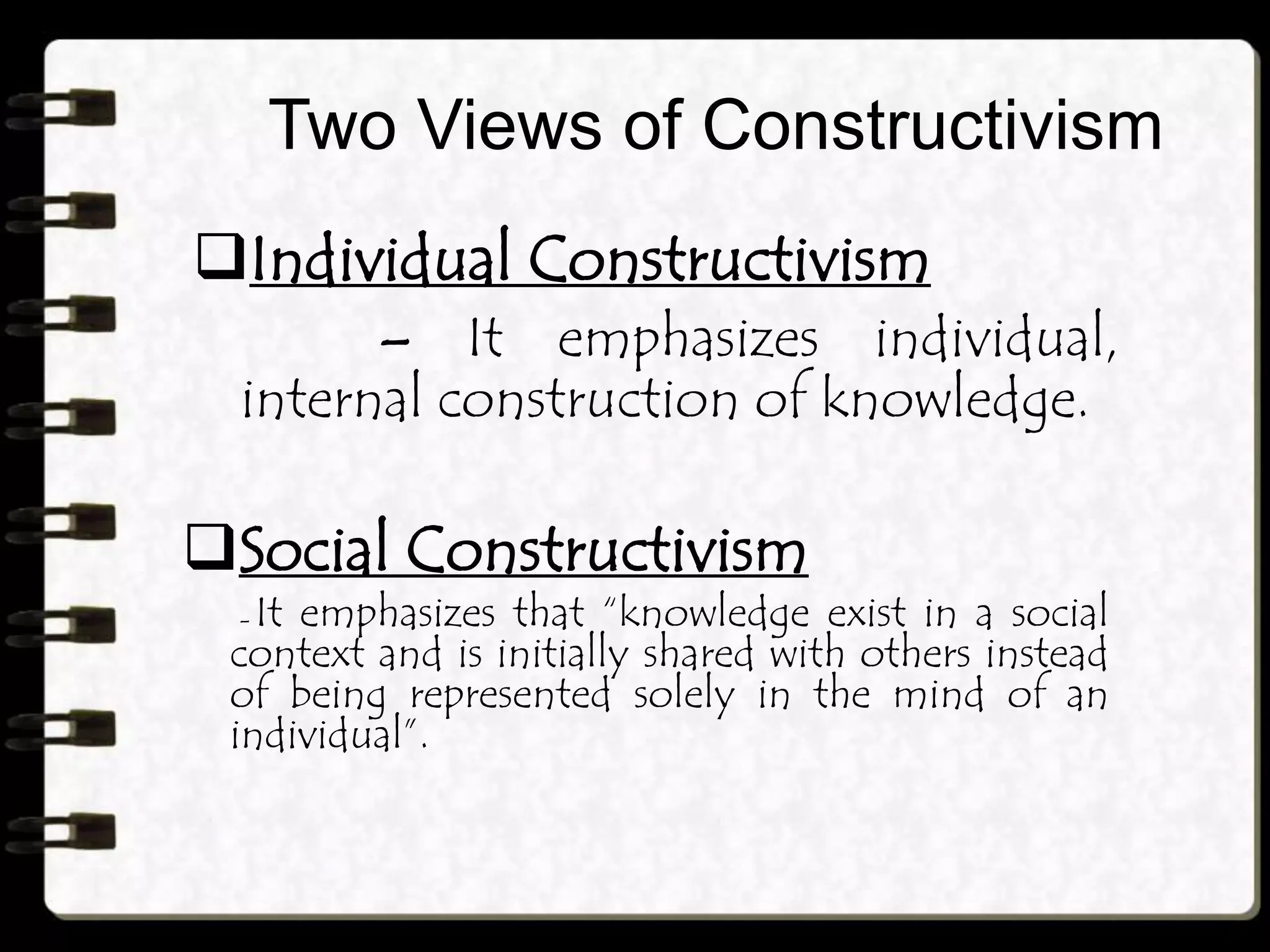
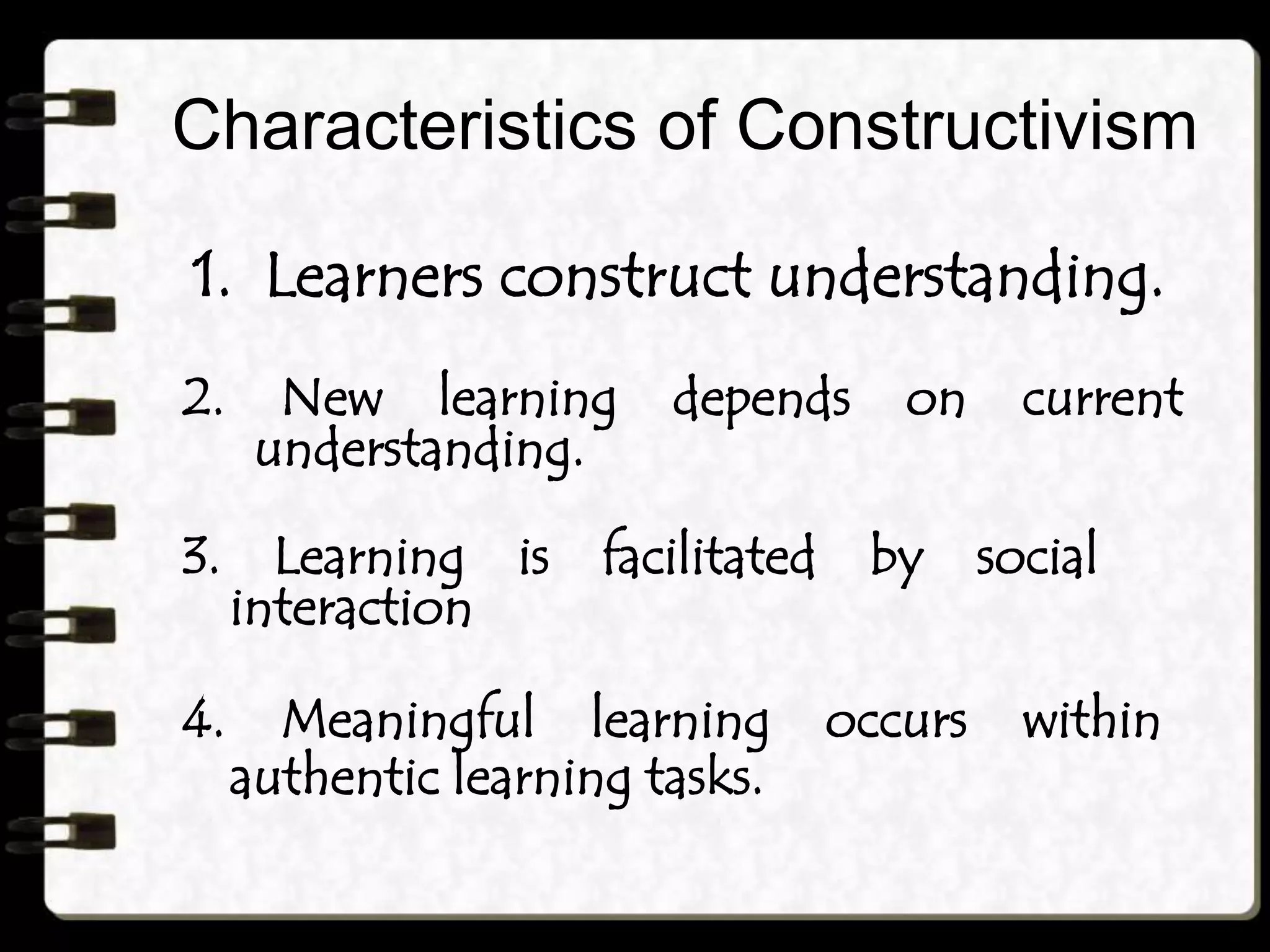
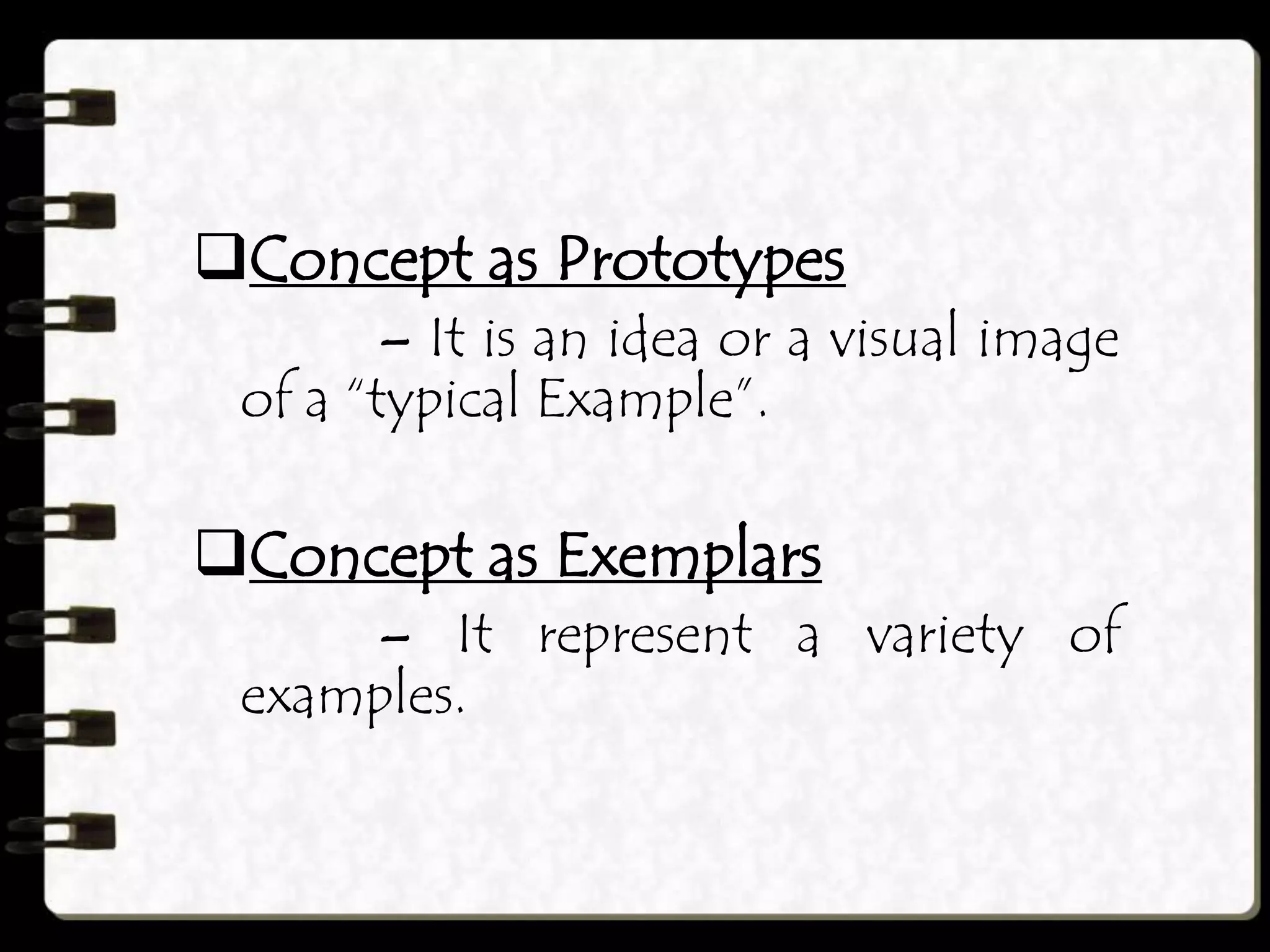
Constructivism focuses on how learners actively construct knowledge through experiences and interactions with their environment. There are two views of constructivism: individual constructivism which emphasizes internal knowledge construction by individuals, and social constructivism which views knowledge as constructed socially and shared with others. Constructivism is characterized by learners constructing their own understanding, new learning building on prior knowledge, social interaction facilitating learning, and meaningful learning occurring through authentic tasks. Concepts are organized knowledge and can be represented as feature lists, prototypes, or exemplars to effectively teach concepts. Constructivism in teaching aims to give learners in-depth understanding through varied examples, opportunities for experimentation and interaction, hands-on activities, and relating topics to