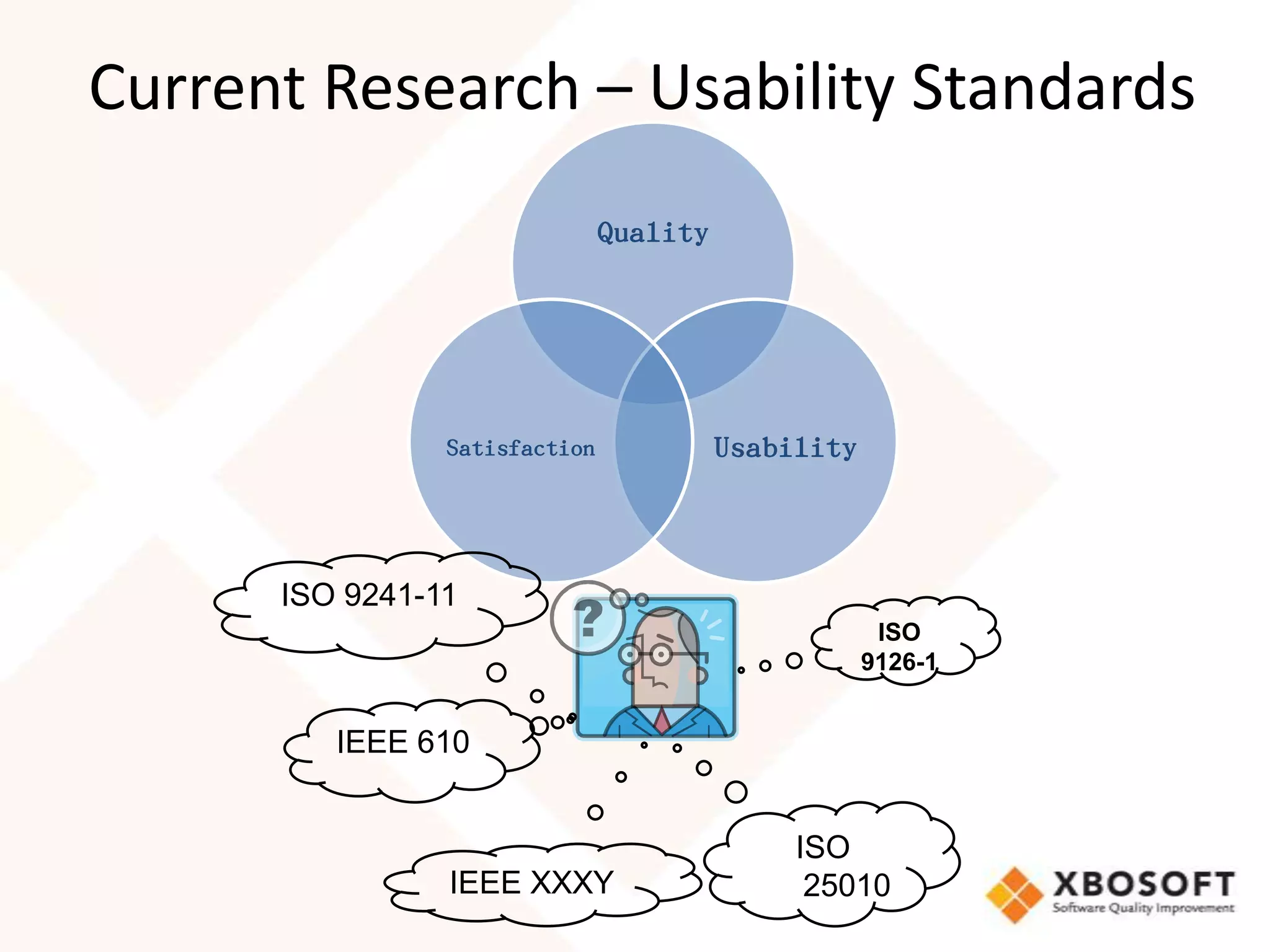
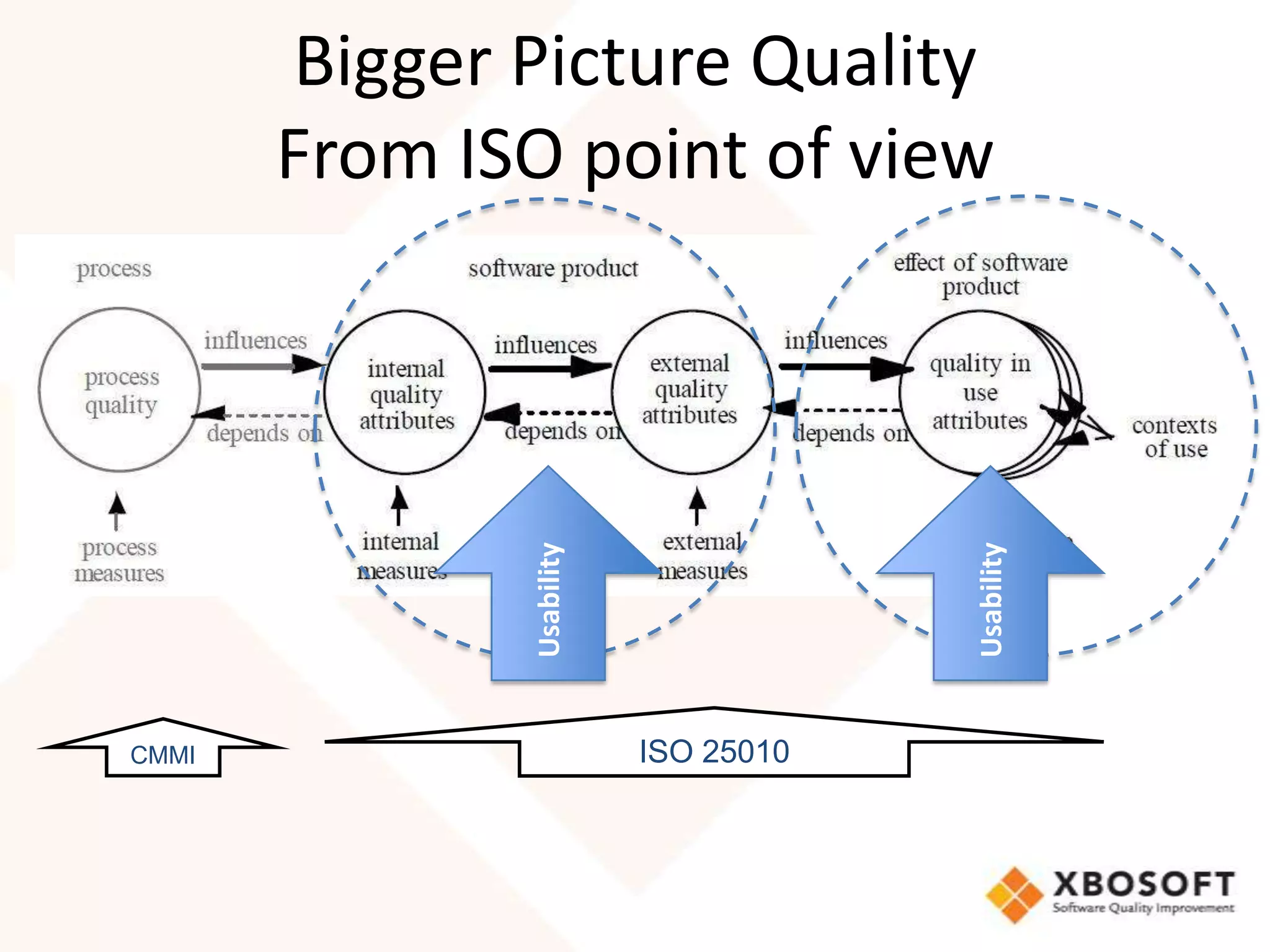
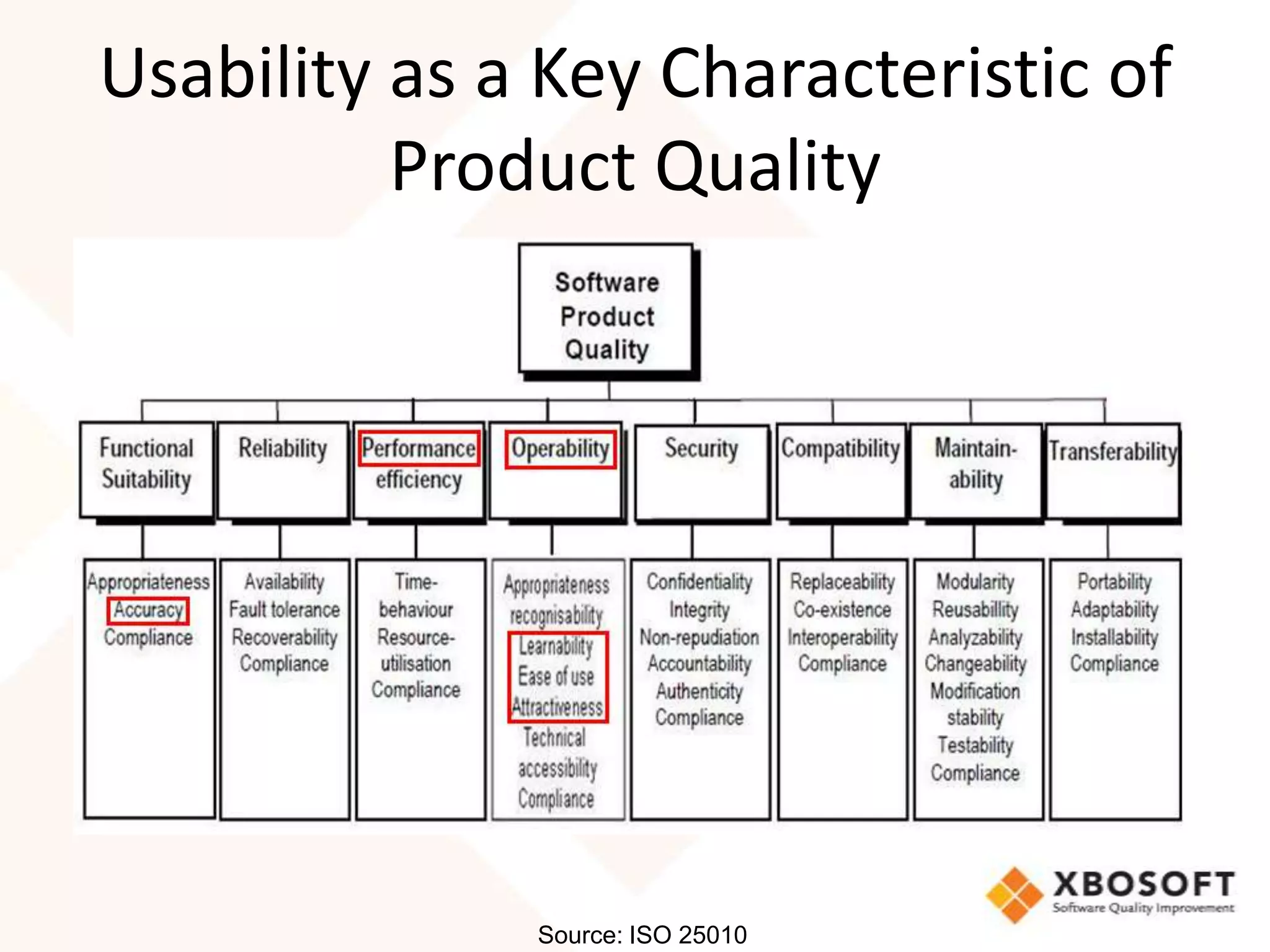
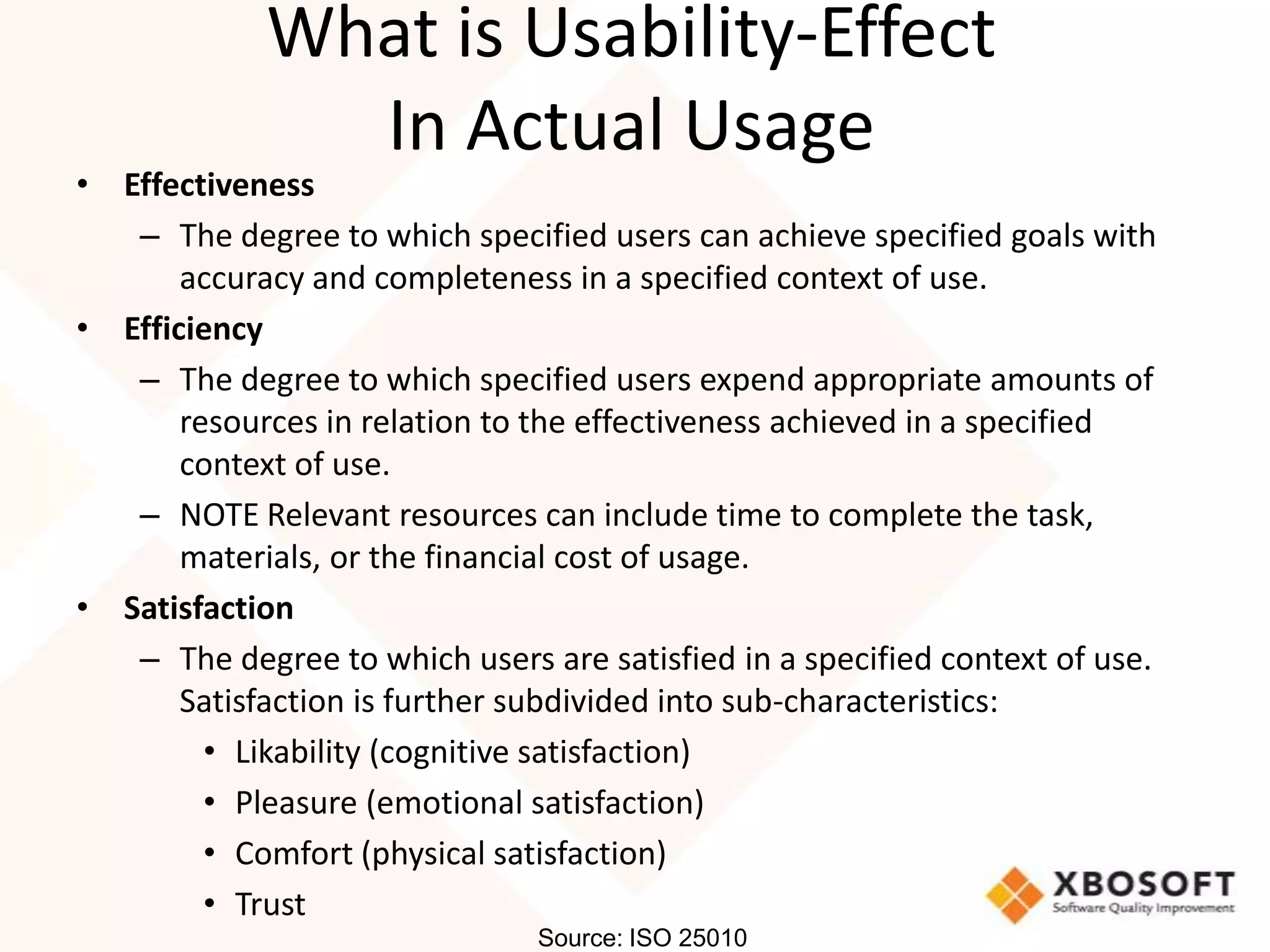
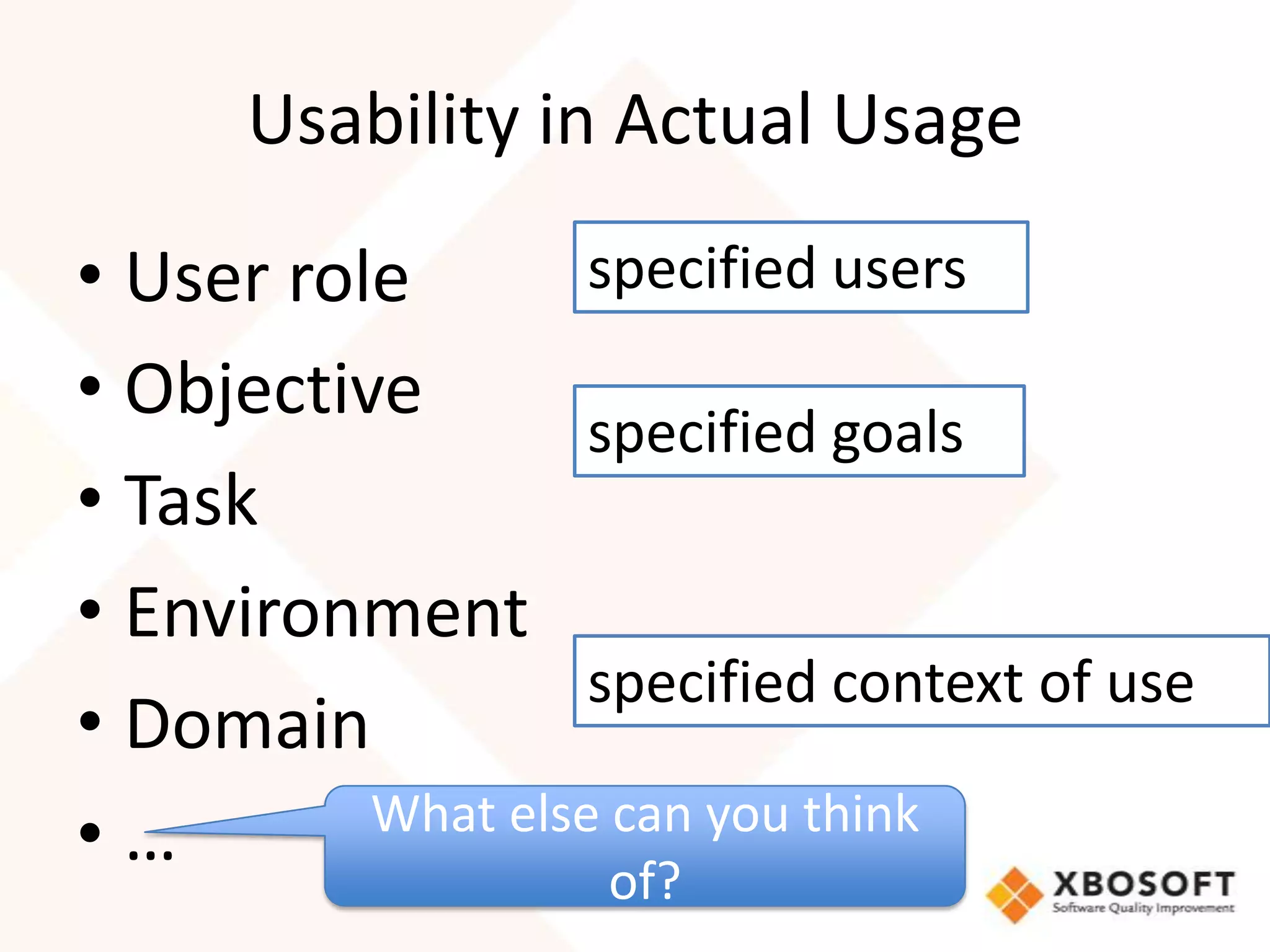
