Embed presentation







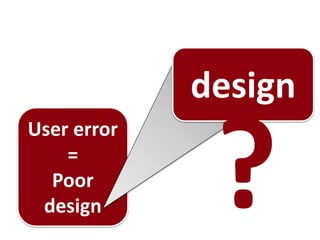





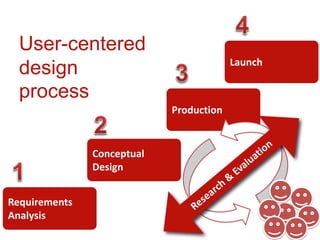
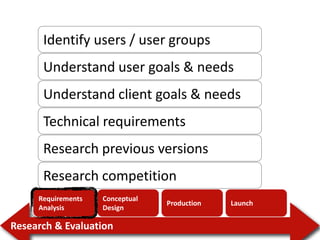

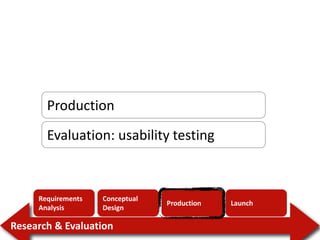









1. The document discusses learning goals around user-centered design (UCD), including appreciating that user error stems from poor design, distinguishing UCD from design as art, and listing the major steps of the UCD process. 2. It provides an overview of the UCD process, which involves requirements analysis, conceptual design, production, launch, and iterative user research and evaluation. 3. Examples of affordances and how they help make products more intuitive by triggering mental models of how to use objects are discussed.



























