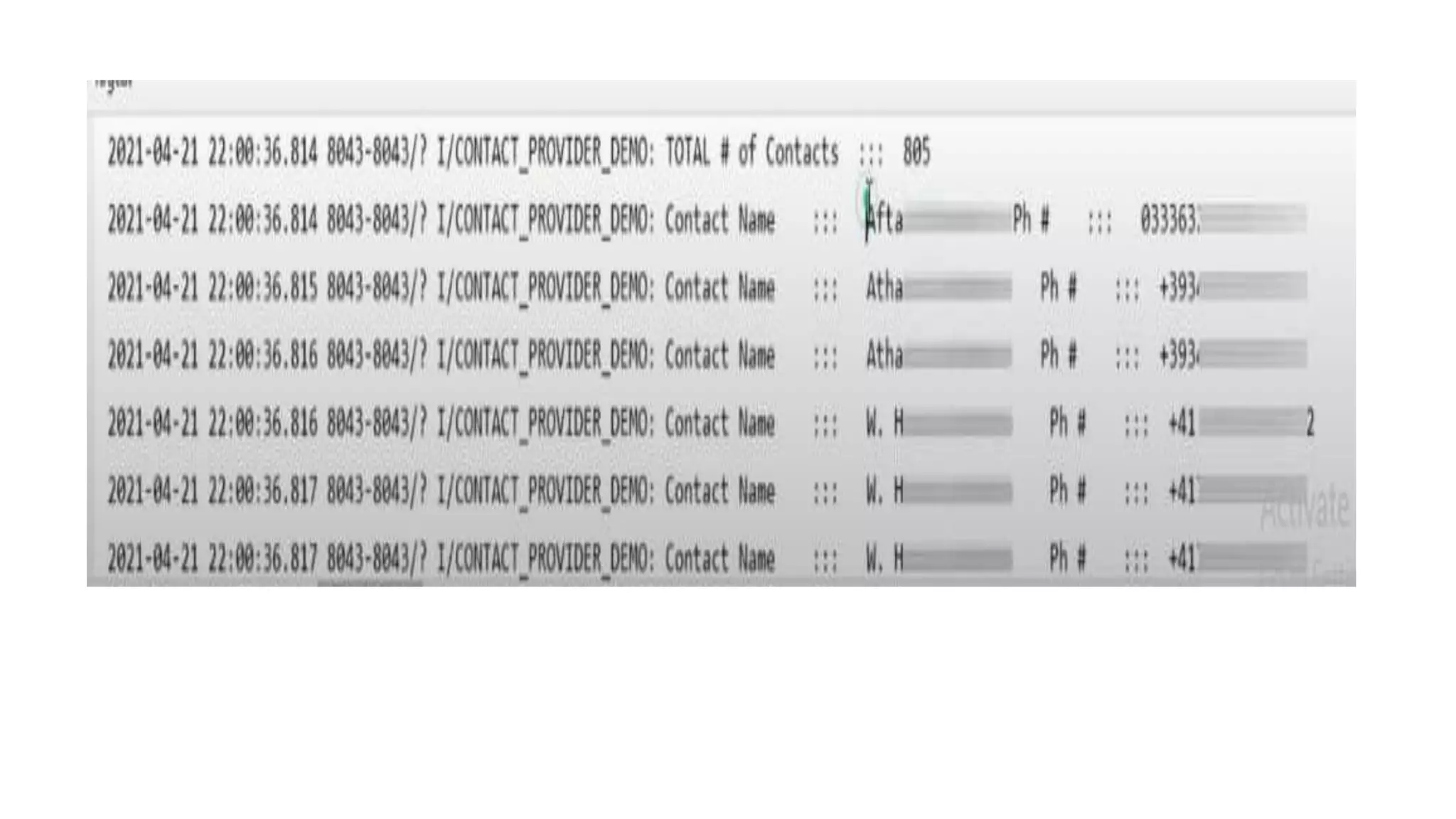
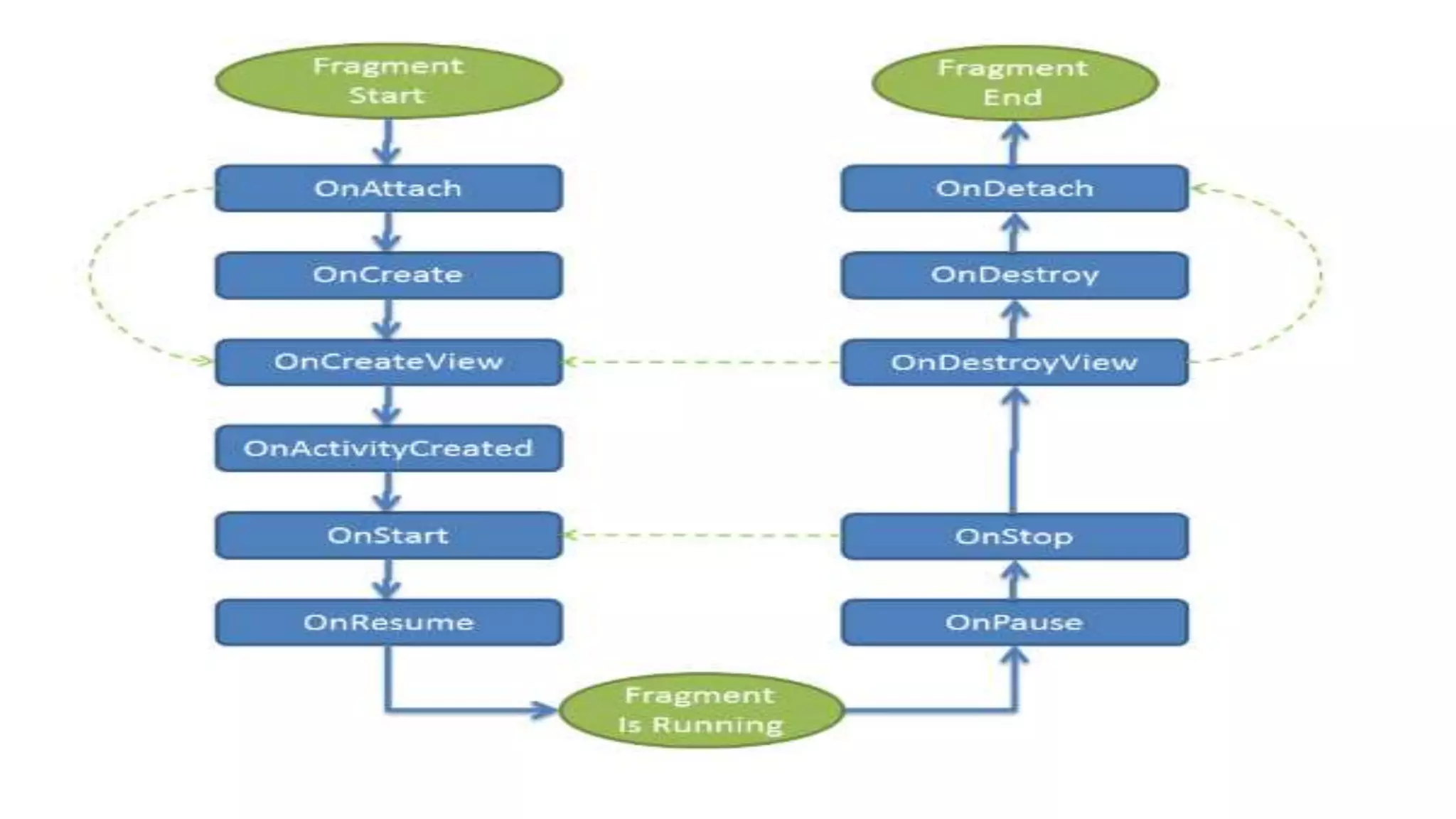
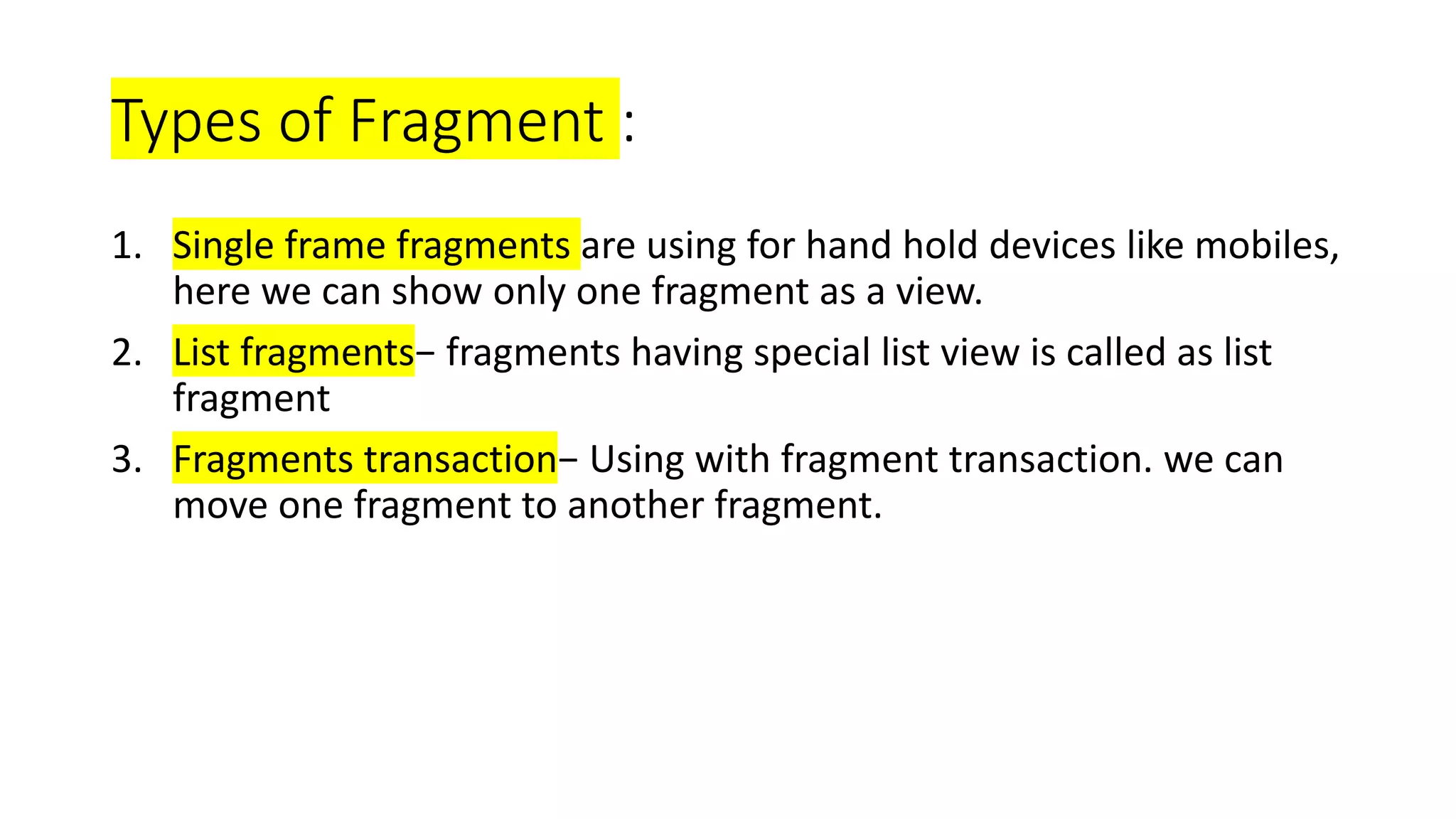
