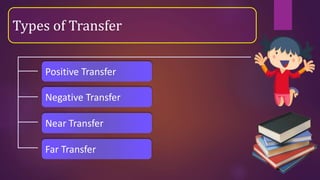
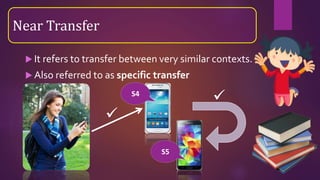
The document discusses the concept of transfer of learning, which is the ability to apply knowledge learned in one context to new situations, outlining its importance and factors affecting it. It identifies types of transfer such as positive, negative, near, and far transfer, and details five stages of transfer from intention to unconscious maintenance. Additionally, it emphasizes conditions necessary for effective transfer, including the relevance of learning and the similarity between learning contexts.