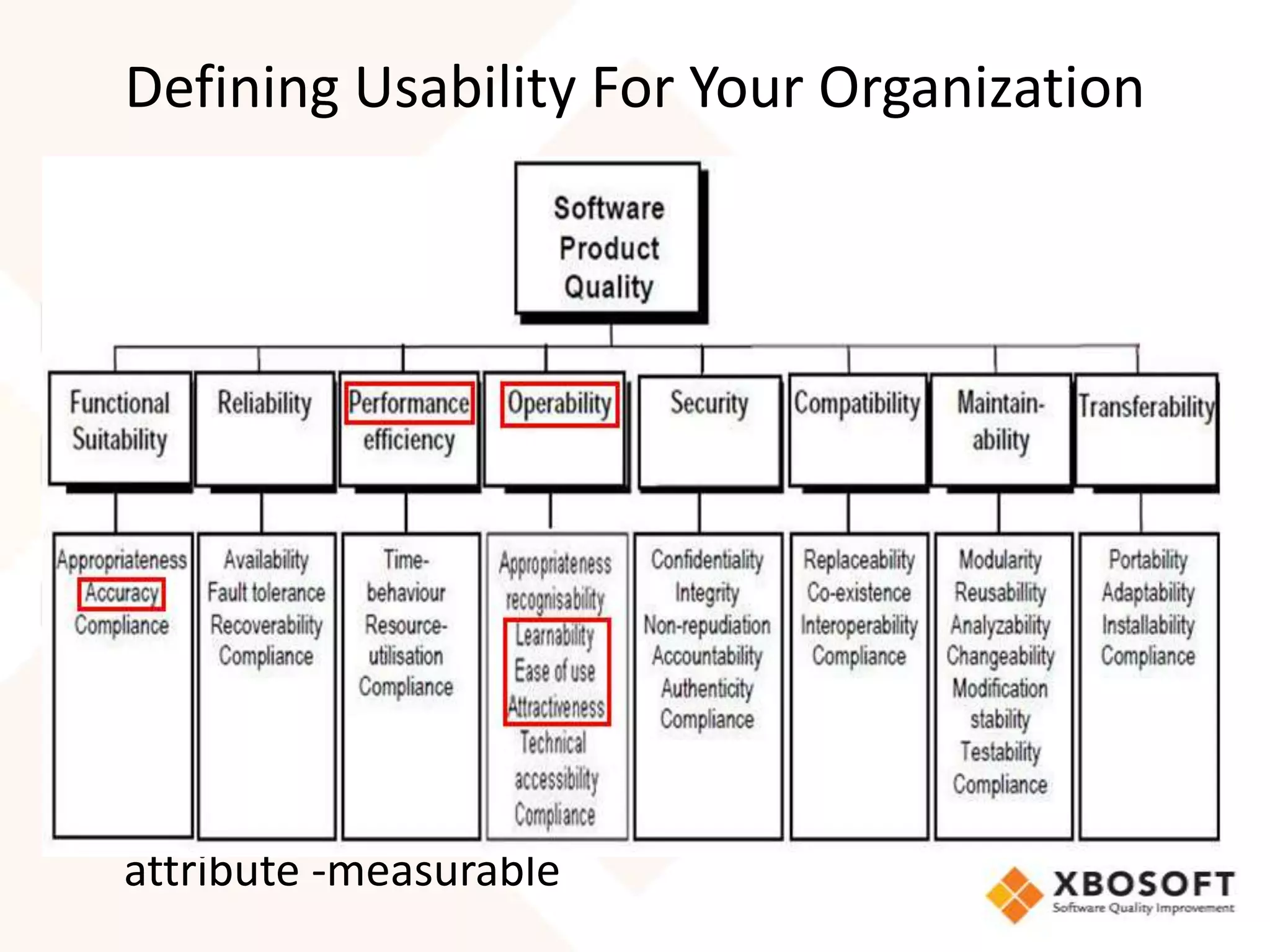
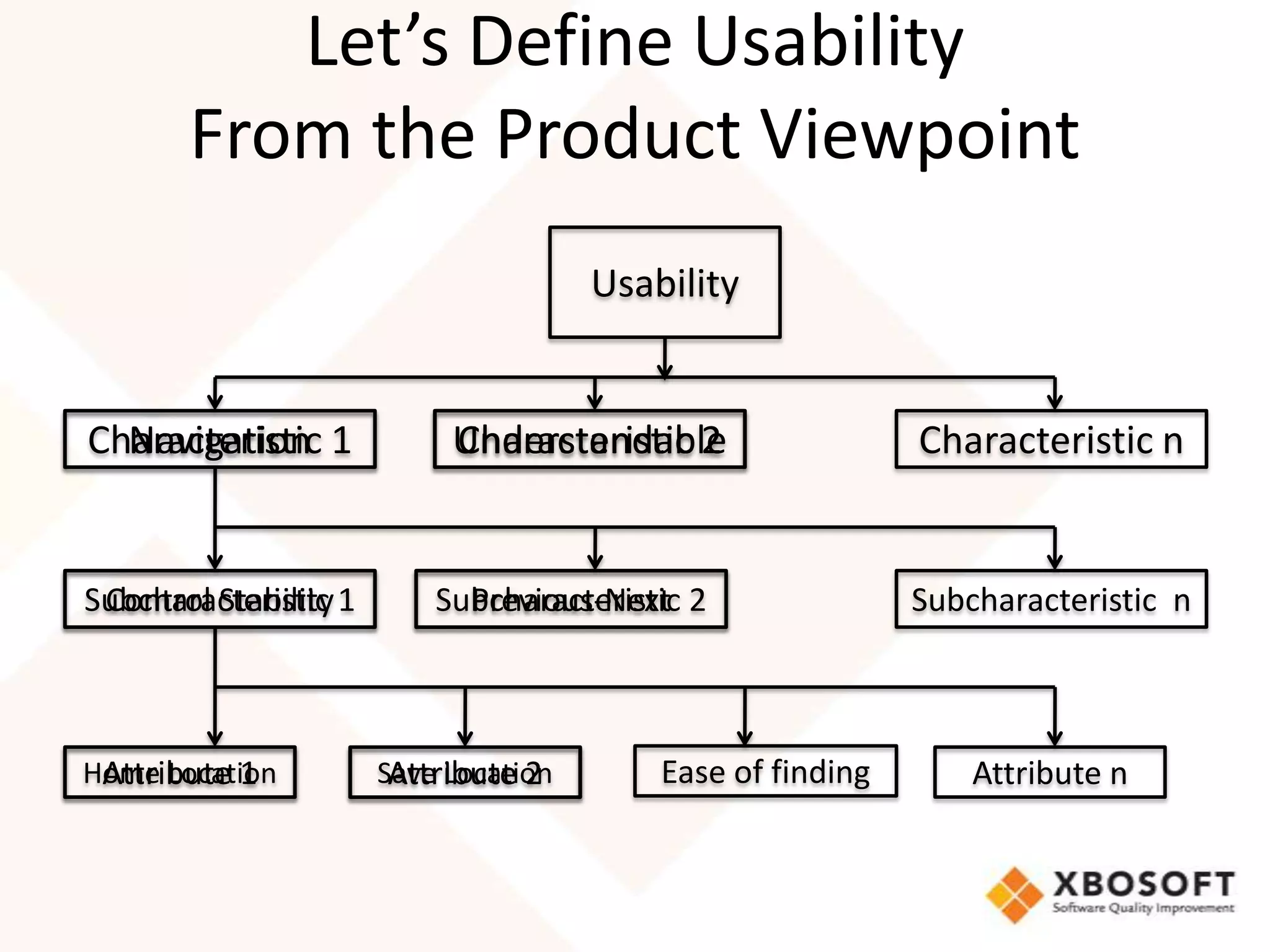
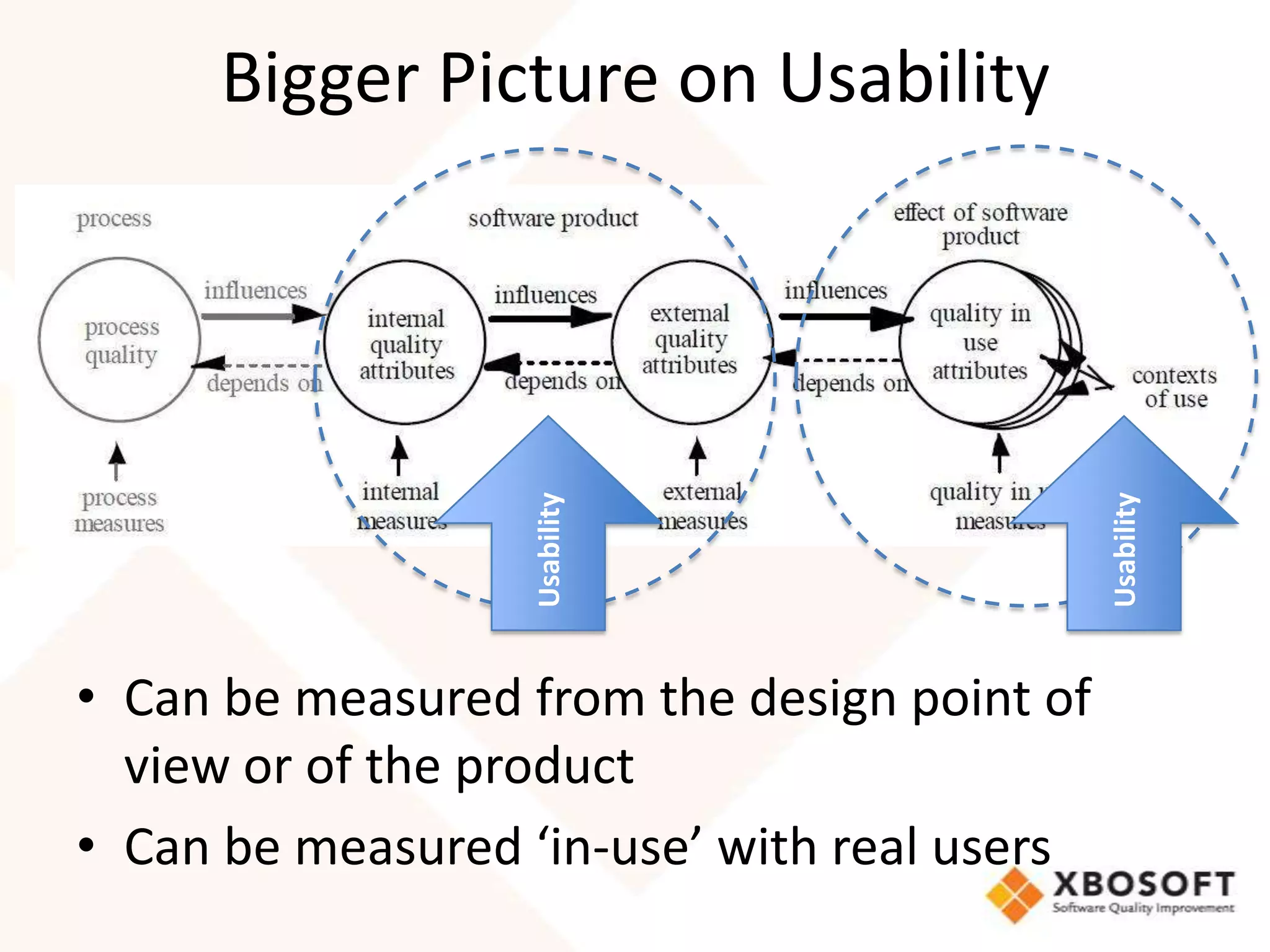
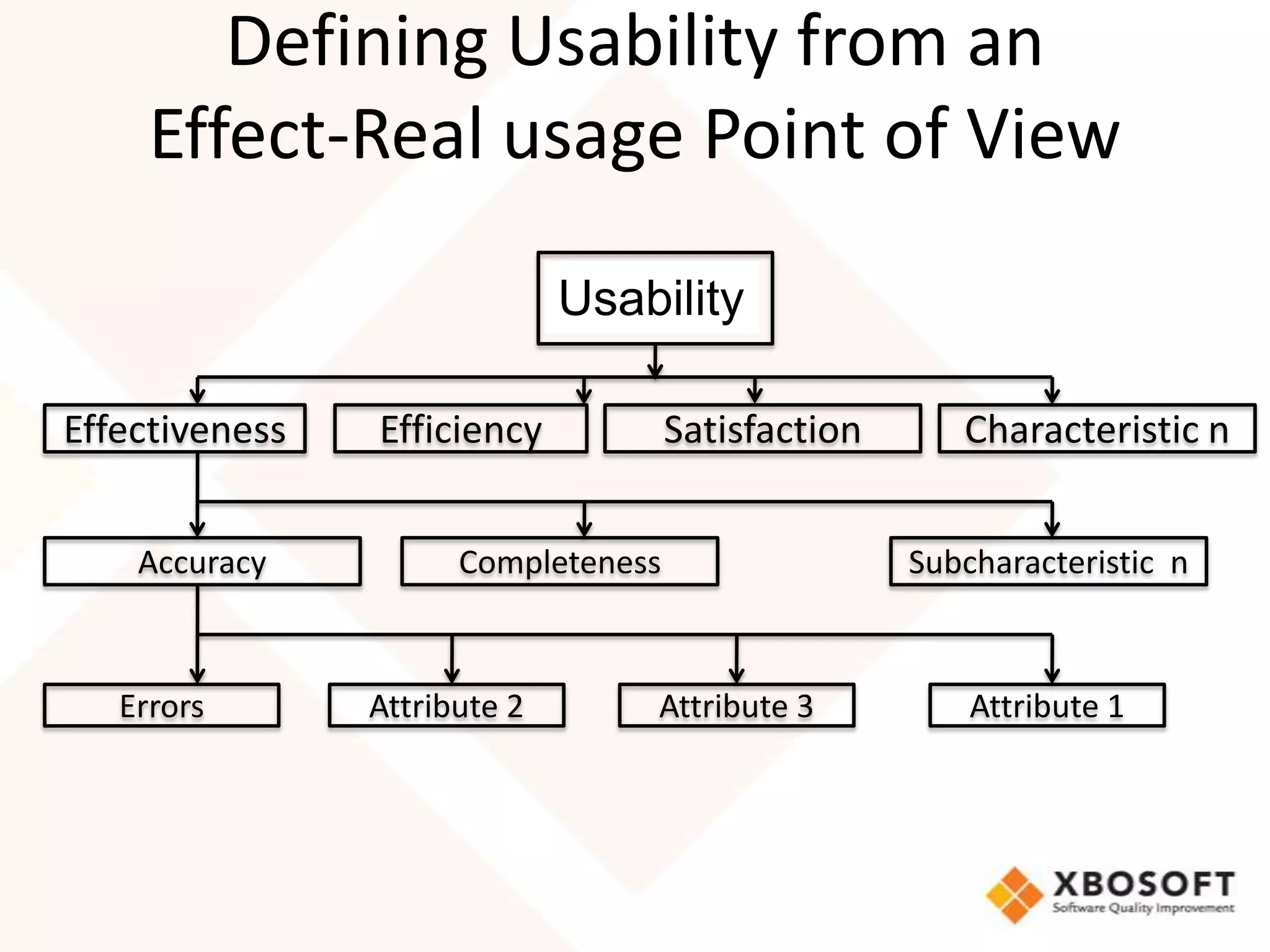
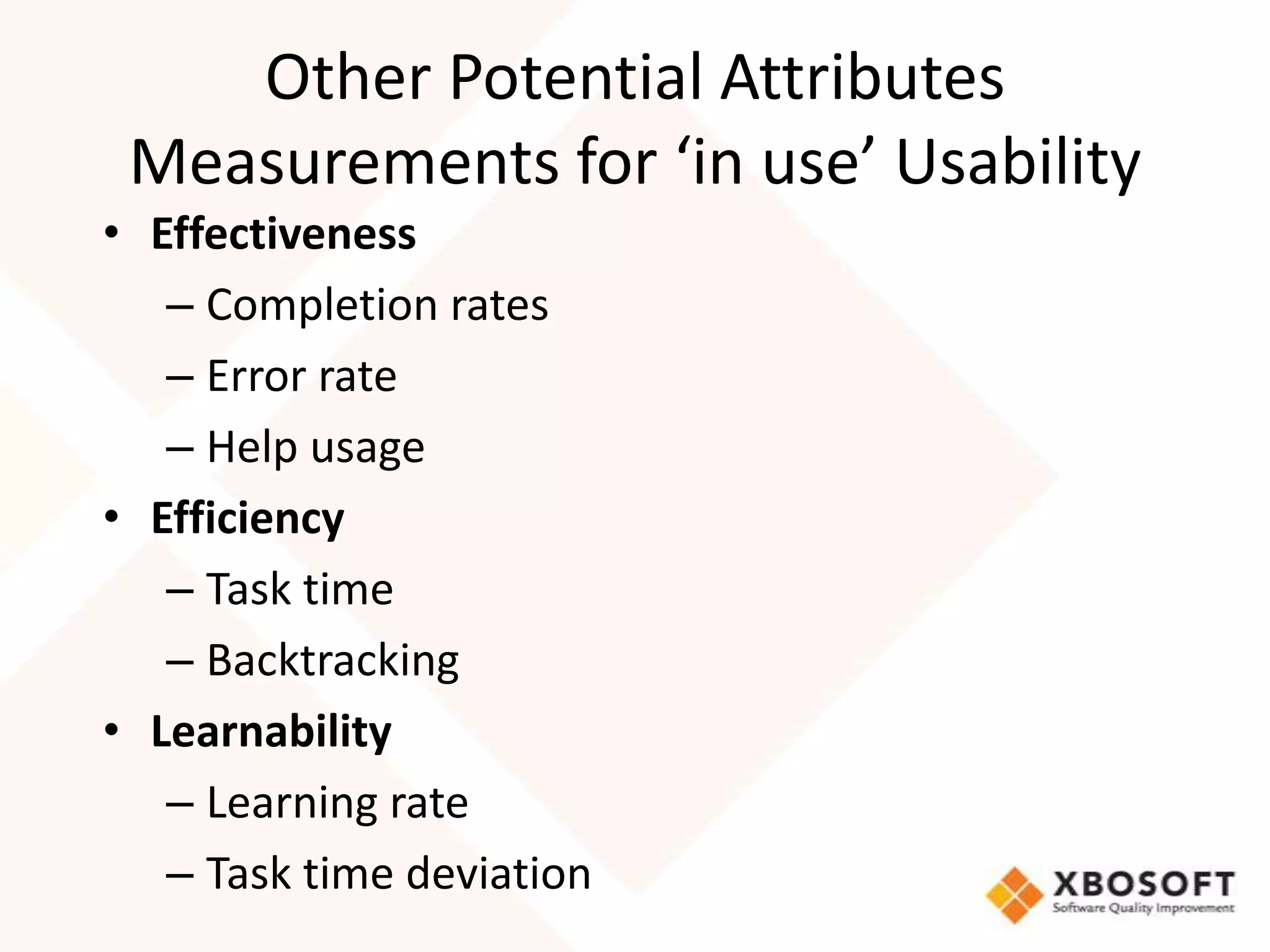
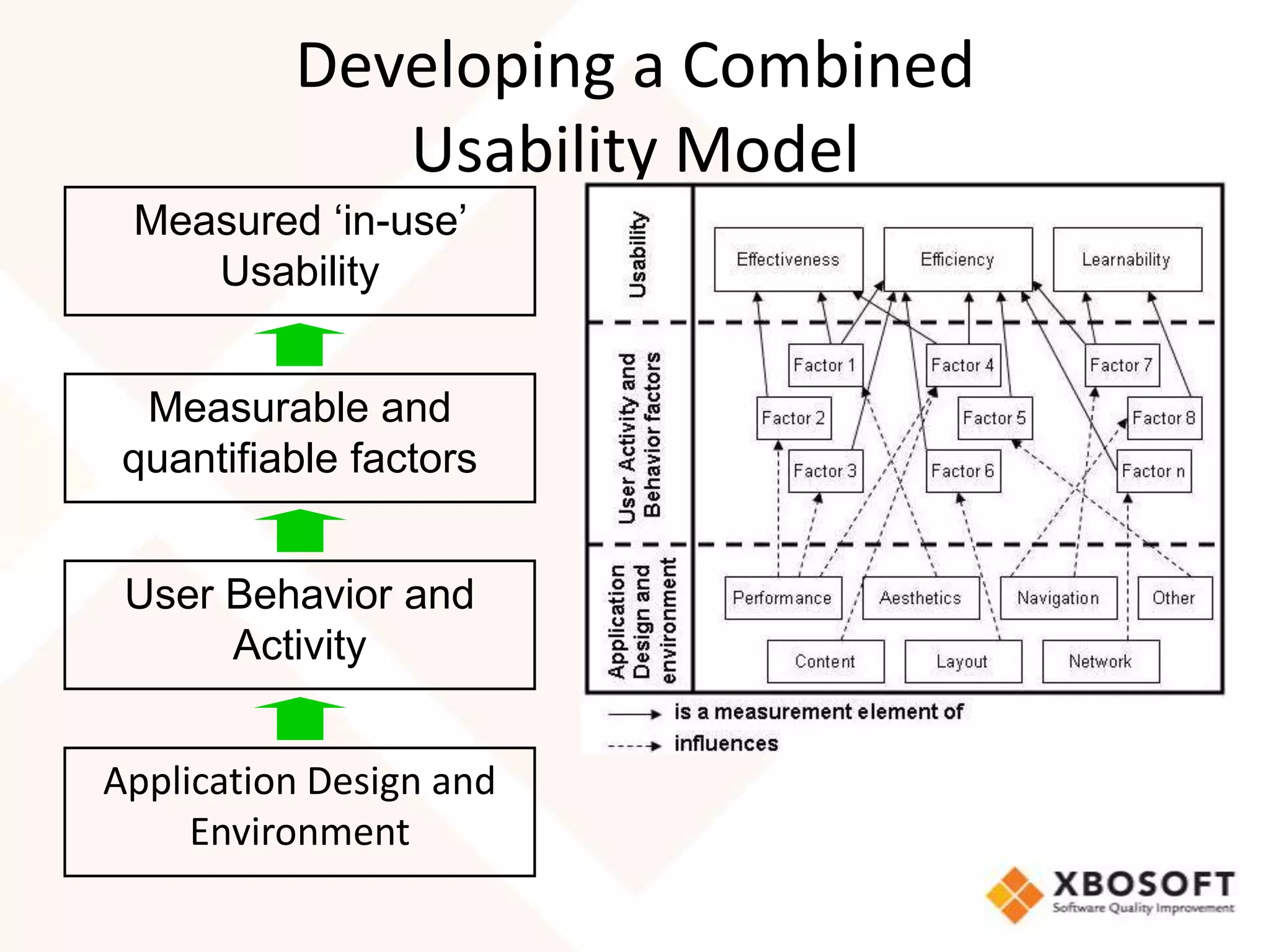
