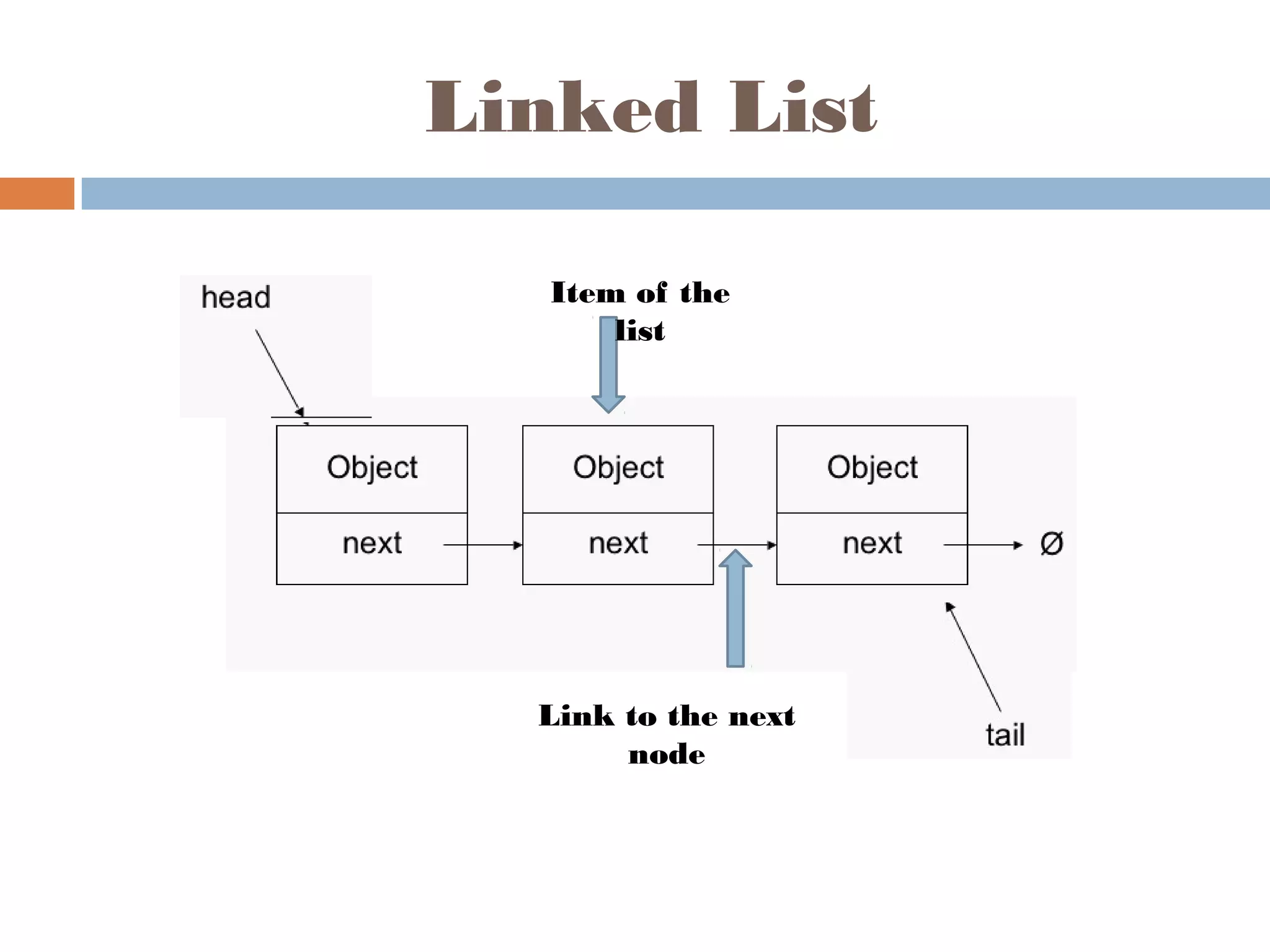
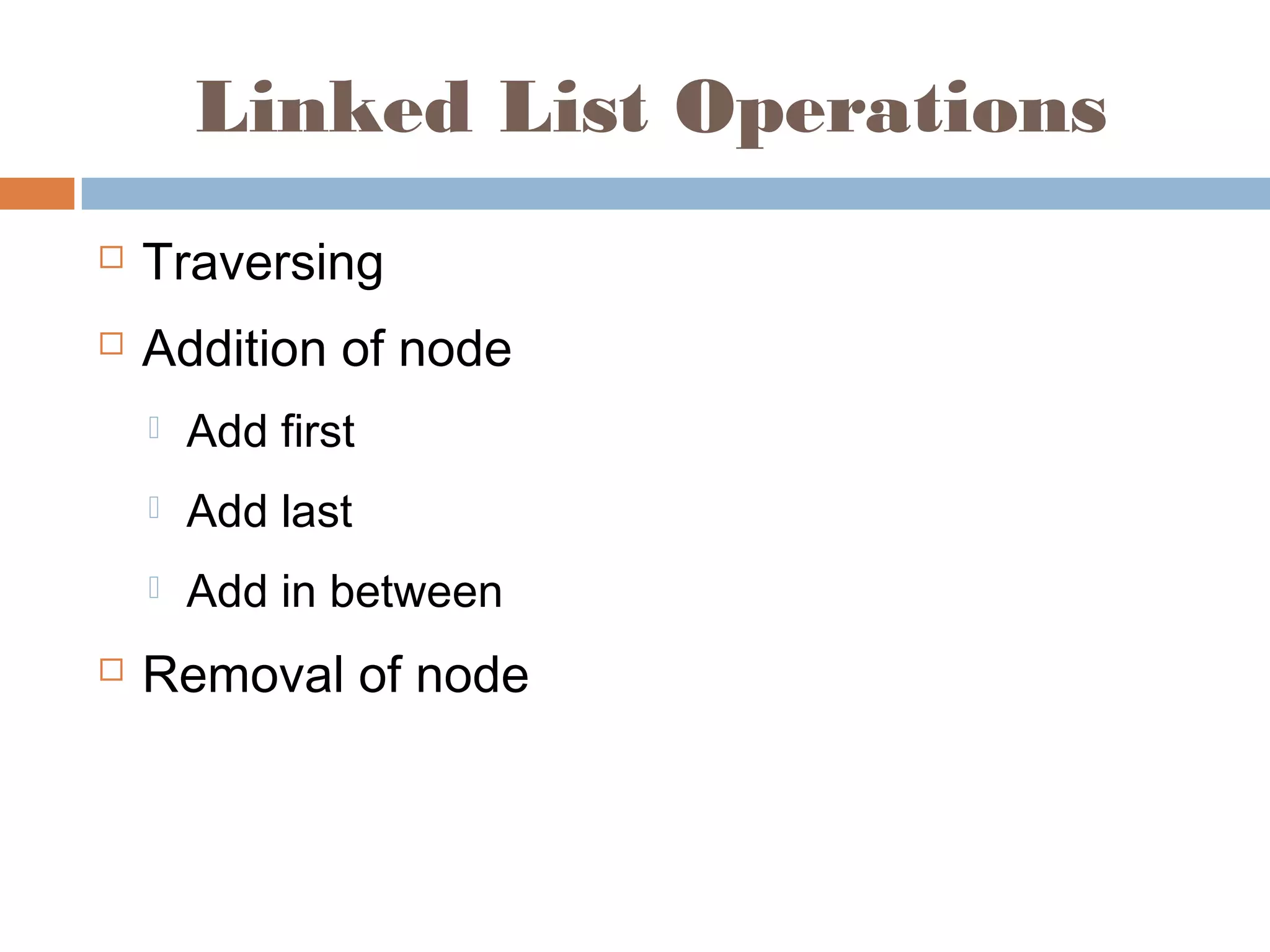
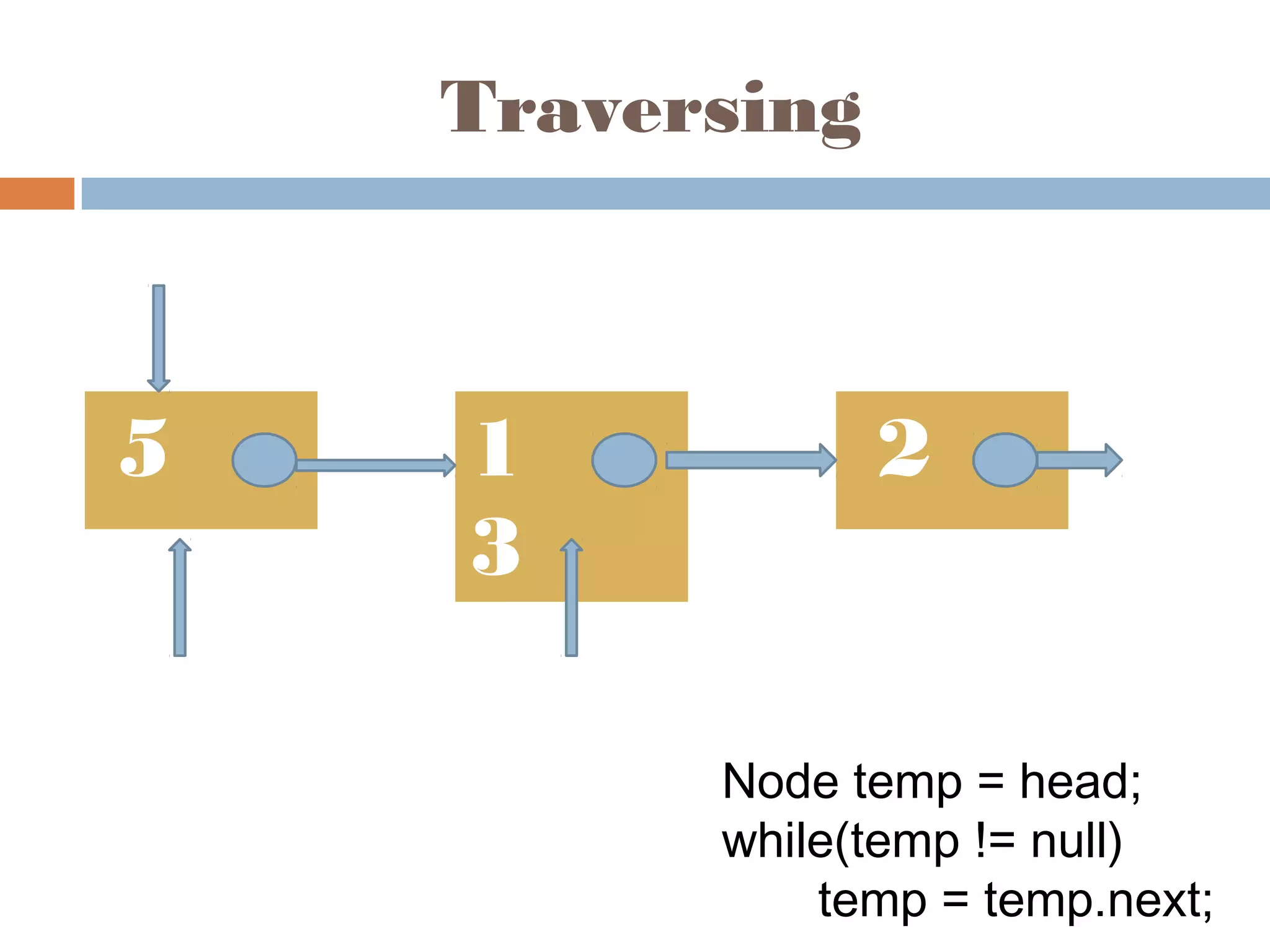
