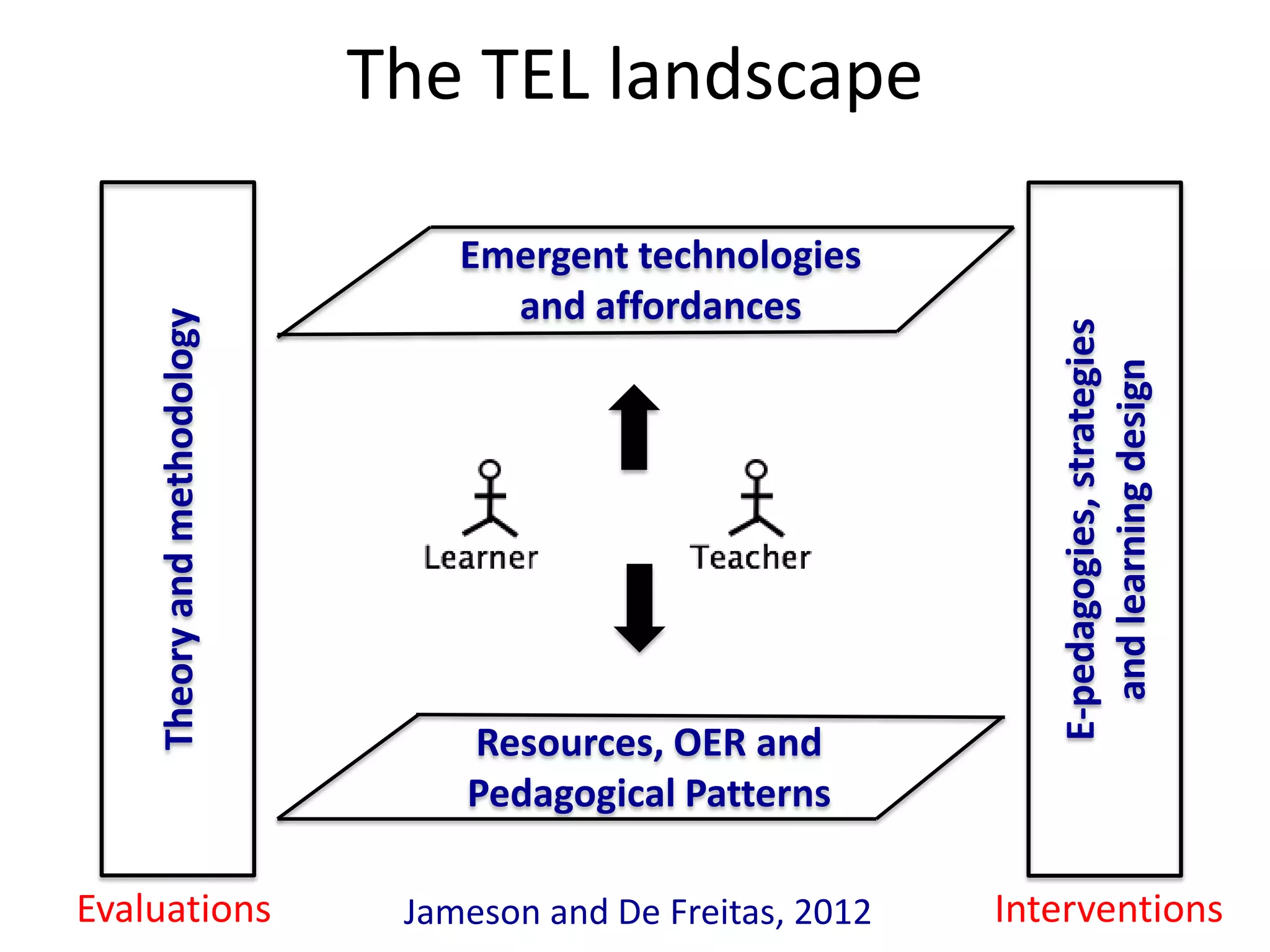