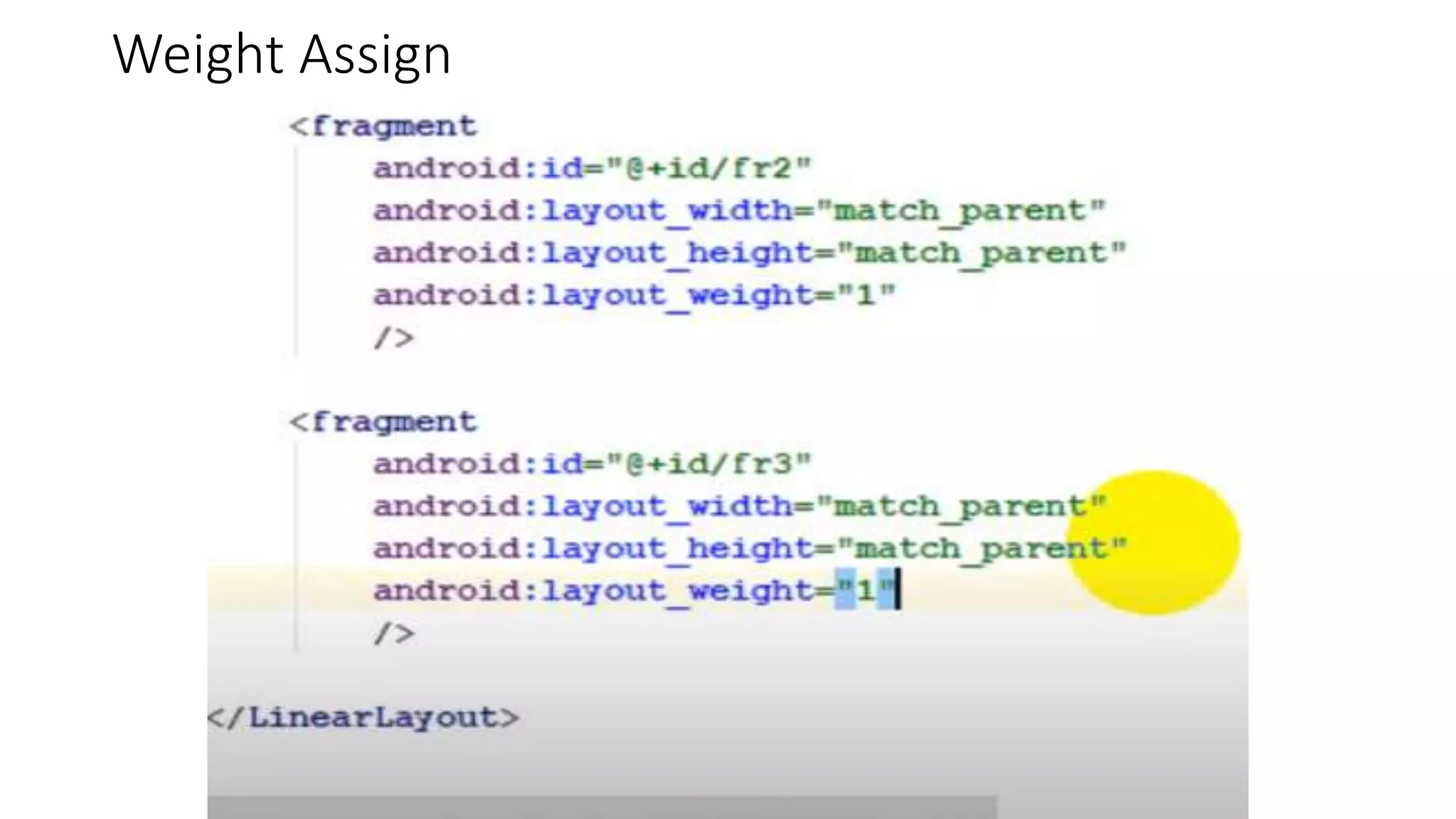
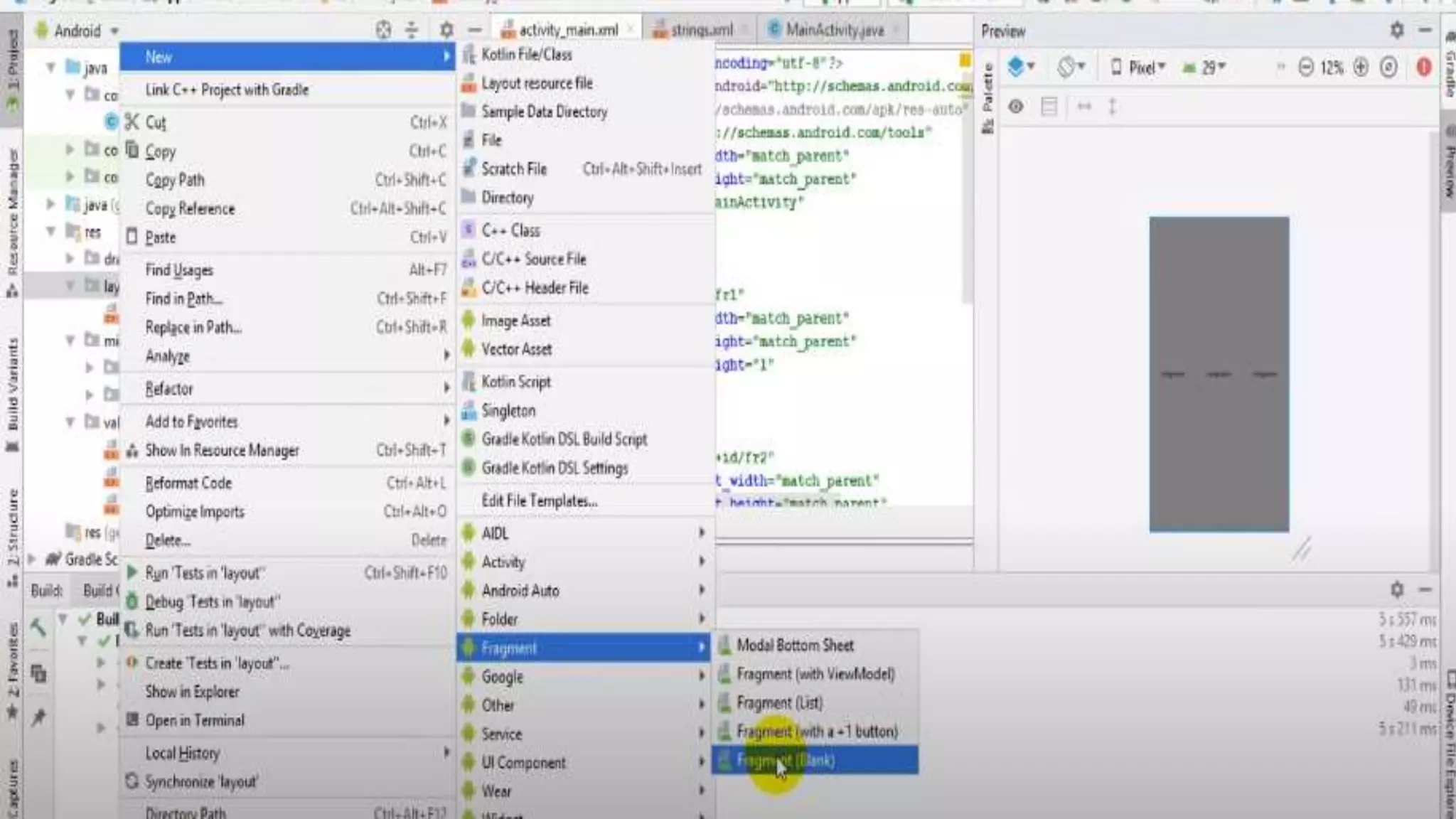
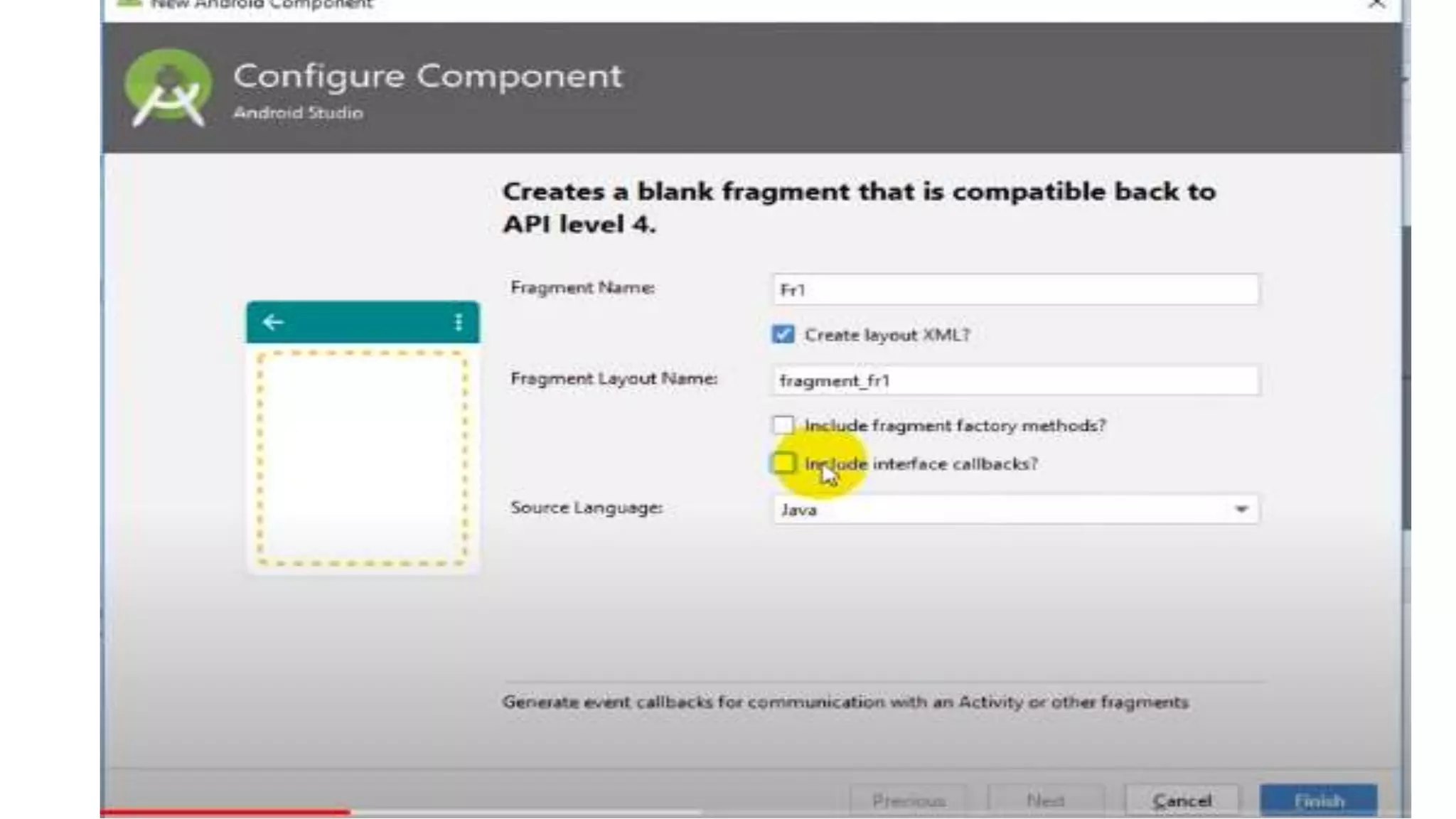