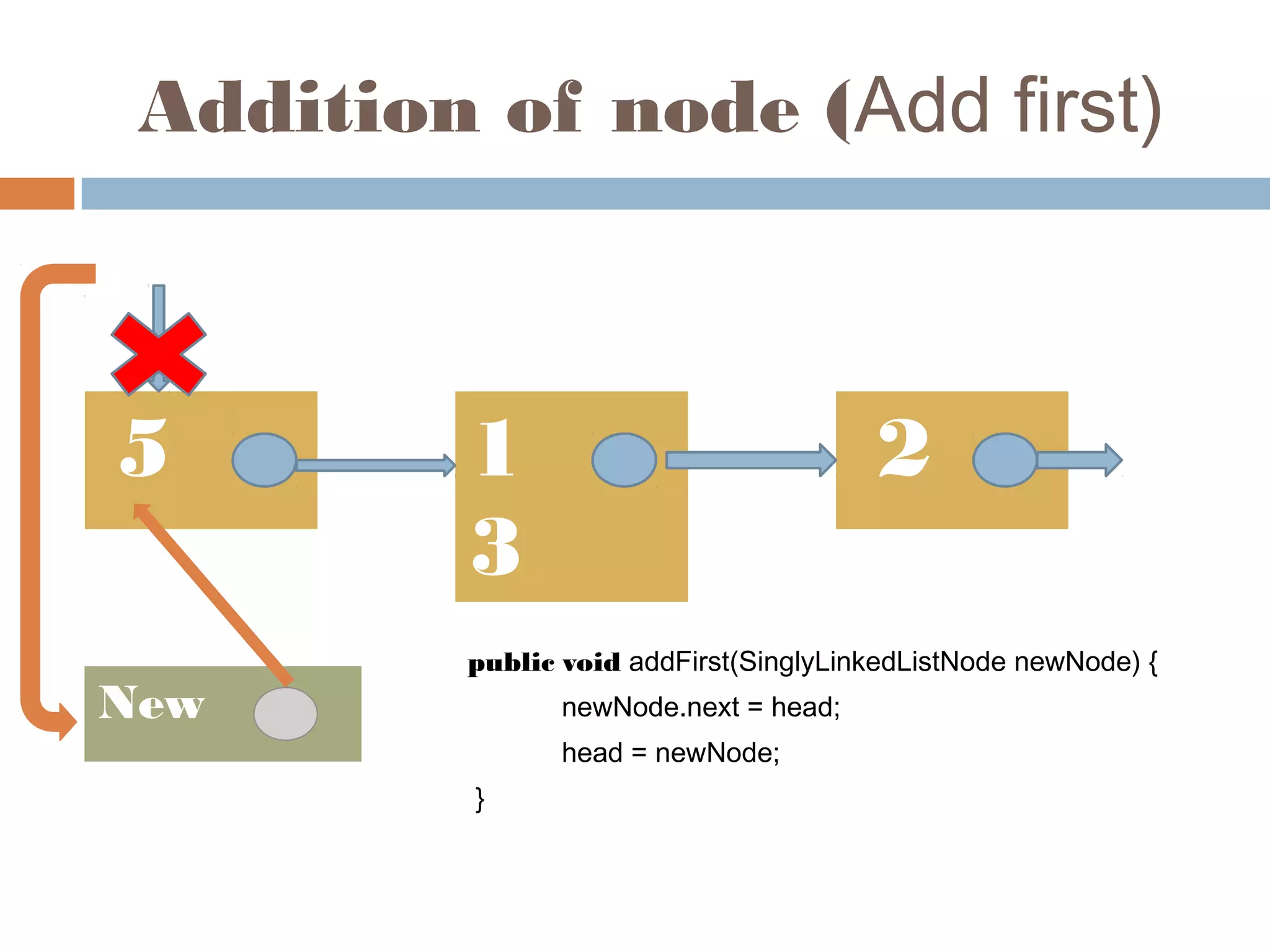
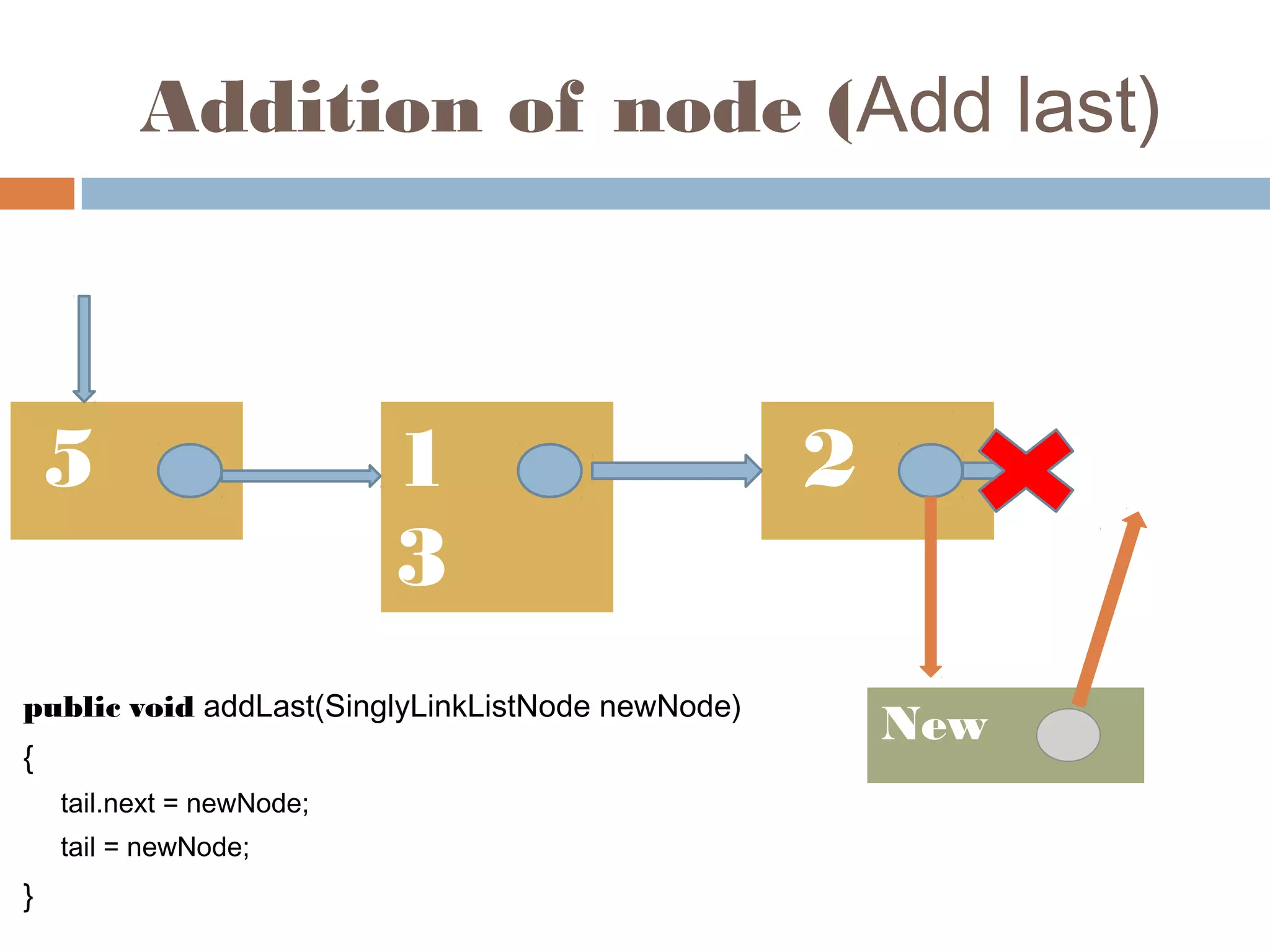
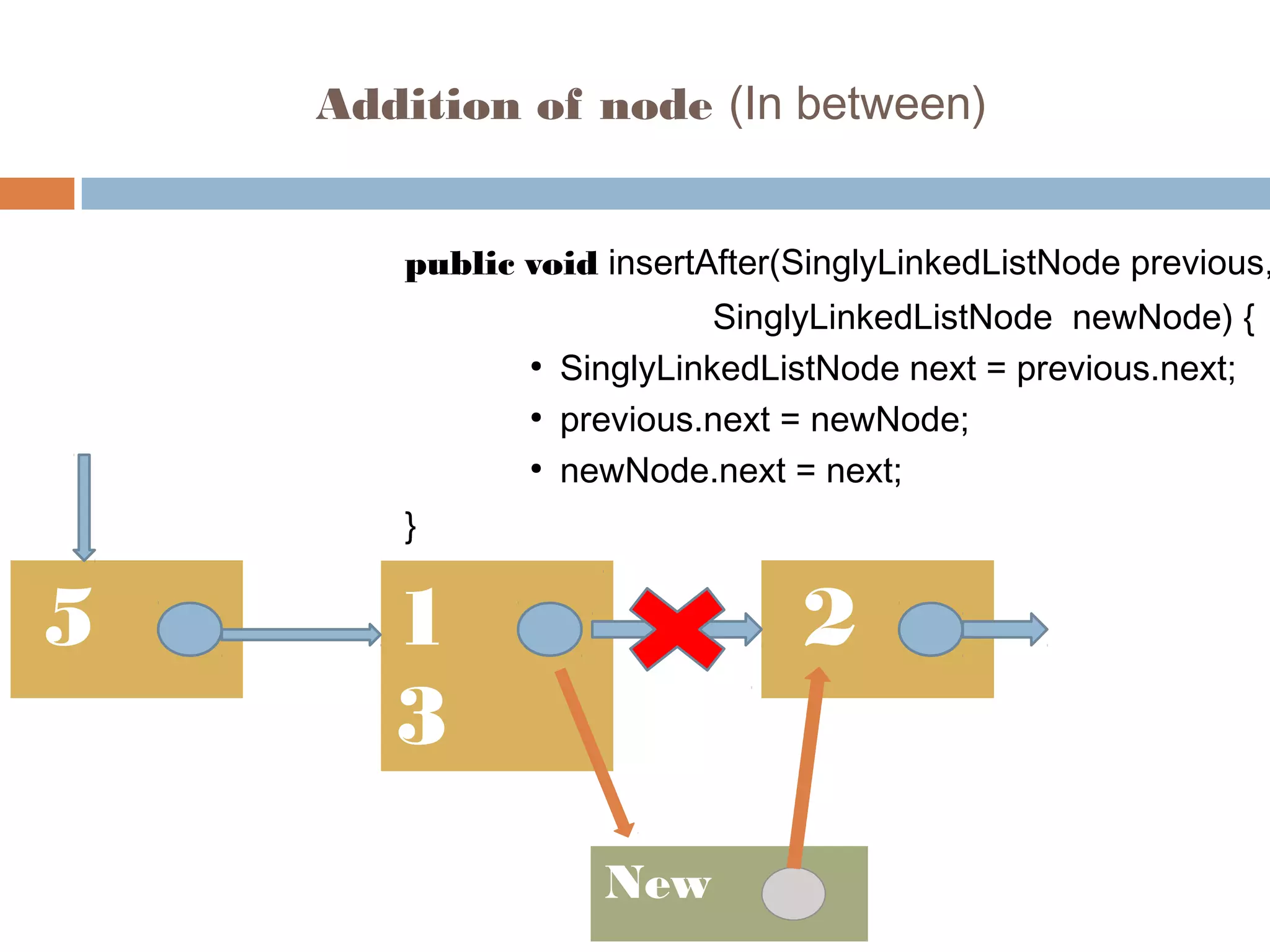
