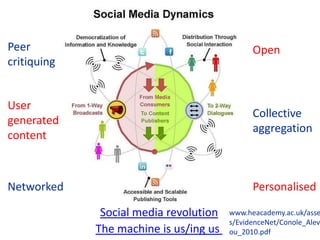
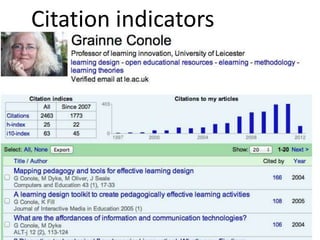
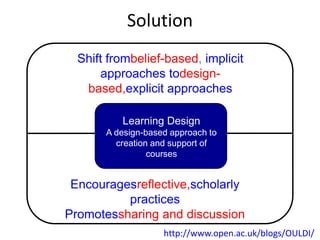
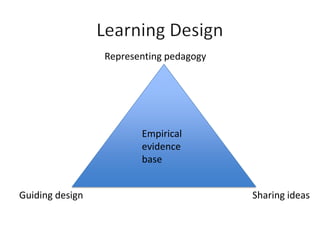
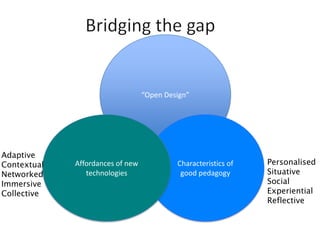
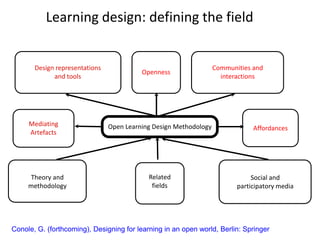
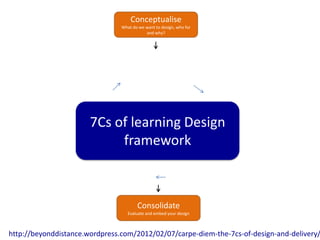
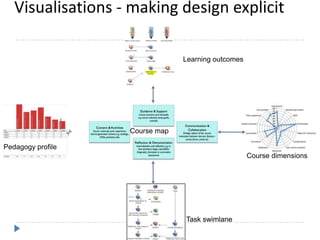
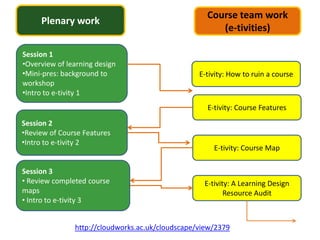
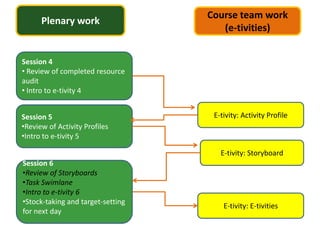
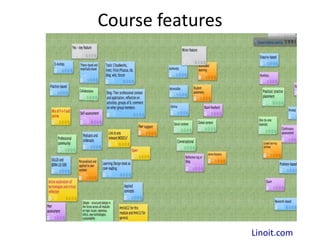
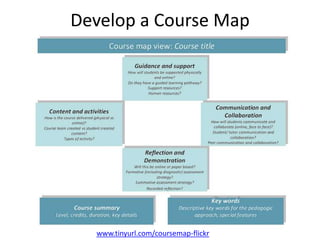
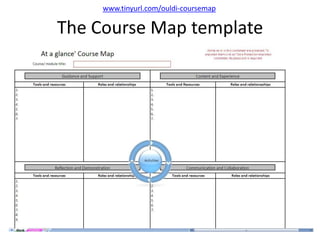
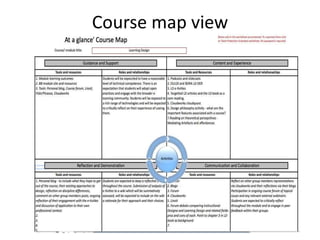
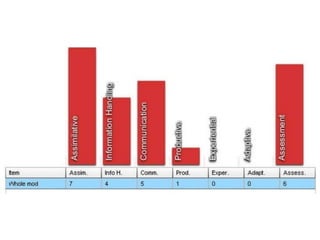
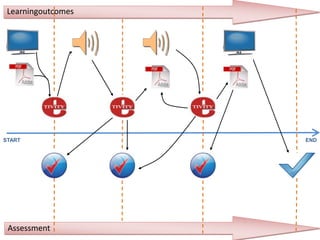
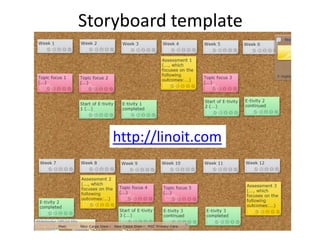
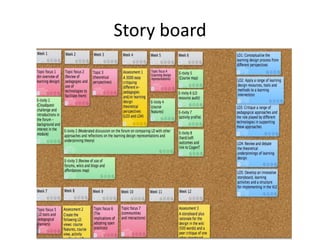
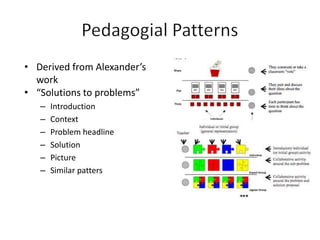
The document discusses how social media and digital technologies have transformed learning, teaching, and research. It outlines the shift from distance education to open educational practices and resources. Key aspects covered include digital literacies, fostering open practices through open resources, courses, accreditation, scholarship and research. The document proposes learning design as a solution to better exploit opportunities while addressing problems like replicating bad pedagogy. Learning design makes the design process more explicit and shareable through representations, tools, and communities of practice.