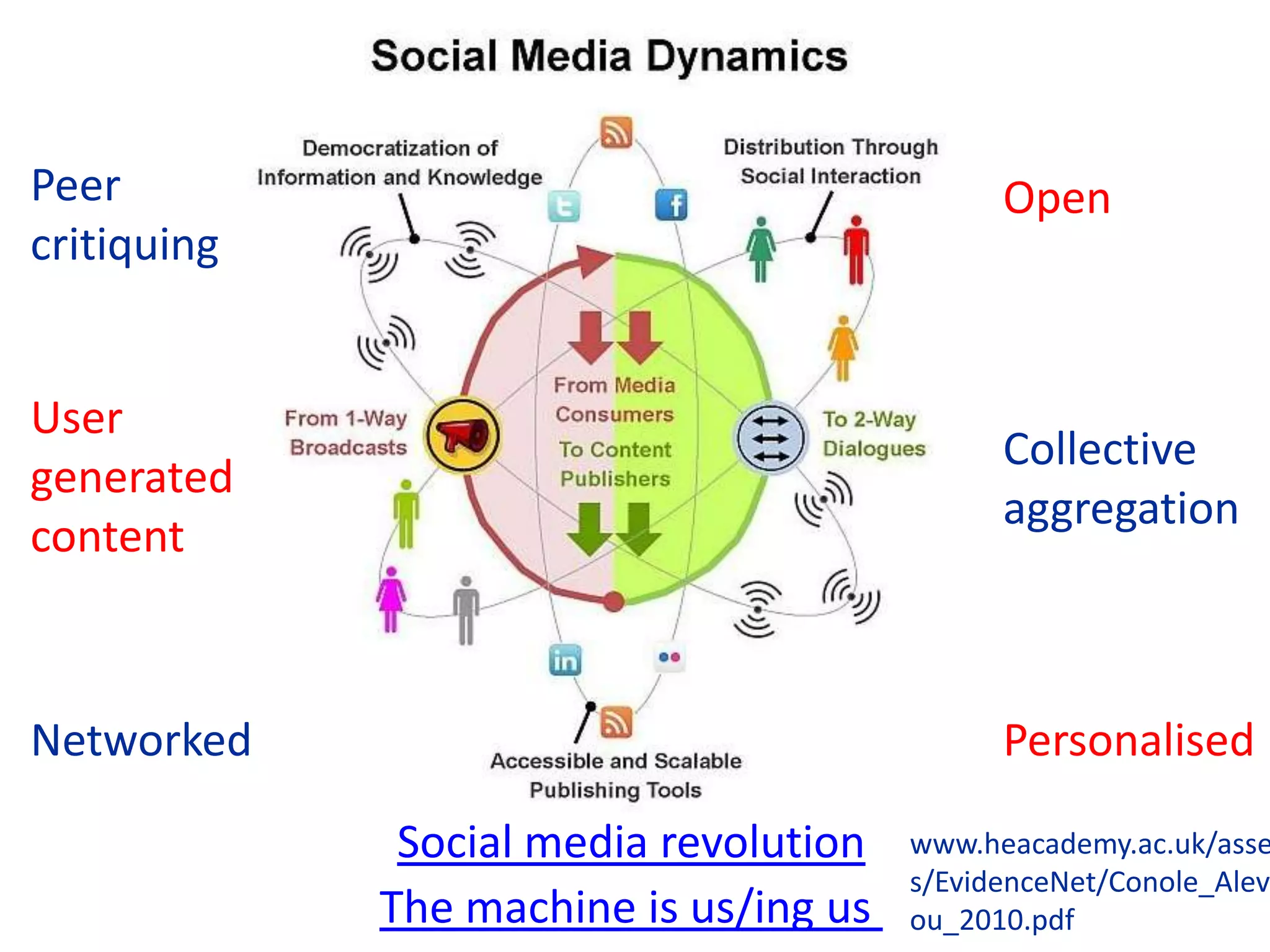