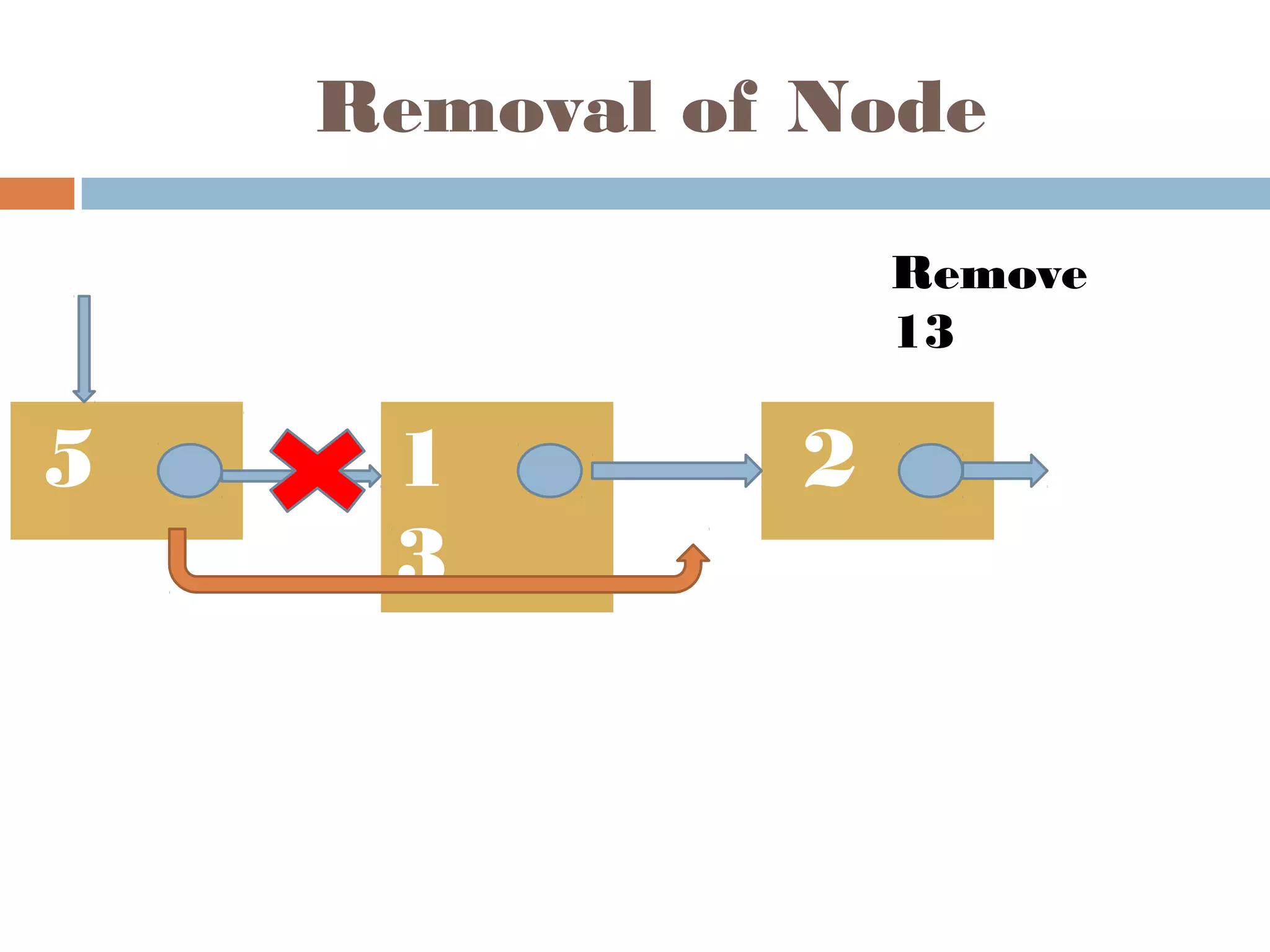
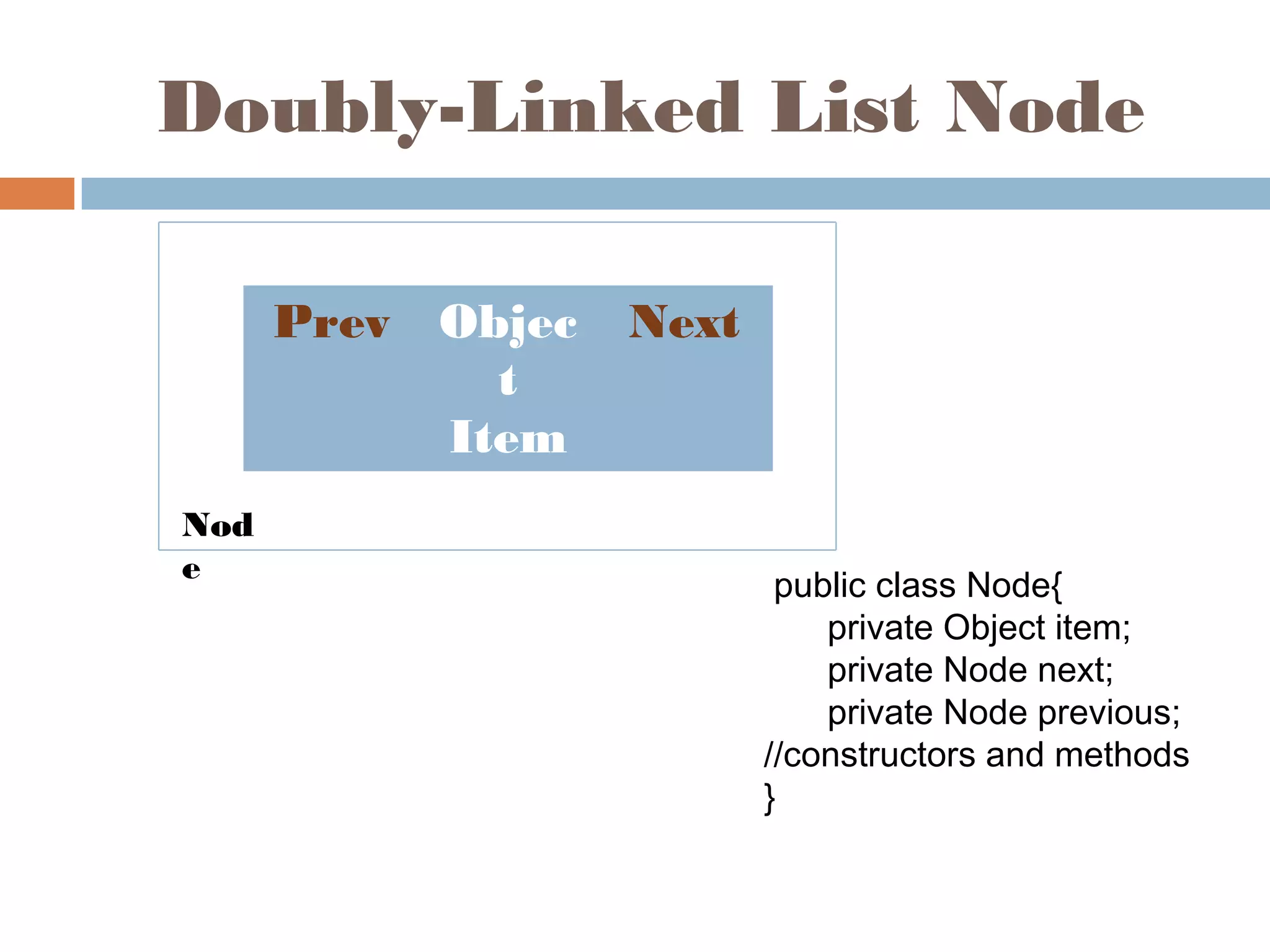
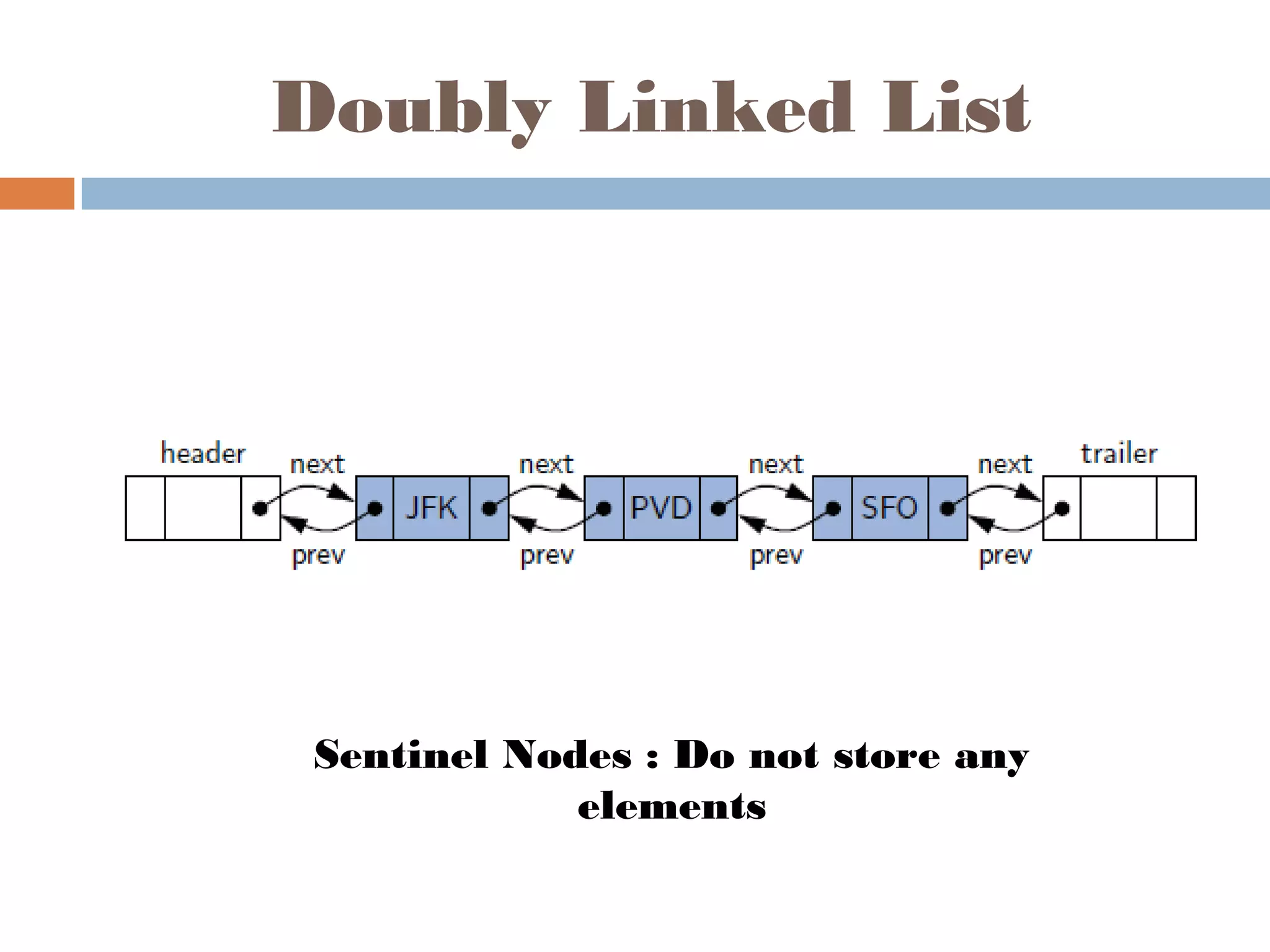