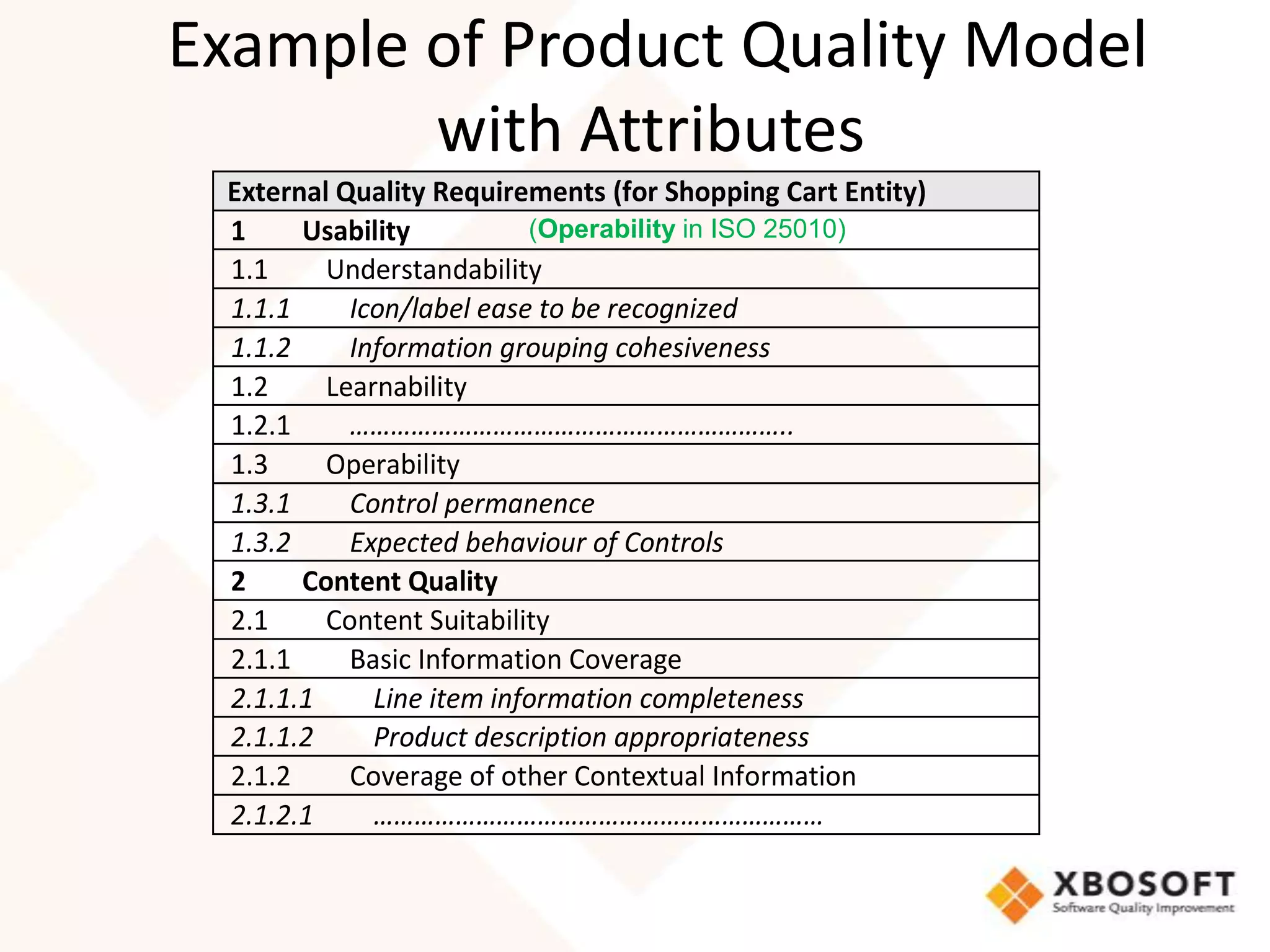
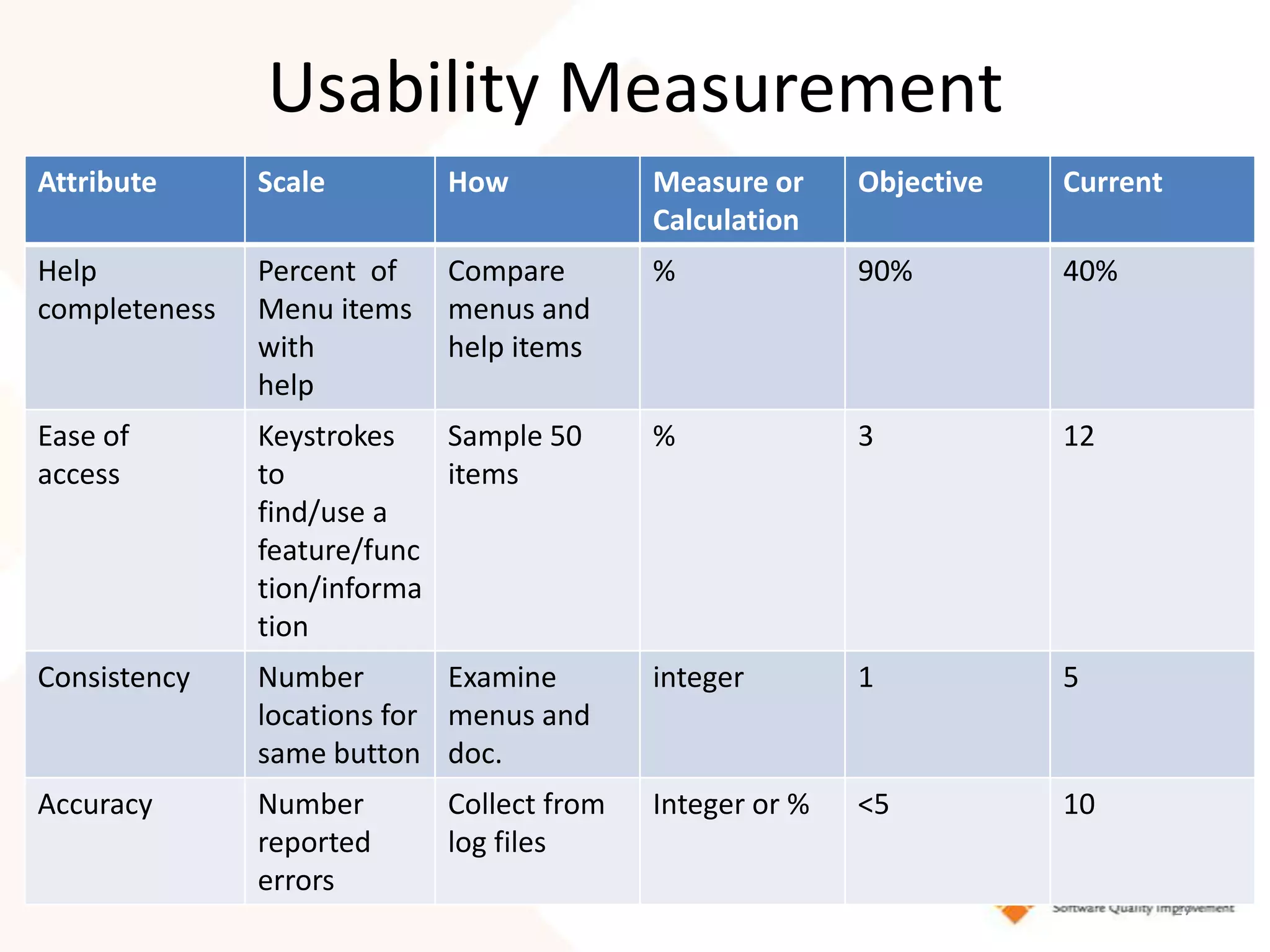
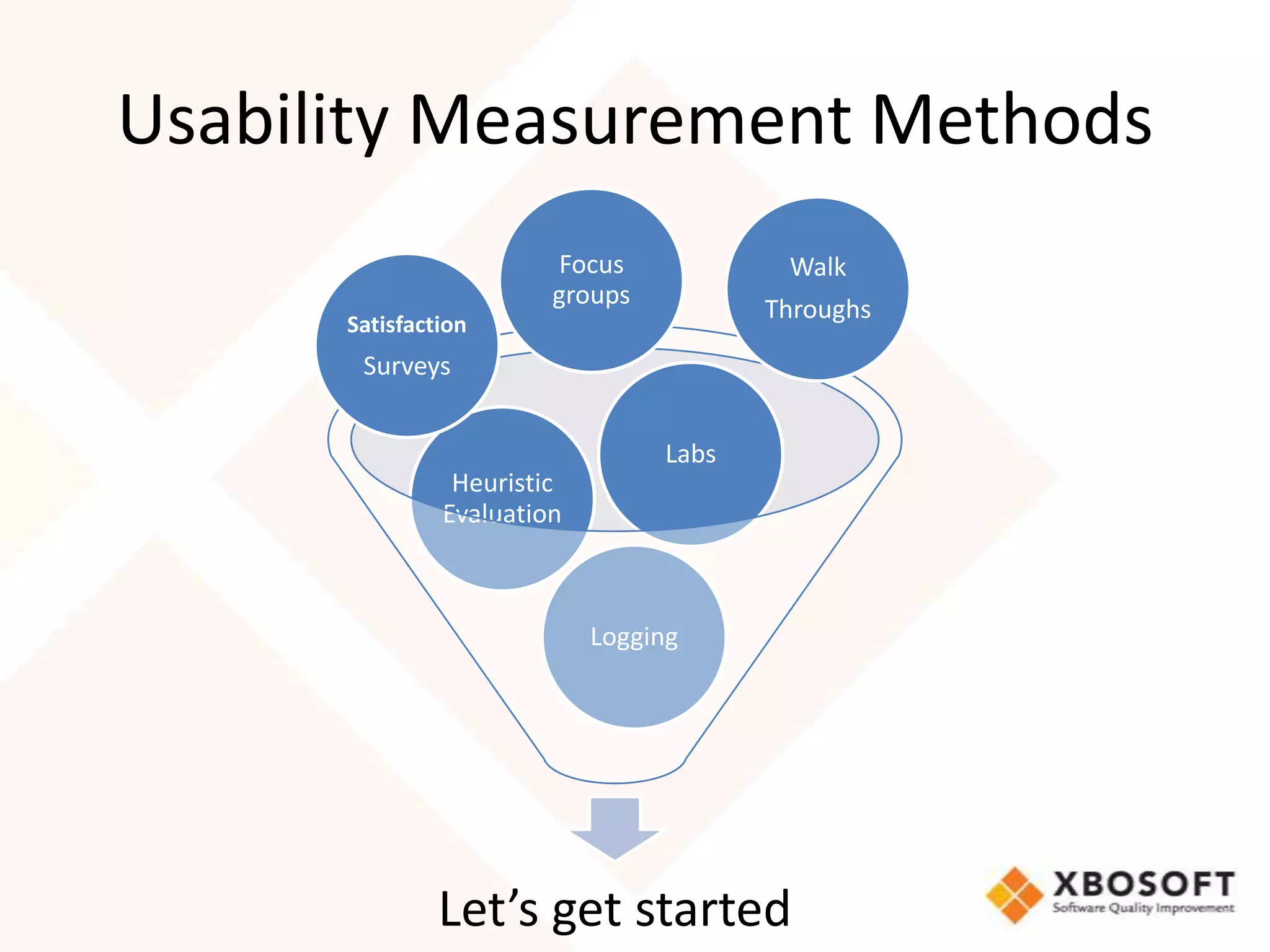
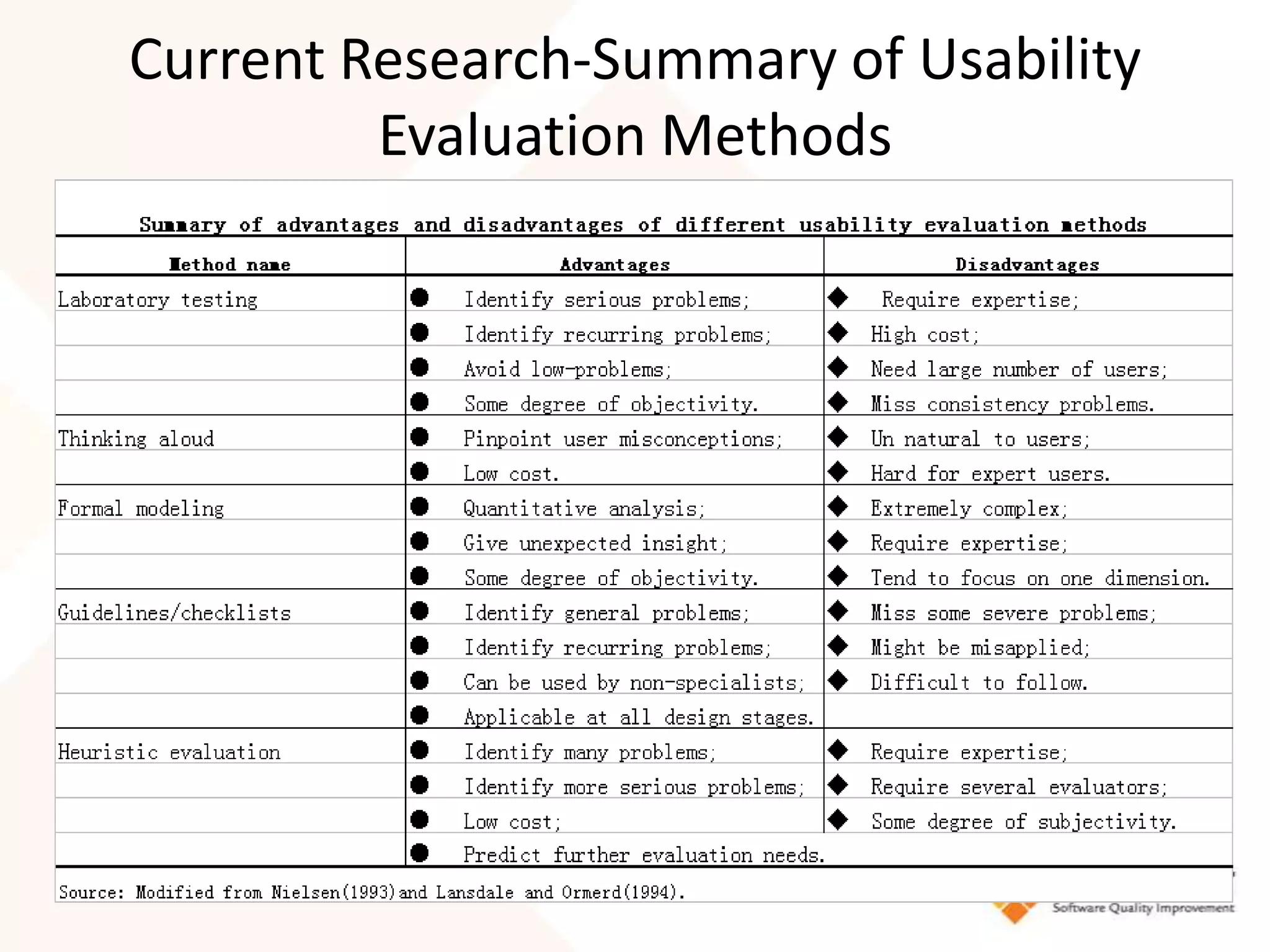
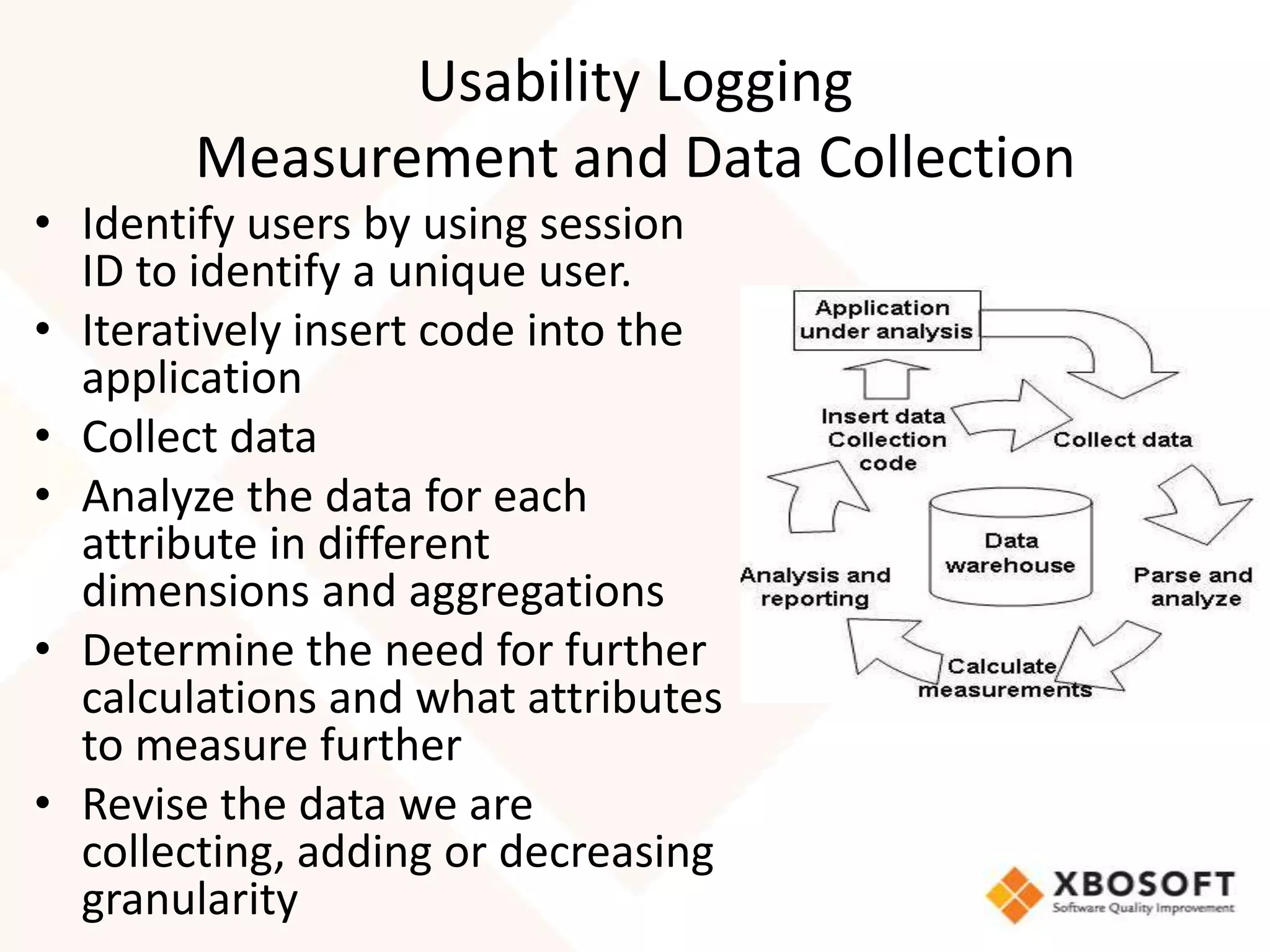