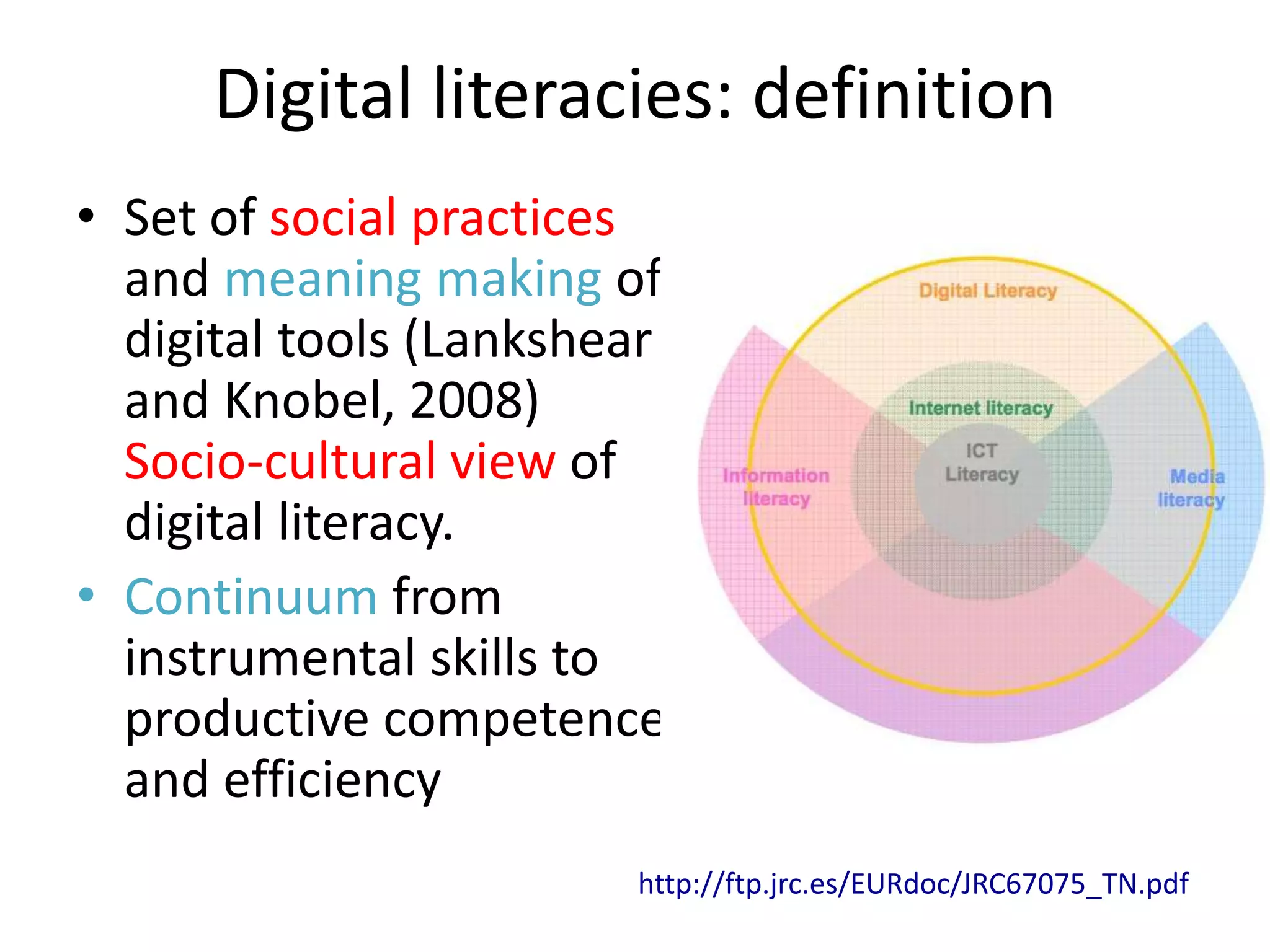
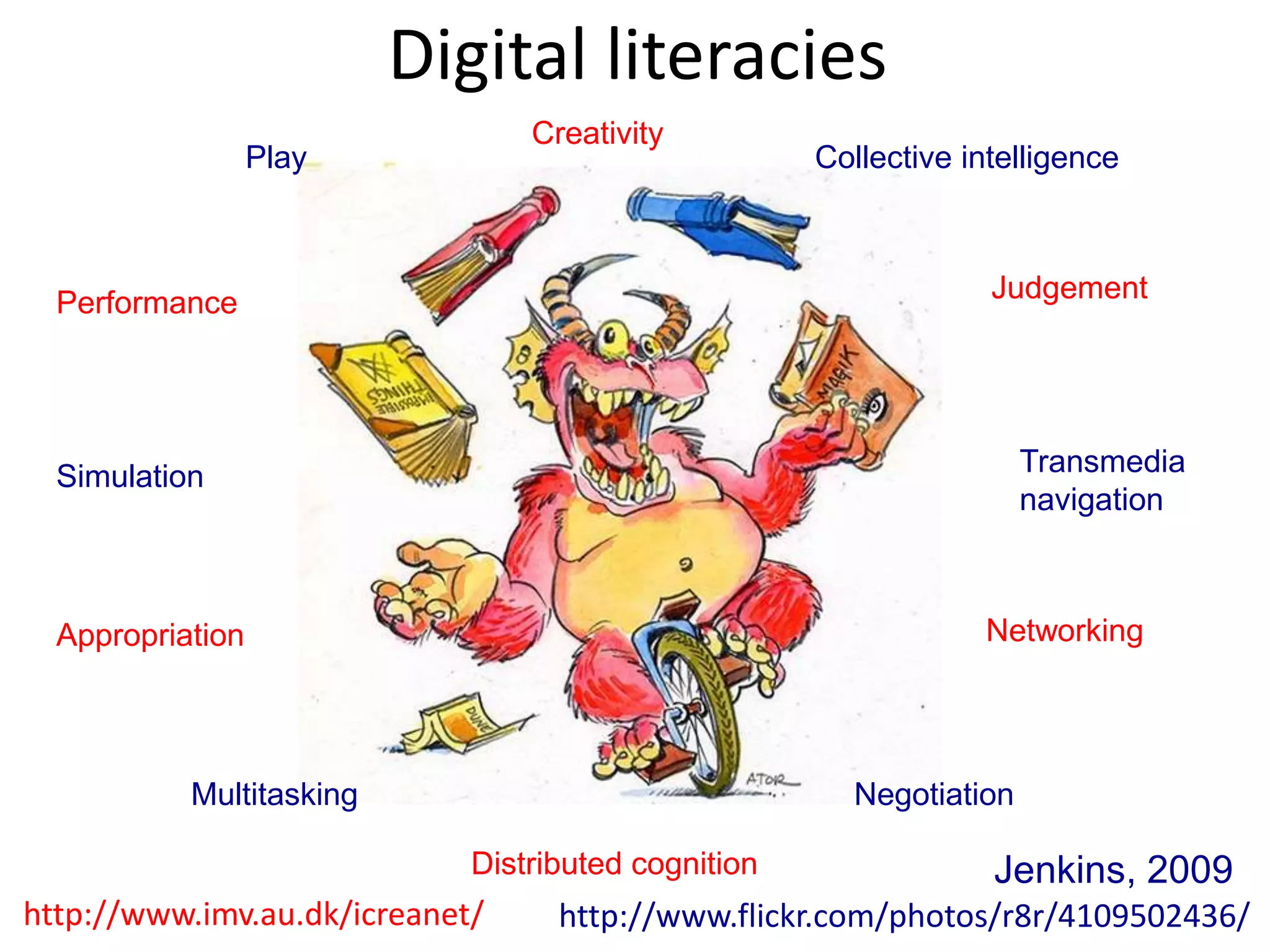