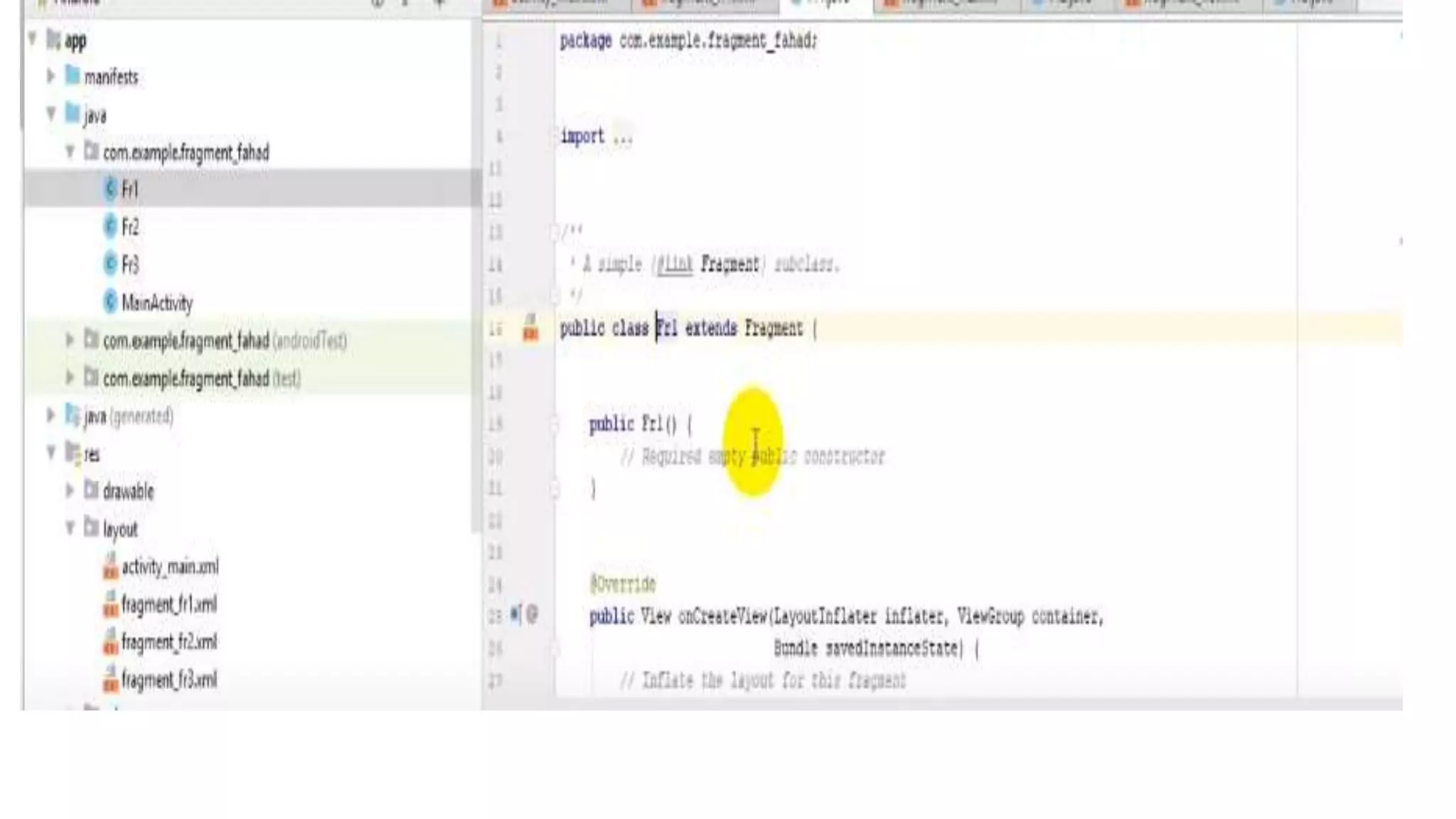
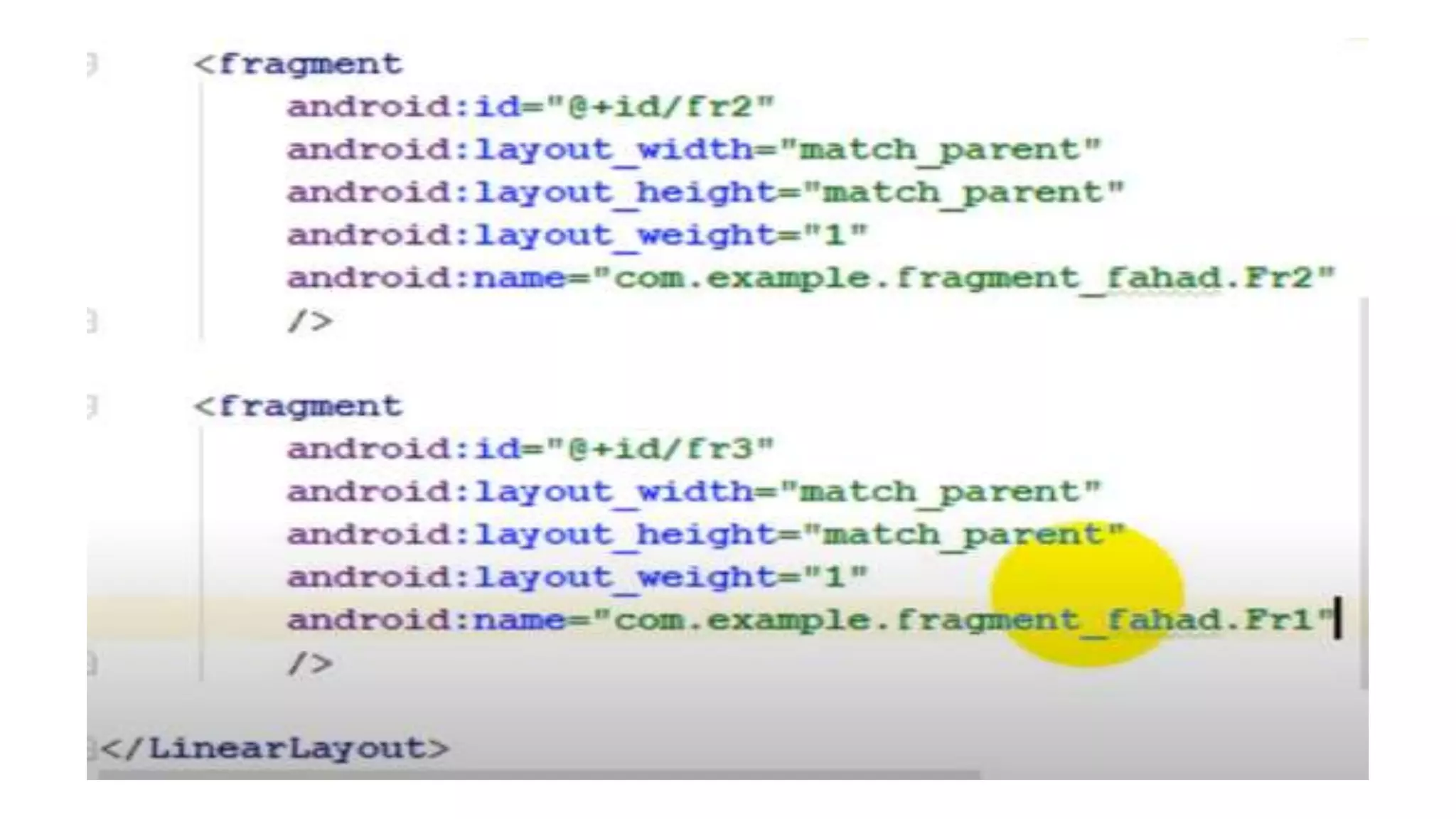
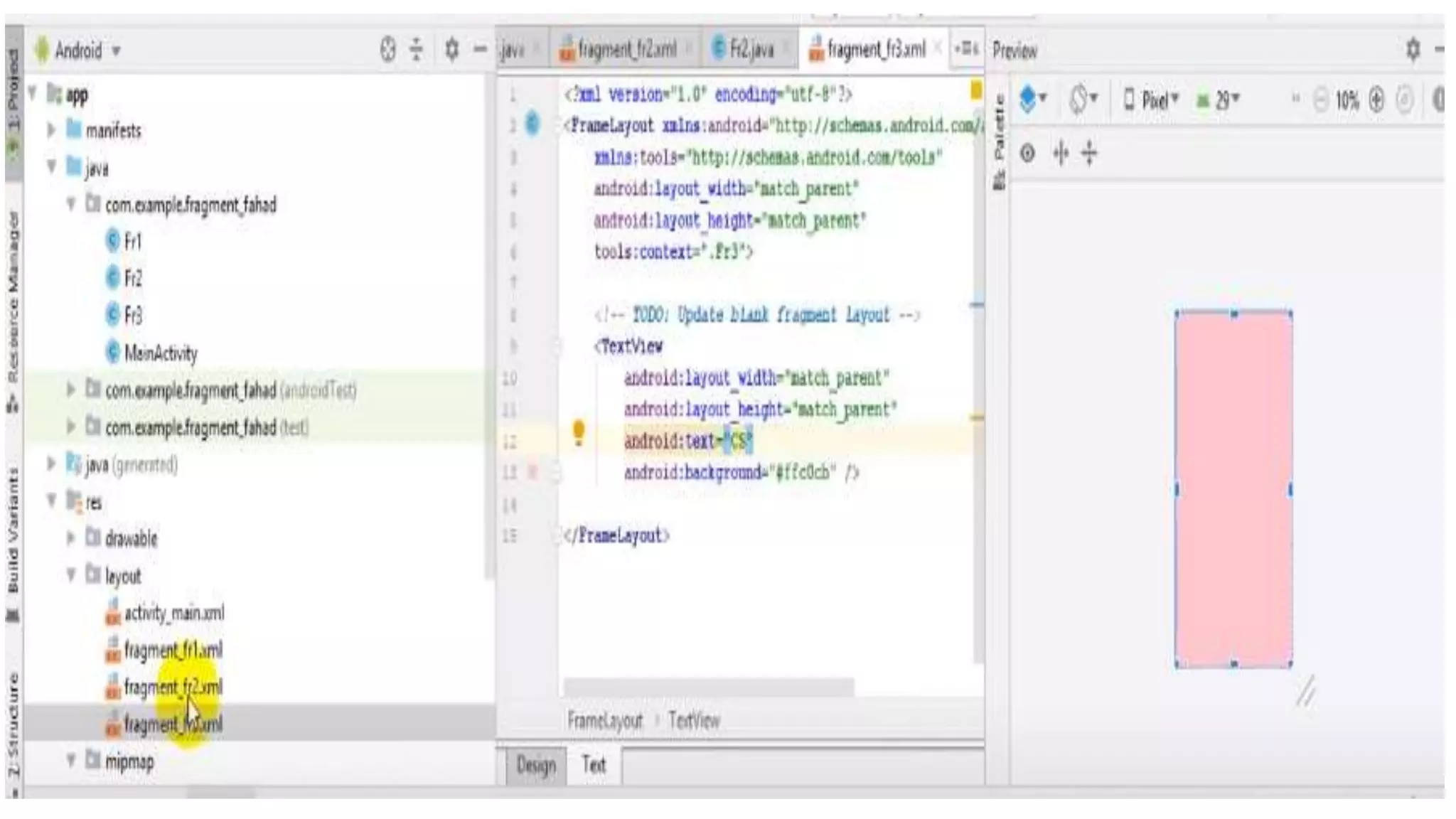
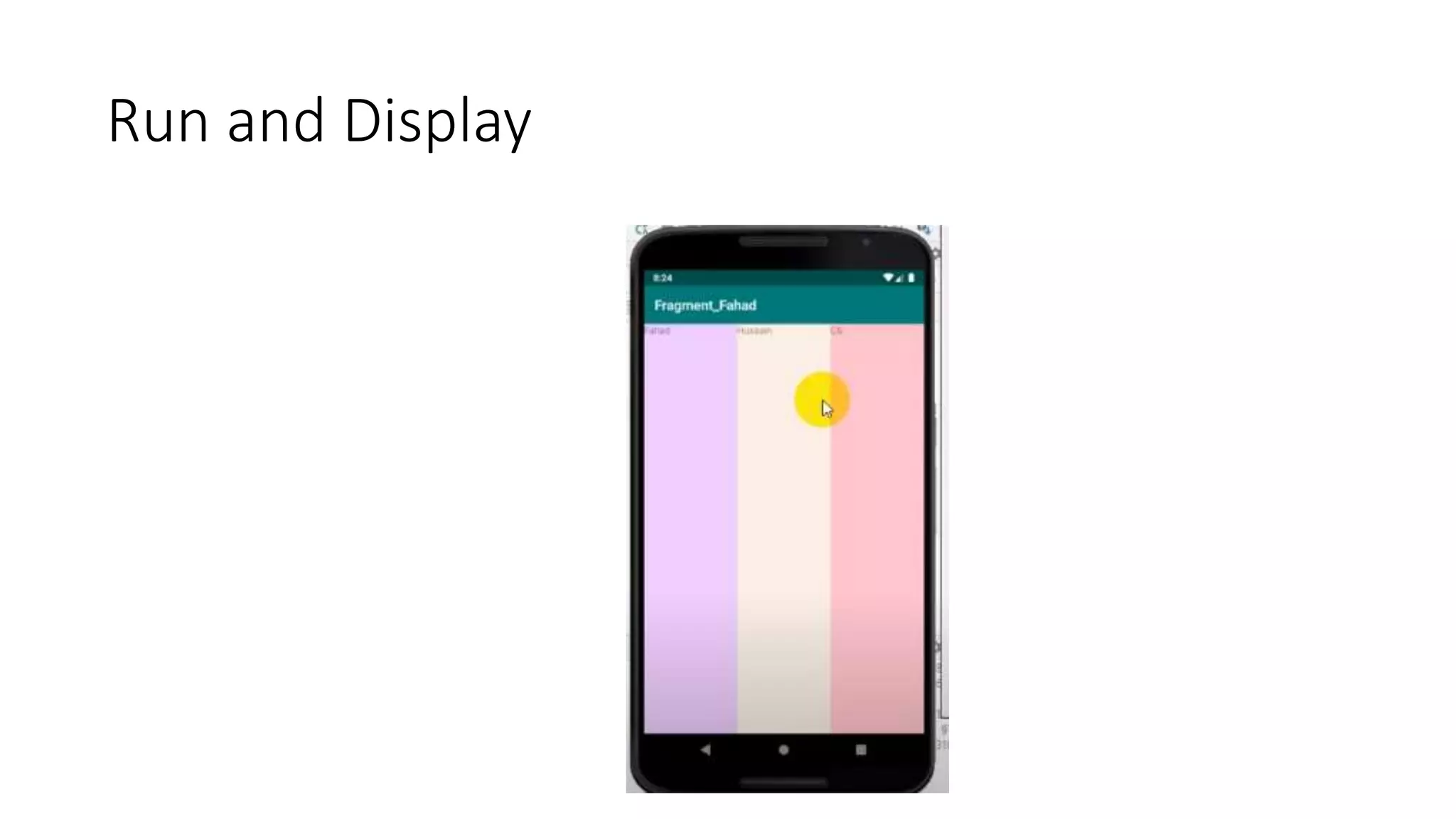
