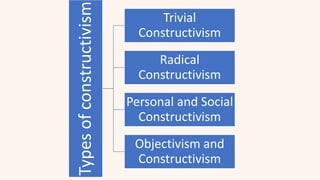
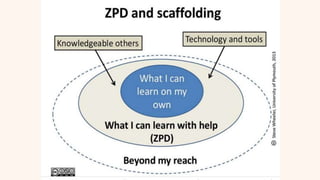
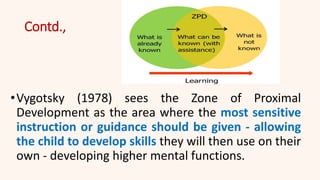
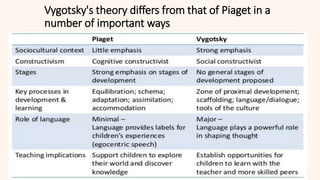
This document discusses constructivism as a learning theory where learners actively construct their own knowledge through experiences rather than passively receiving information from teachers. It covers the origins of constructivism from ancient philosophers like Socrates, influential early thinkers like John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and definitions from Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky, and John Dewey. The key principles of constructivism like active learning, prior knowledge, social context, and reflection are outlined. Examples of constructivist classrooms and educational implications are provided. Different types of constructivism like trivial, radical, and social constructivism are defined. Jean Piaget's cognitive constructivism and Lev Vygotsky