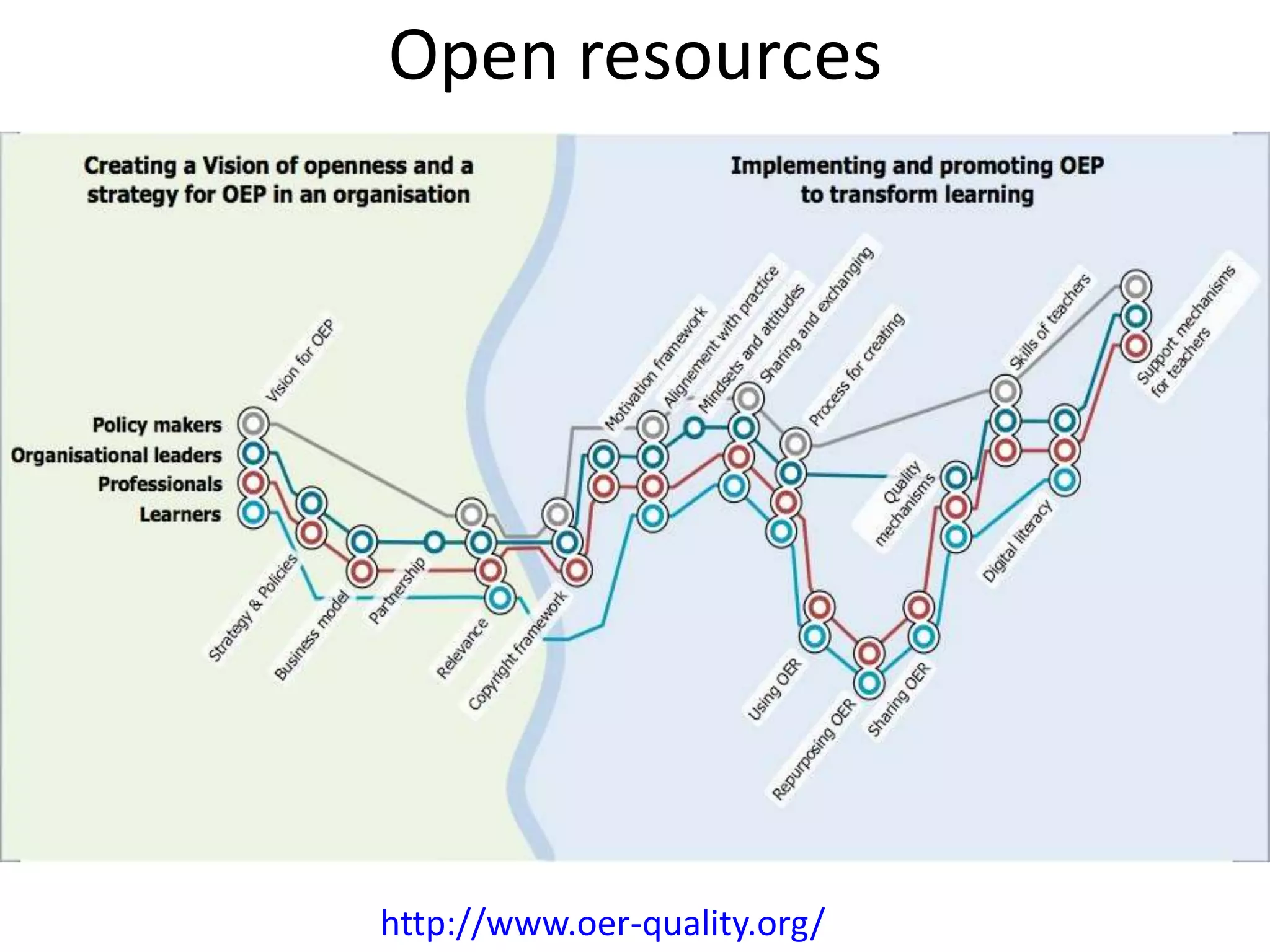
