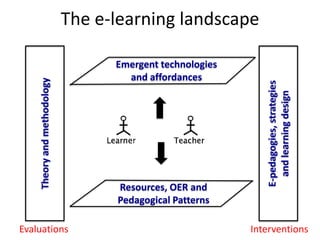
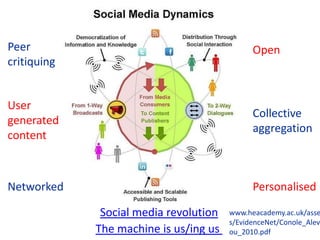
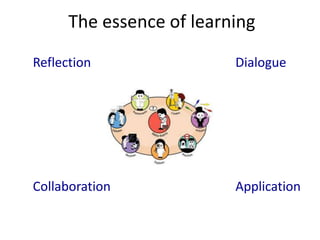
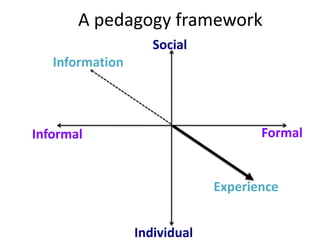
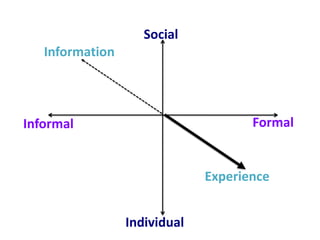
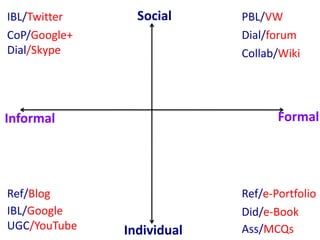
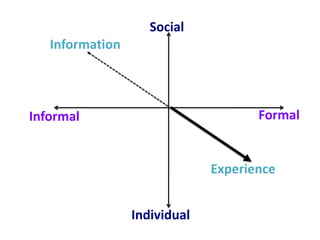
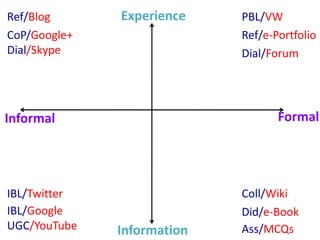
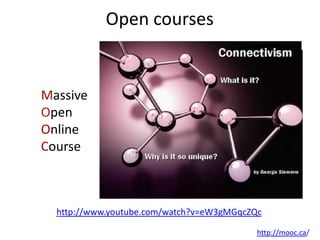
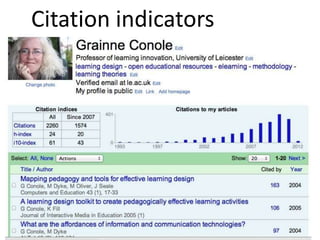
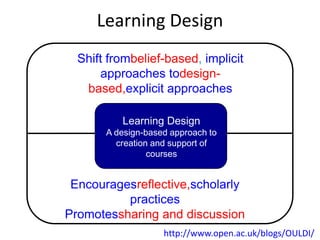
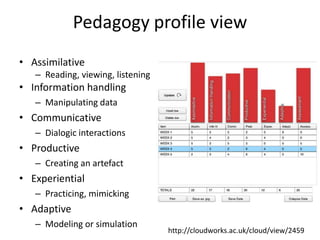
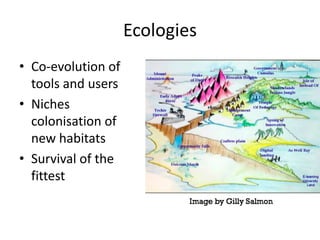
This document provides an overview of contemporary perspectives in e-learning research. It discusses the evolving e-learning landscape including new technologies, learner experiences, and pedagogical approaches. It also examines open practices in resources, courses, scholarship, and research. Key topics covered include the shift from Gutenberg to digital technologies, disruptive innovations, mapping pedagogies to technologies, and metaphors like ecologies, spaces, memes, and rhizomes for conceptualizing e-learning.