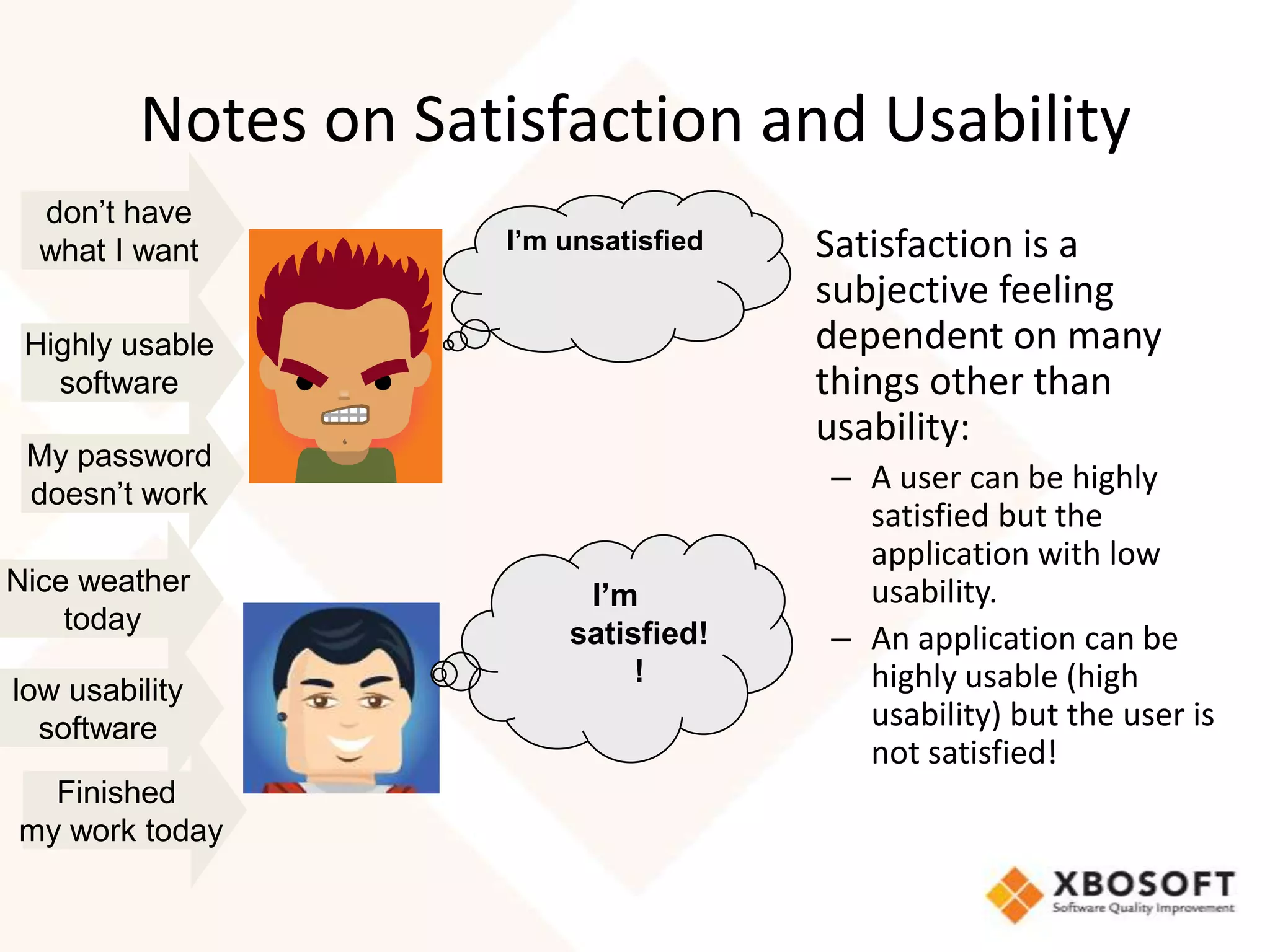
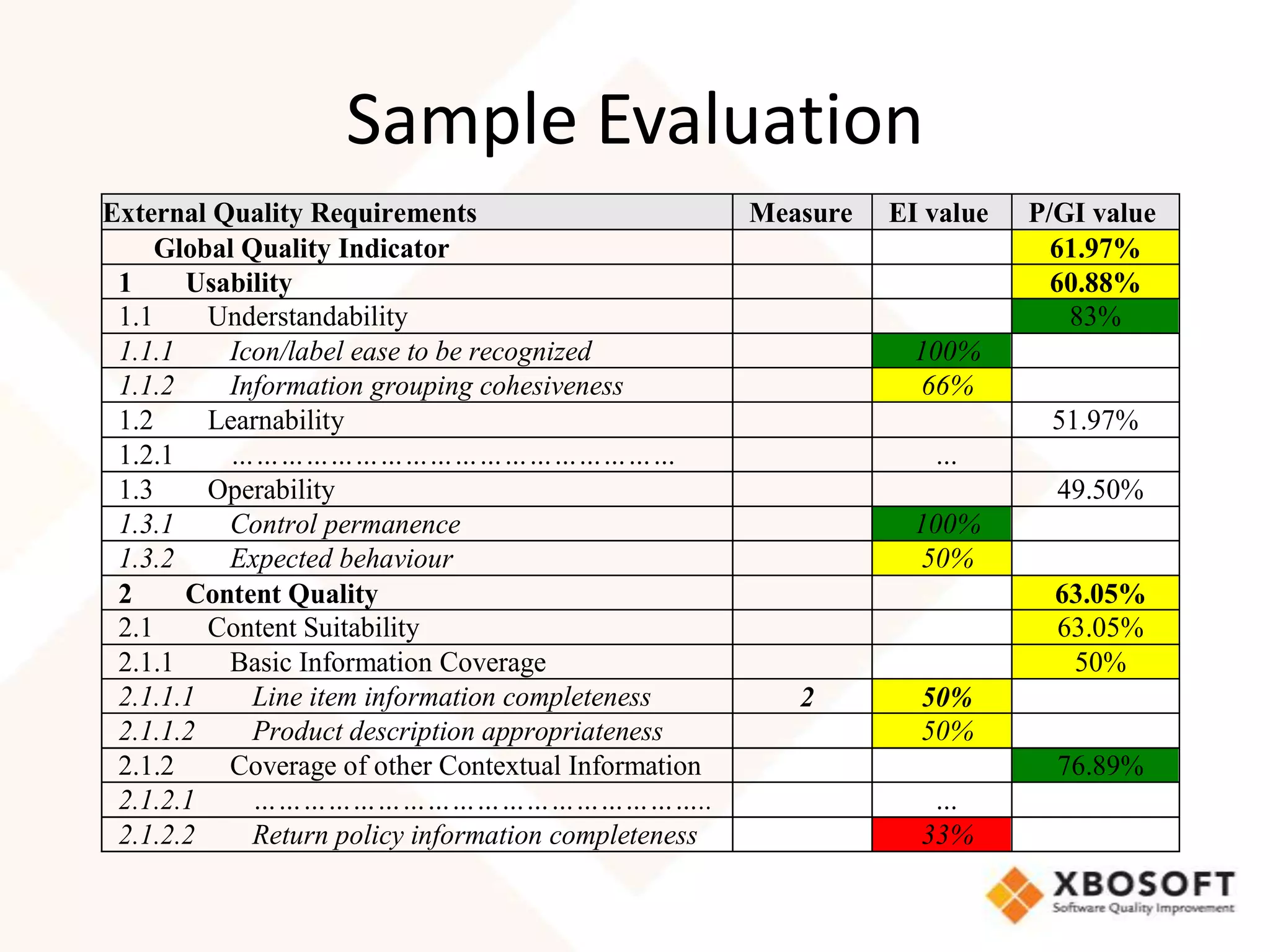
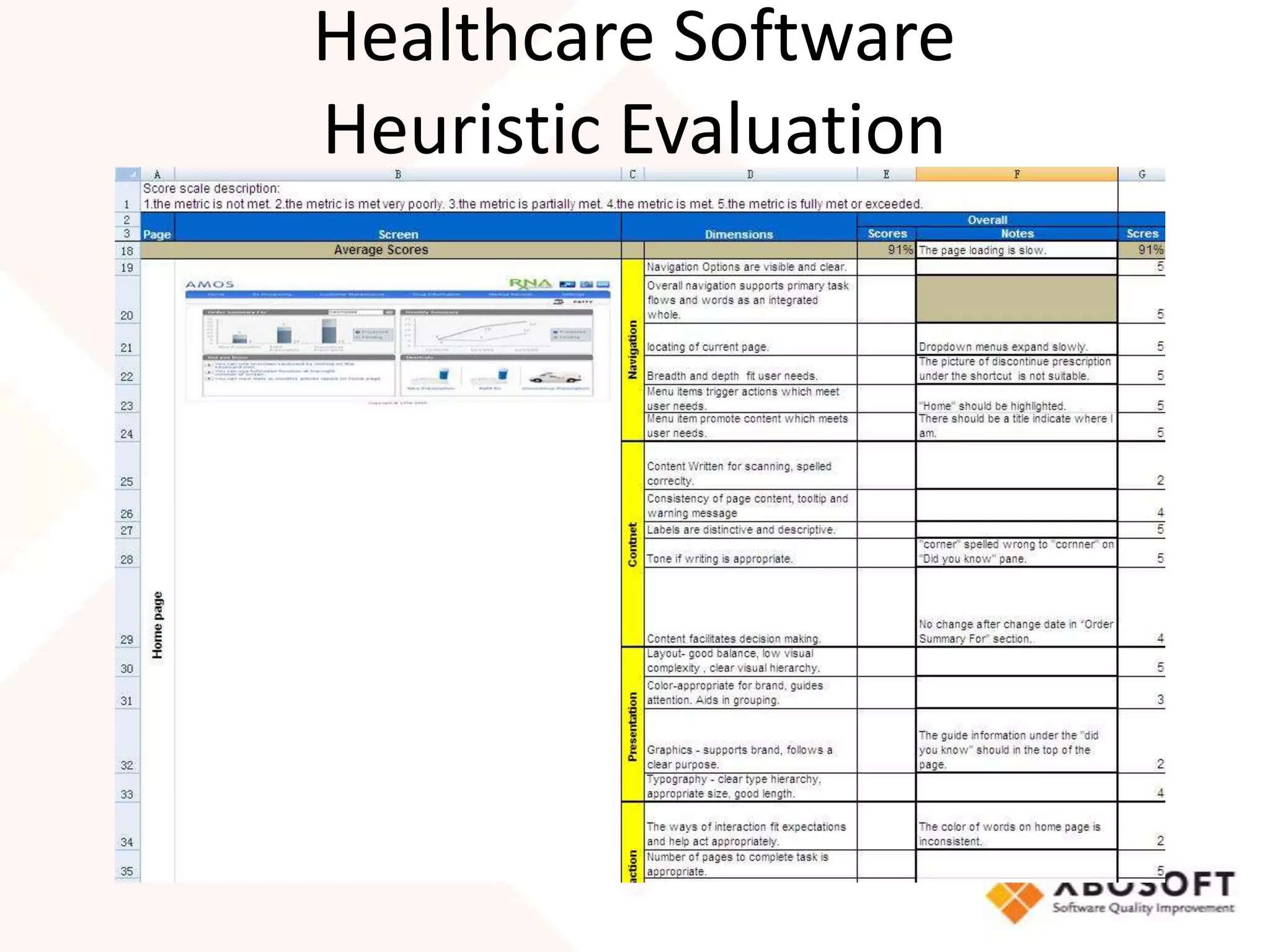
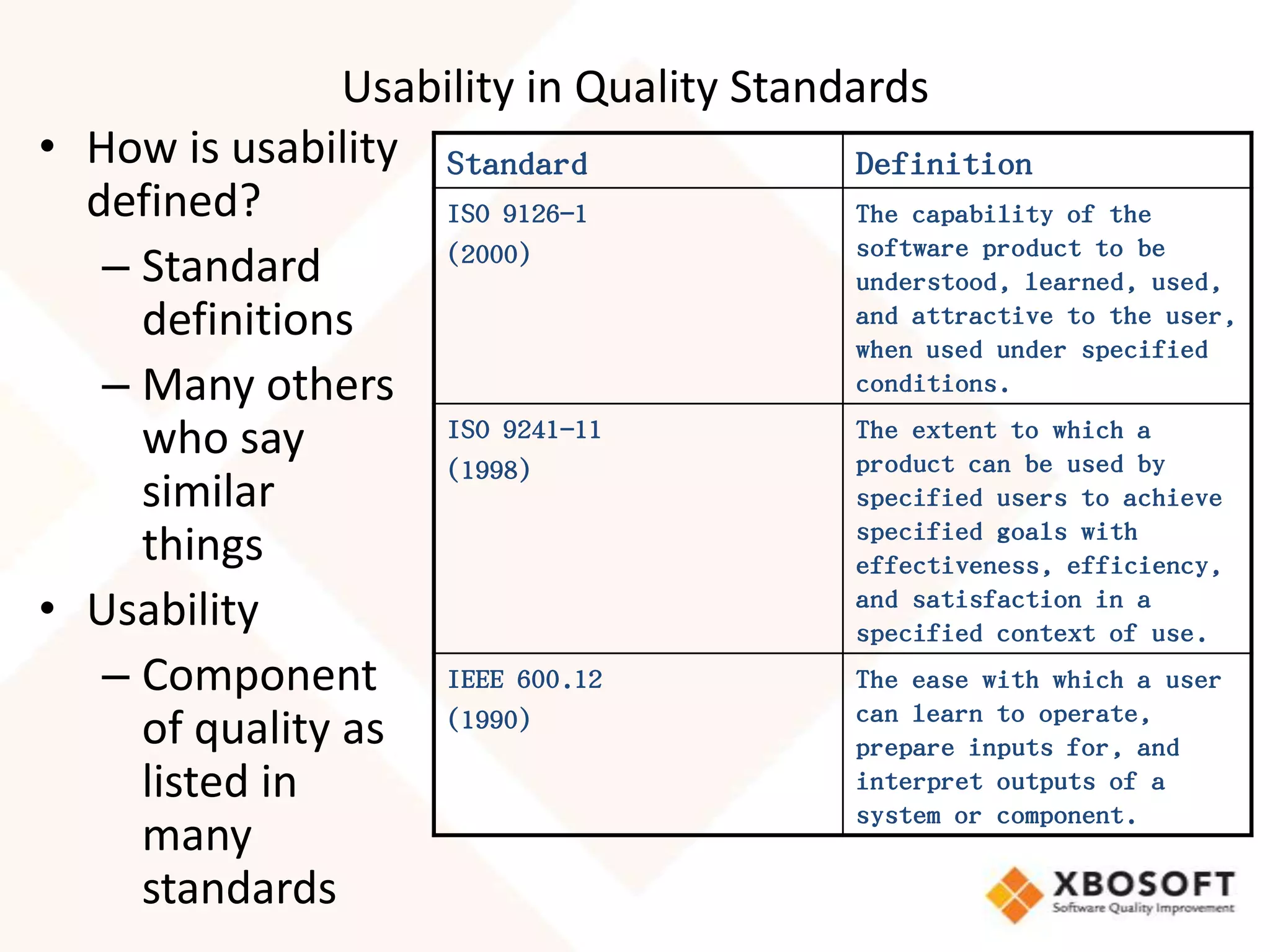
This document discusses usability modeling and