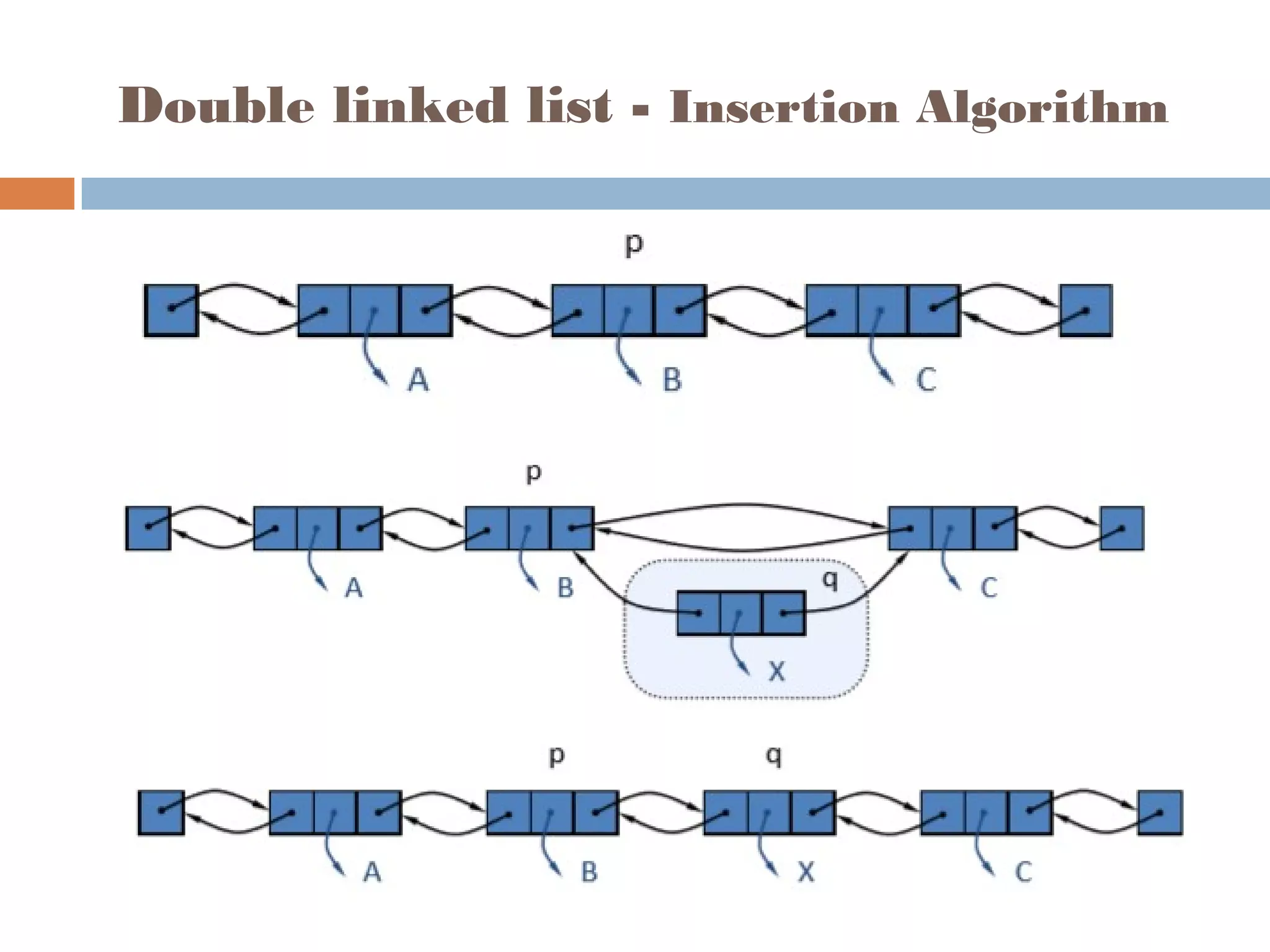
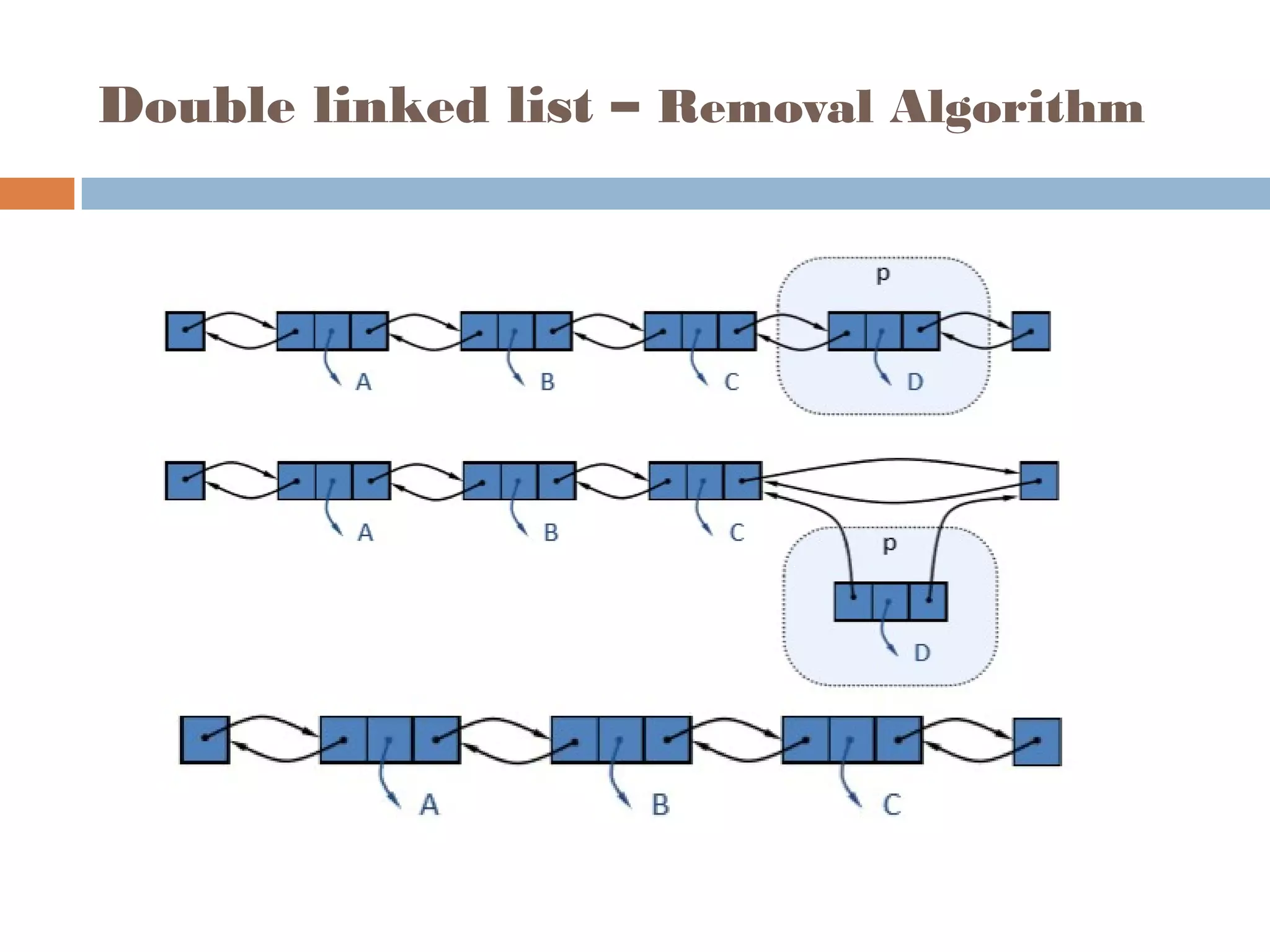
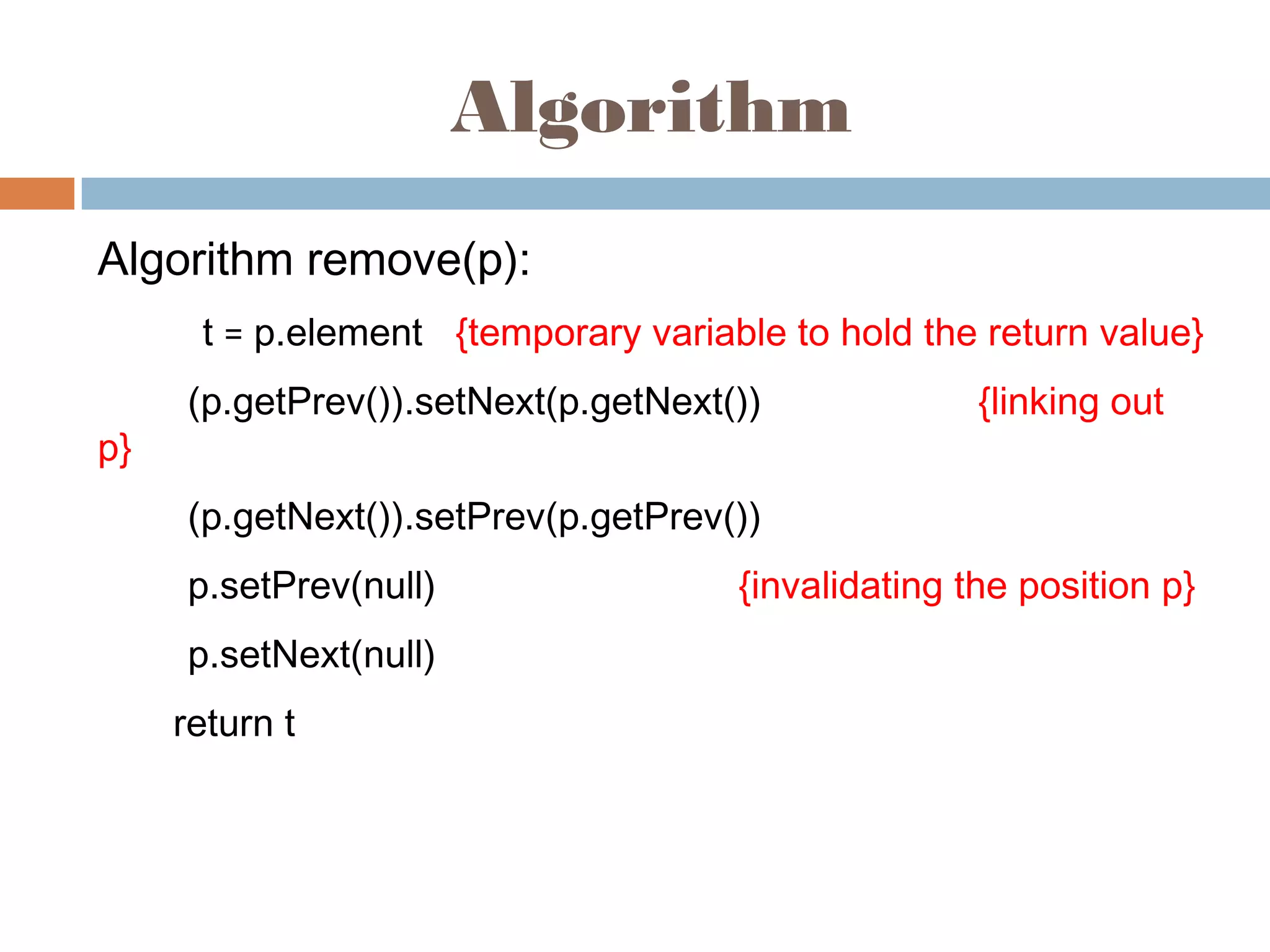