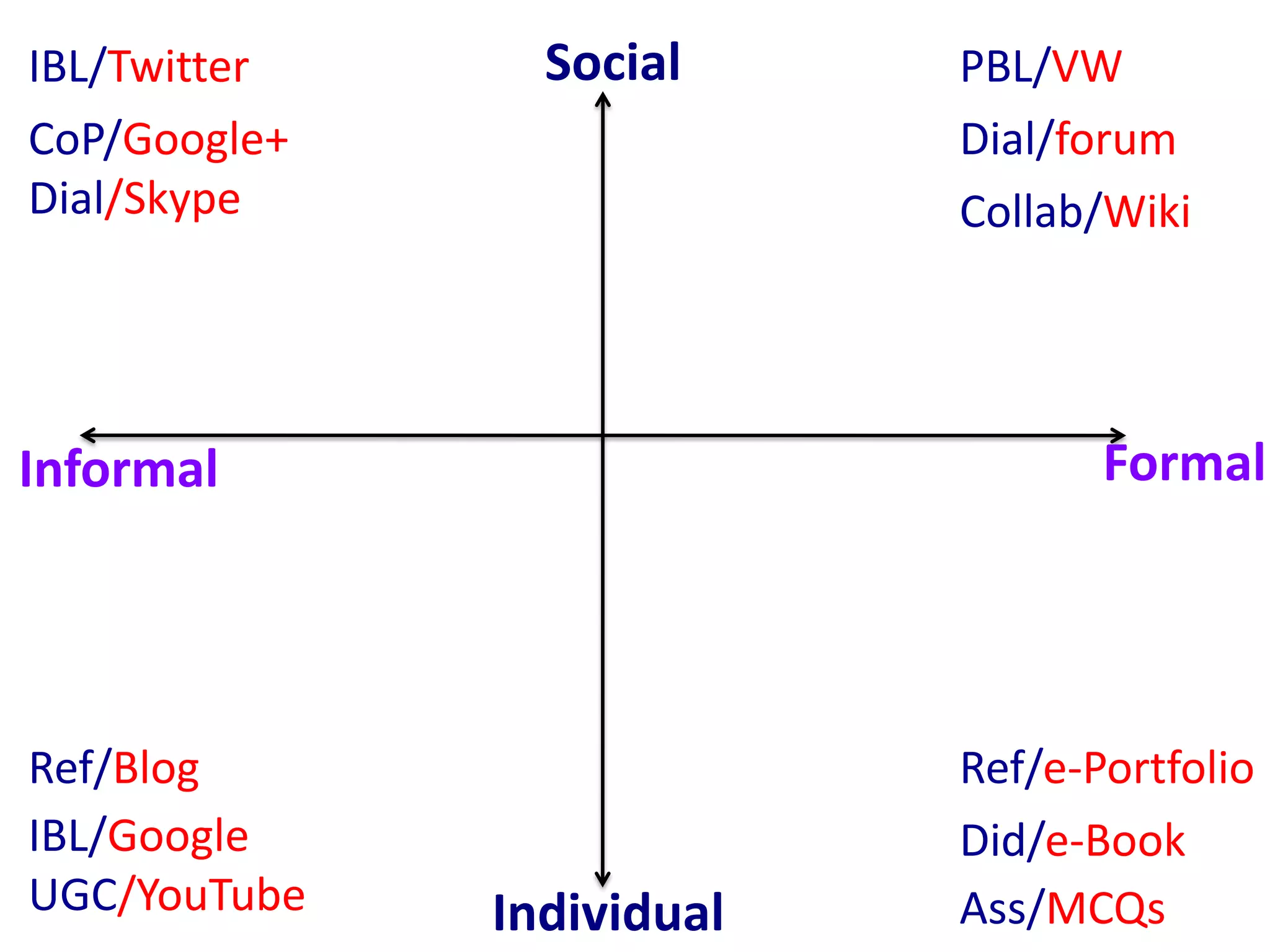
