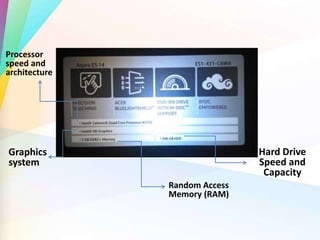
The document discusses several key factors that affect computer performance: processor speed and architecture, which refers to its basic design and complexity; random access memory (RAM) which is measured in megabytes and gigabytes and used to temporarily store information when a program is running; graphics system which determines how well it can handle visual output; and hard drive speed and capacity which are determined by rotational velocity, interface type, and size. These specifications must be met for software and hardware to run properly on a computer system.