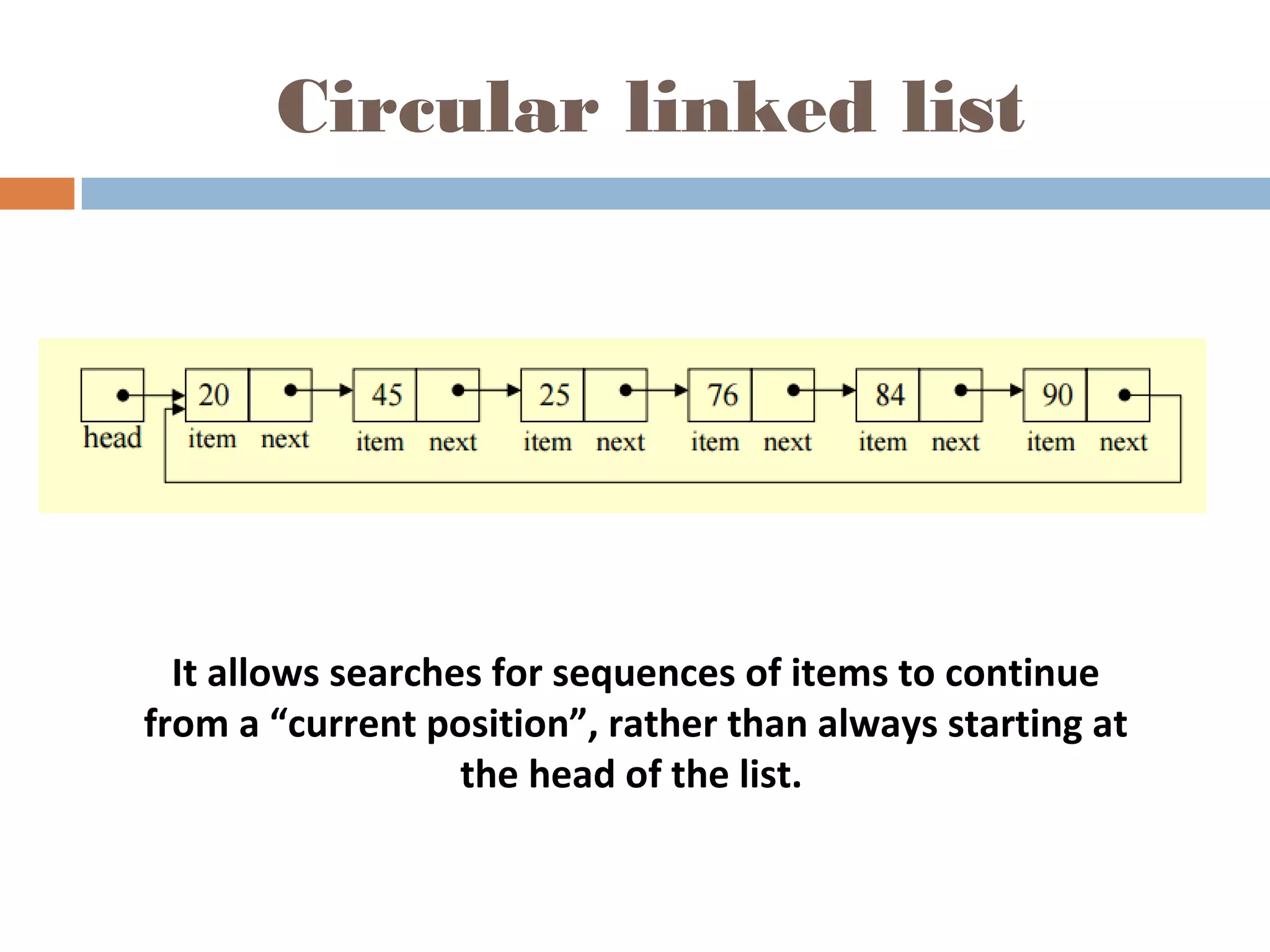
The document discusses linked lists, highlighting their advantages over arrays, such as dynamic memory usage and efficient additions or removals of elements. It explains various operations on linked lists including traversing, adding, and removing nodes, and provides algorithms for singly and doubly linked lists. Additionally, it mentions circular linked lists and their application in searching sequences of items.