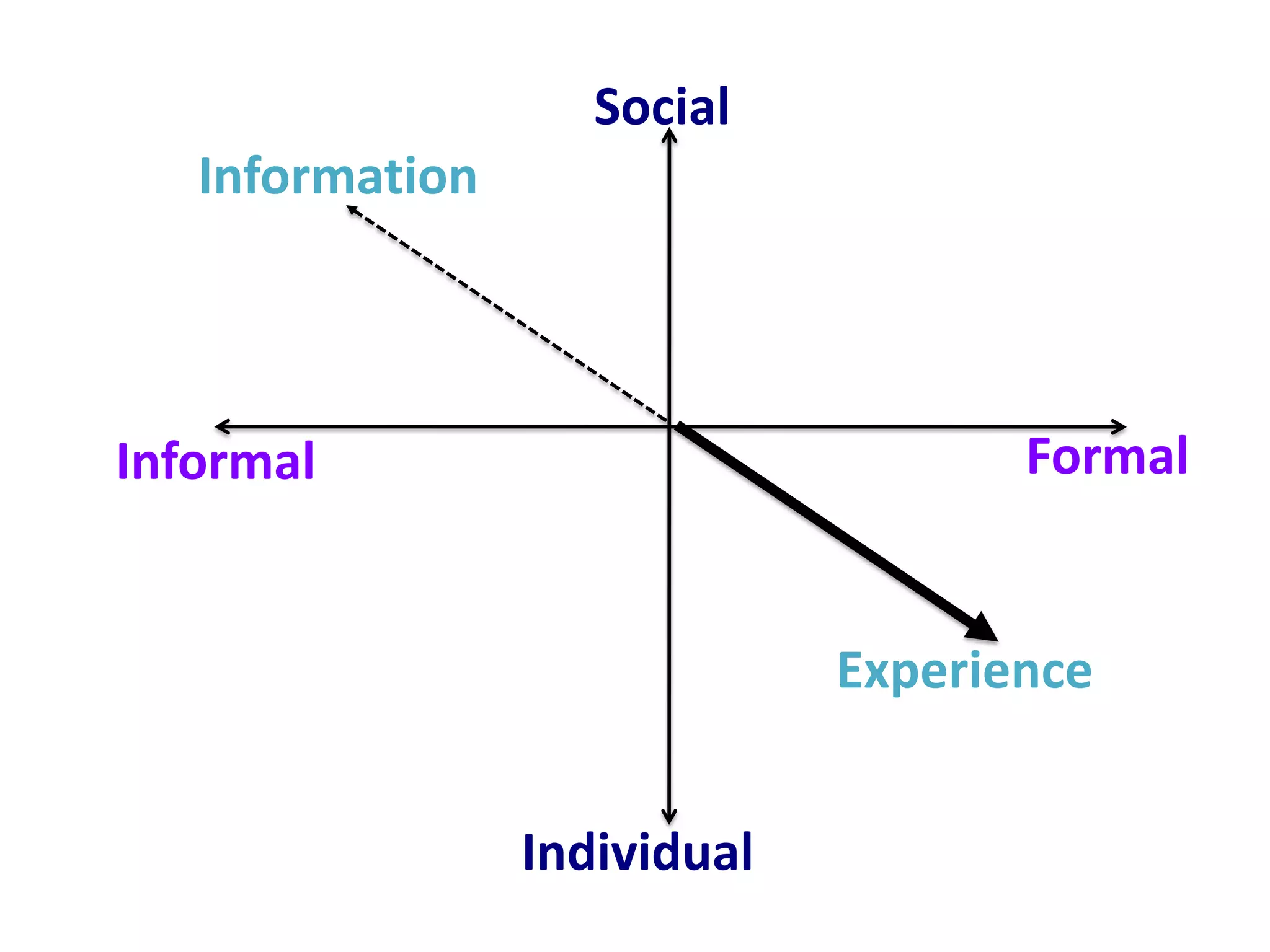
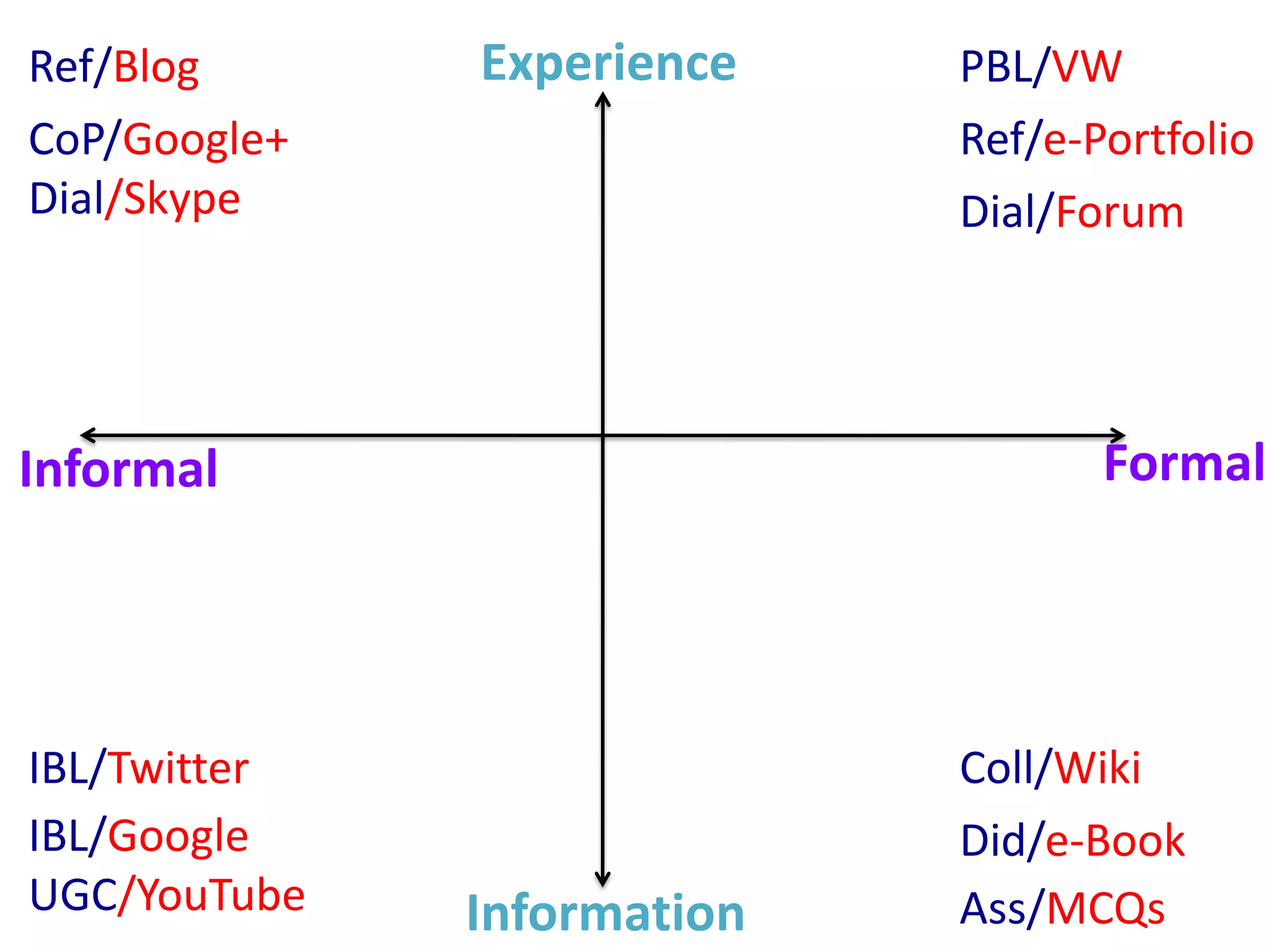