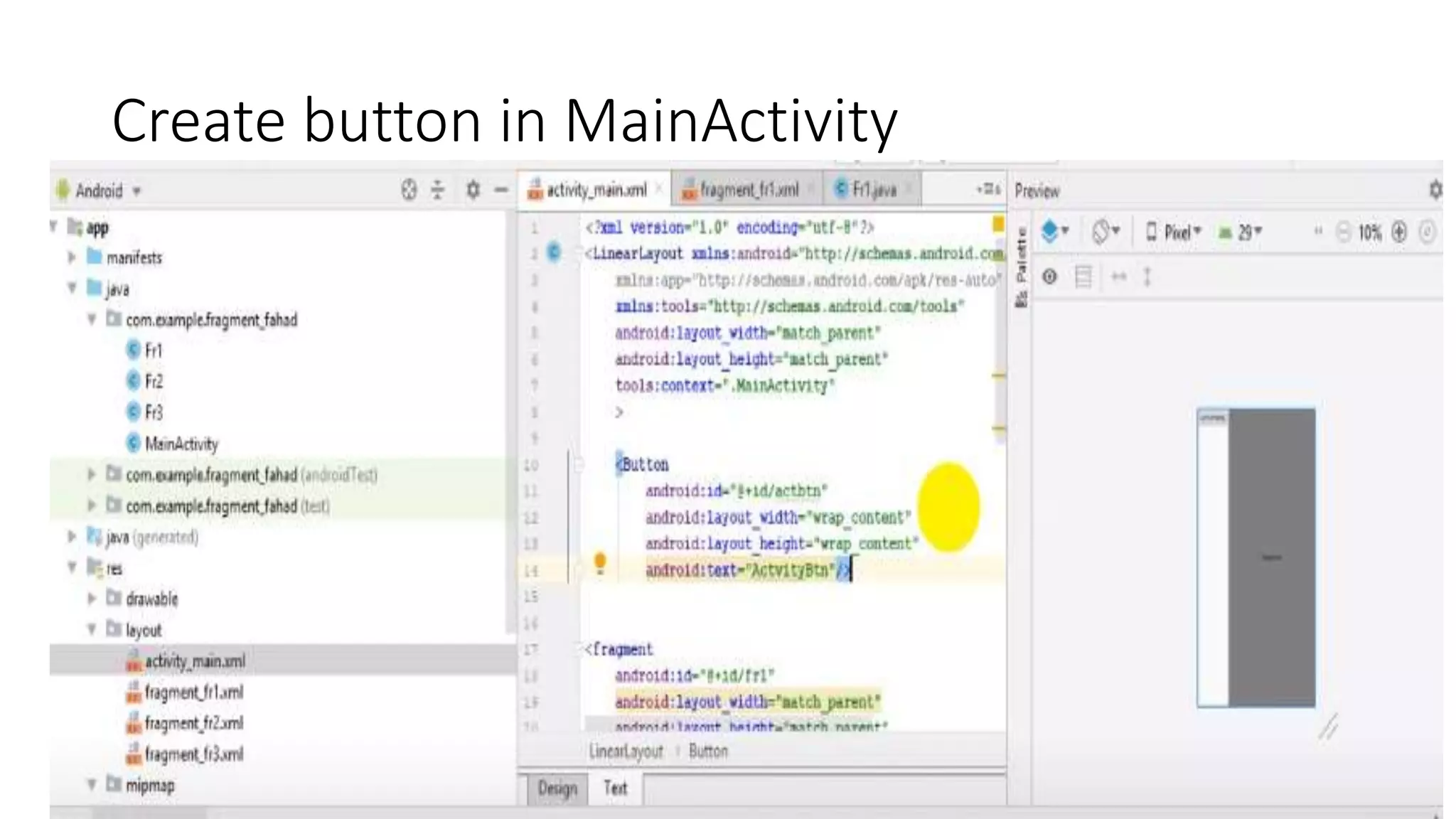
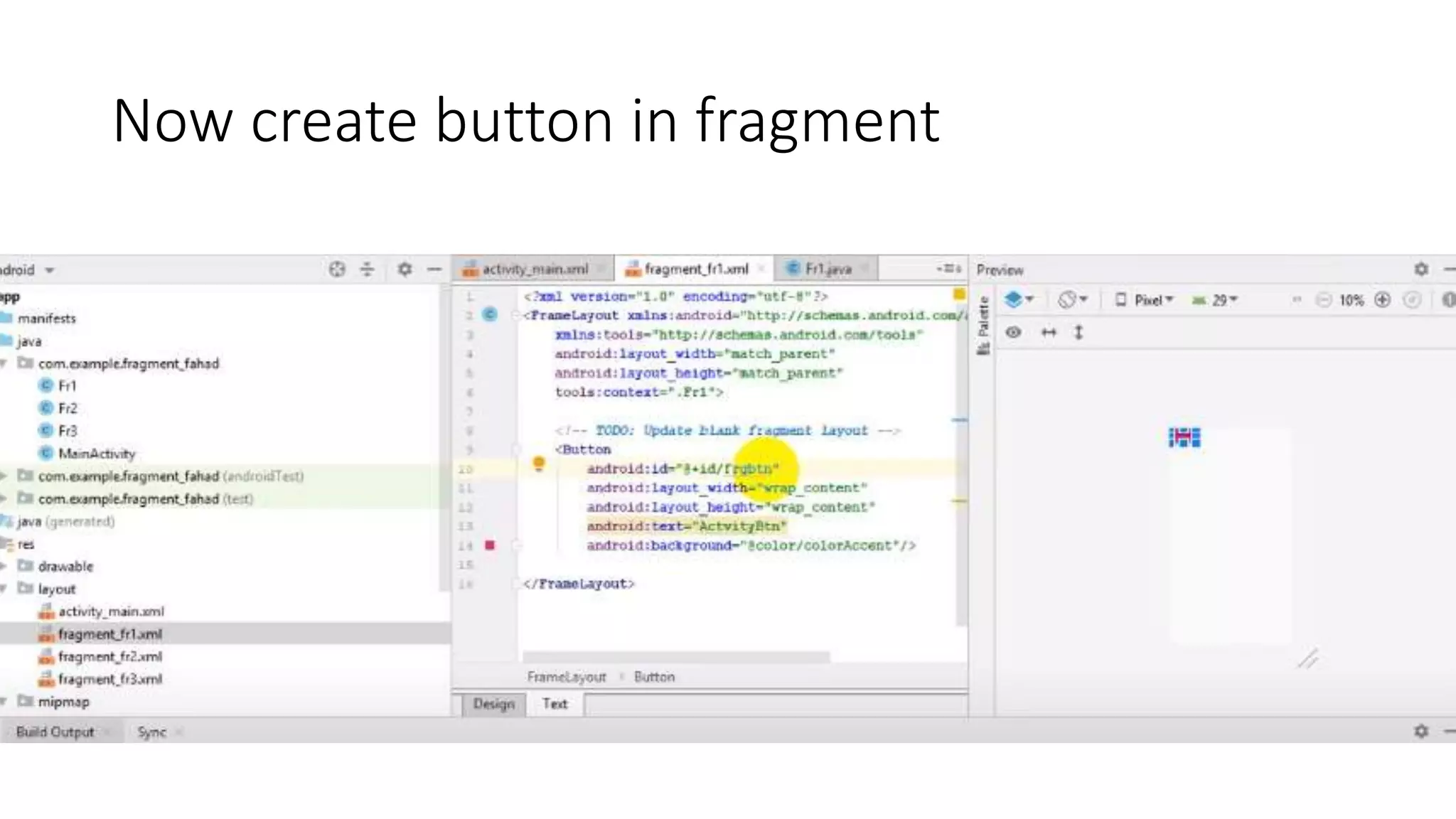
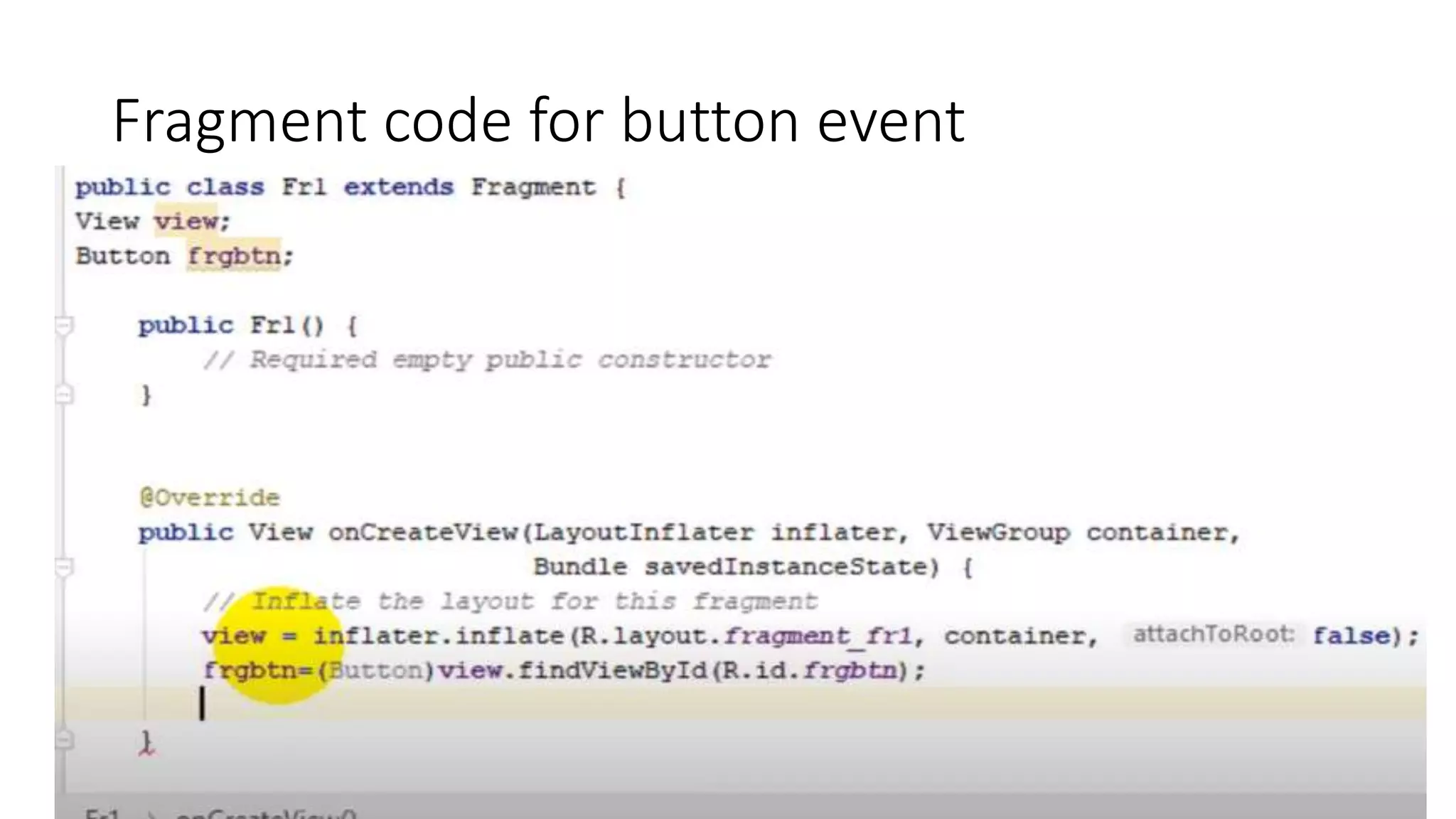