measurement. It defines usability and explains why it is important, especially for web and mobile applications. It describes various usability models and standards. The document outlines how to develop a usability model for an organization by defining measurable attributes and characteristics. It also discusses different usability evaluation methods like surveys, heuristic evaluation, and logging. The key steps are to define a model, identify attributes to measure, collect data, analyze the results, and refine measurements. Taking these steps allows an organization to systematically evaluate and improve usability.









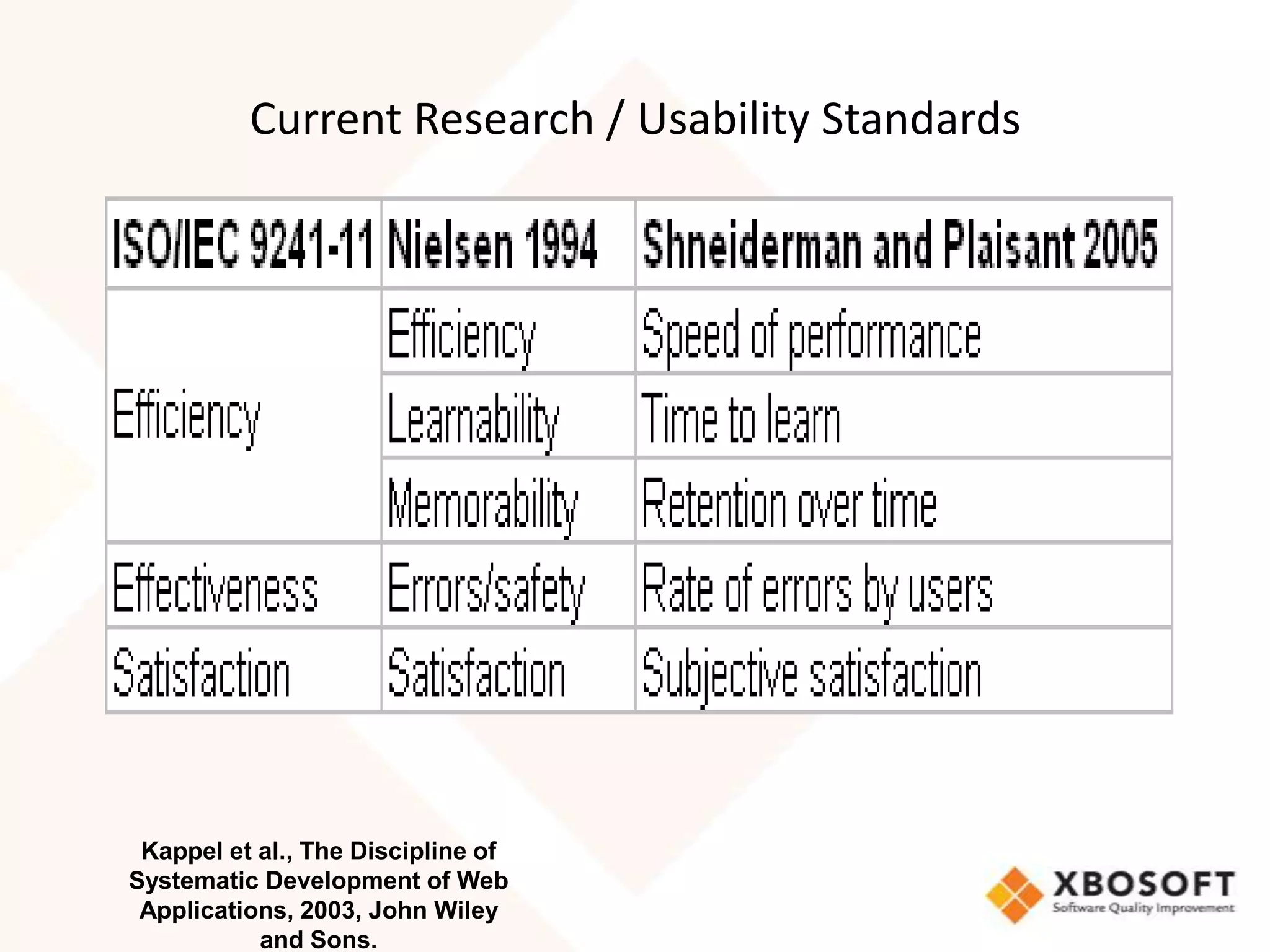
![Usability Model Comparisons
Seffah [33]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usabilitymodelingandmeasurement-120114172351-phpapp01/75/Usability-modeling-and-measurement-11-2048.jpg)