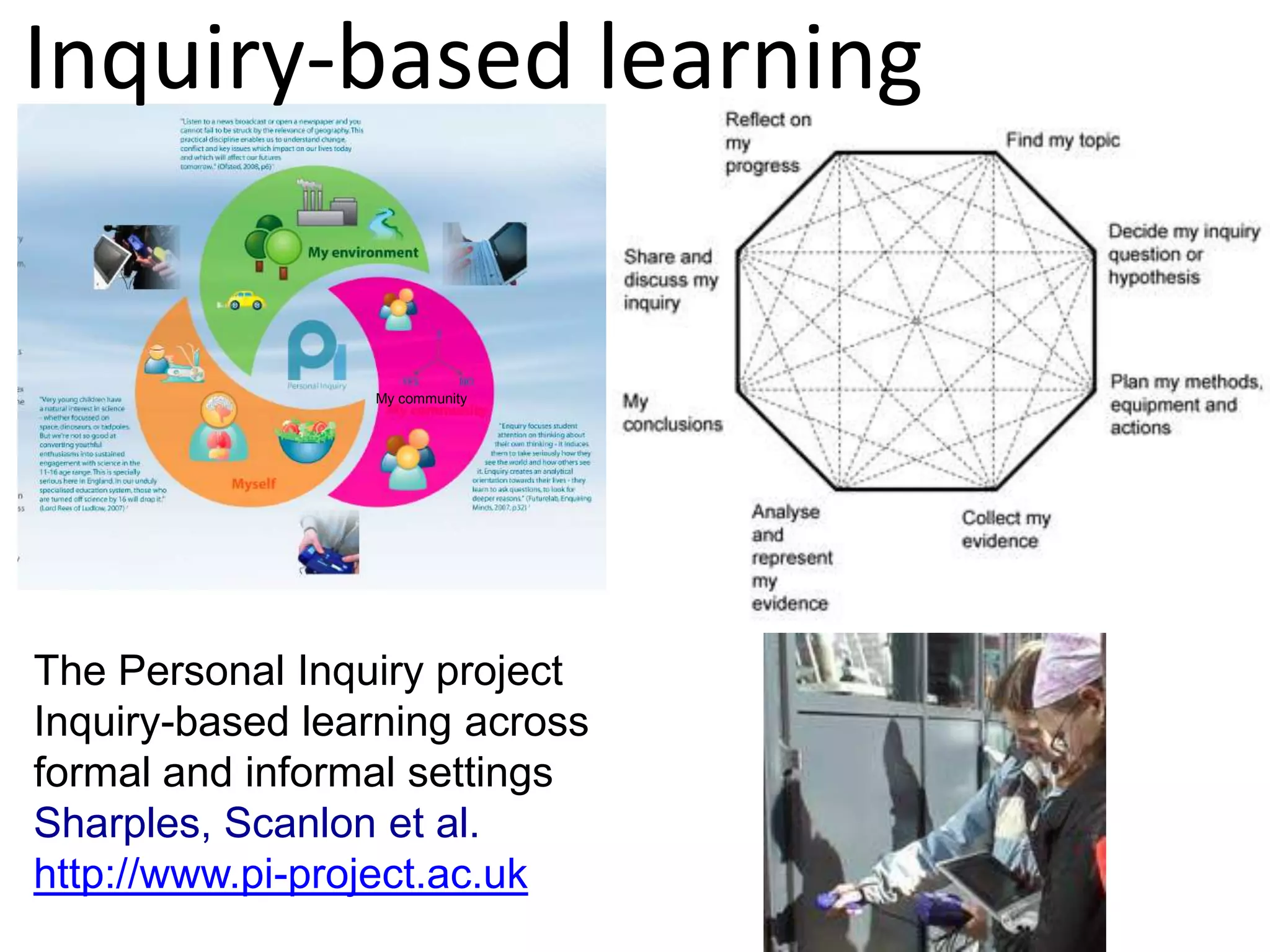