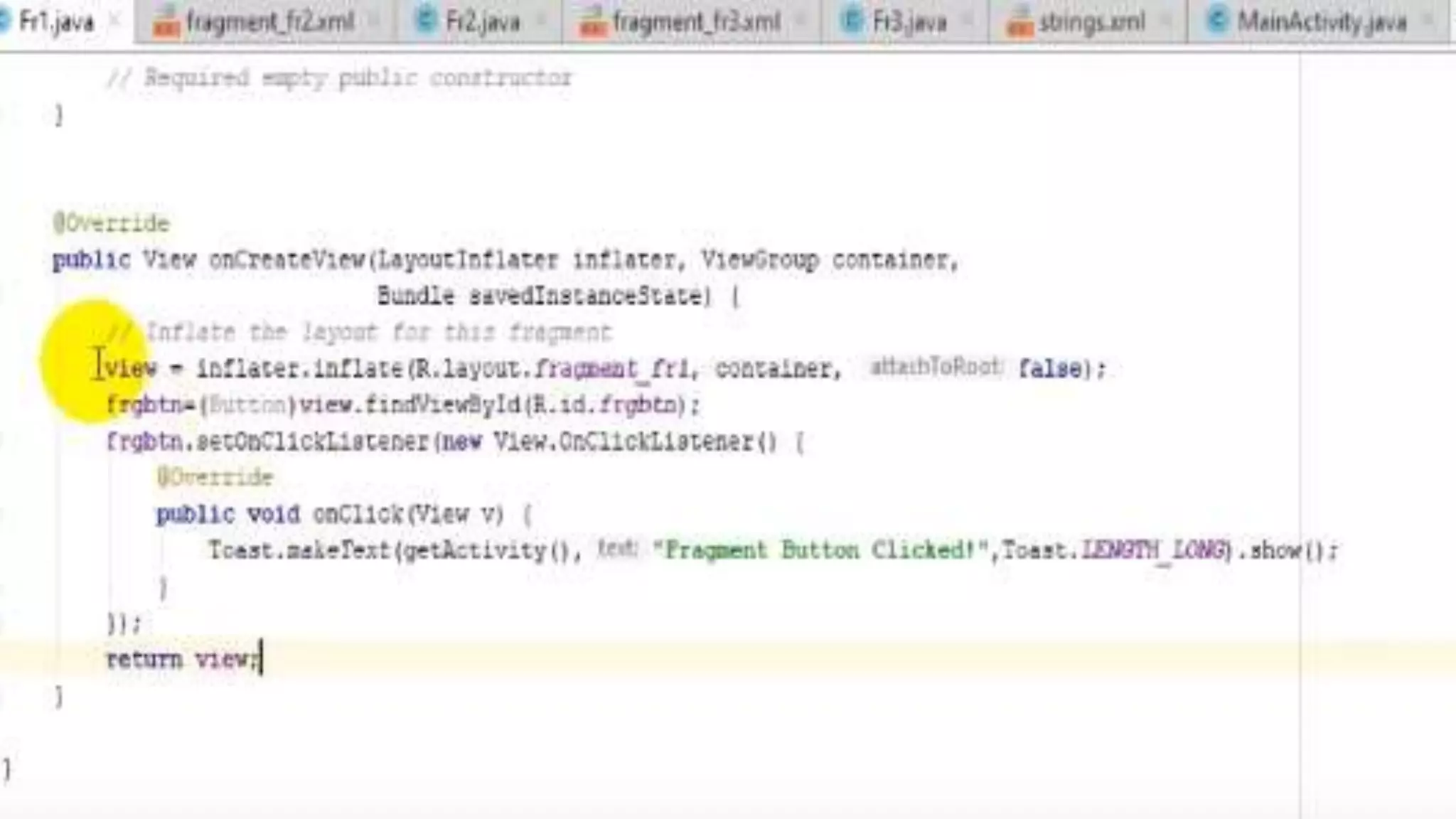
The document discusses content providers in Android. It describes content providers as a central repository that stores application data and makes it available to other applications. Content providers can store data in SQLite databases, files, or over a network. The ContentResolver class is used to access data from content providers using content URIs. Content providers receive data requests from clients, perform actions like create, update, delete, retrieve, and return results.