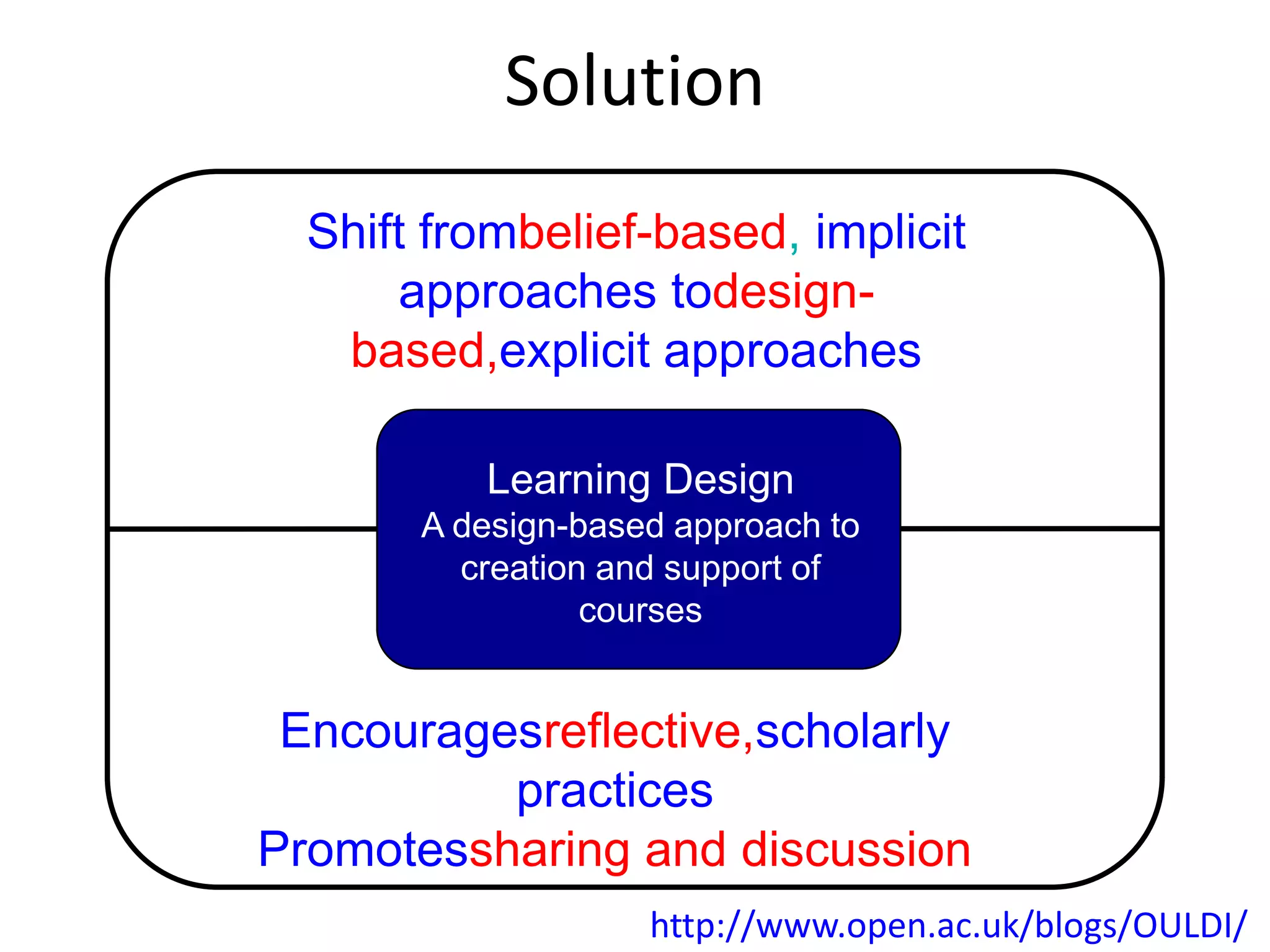
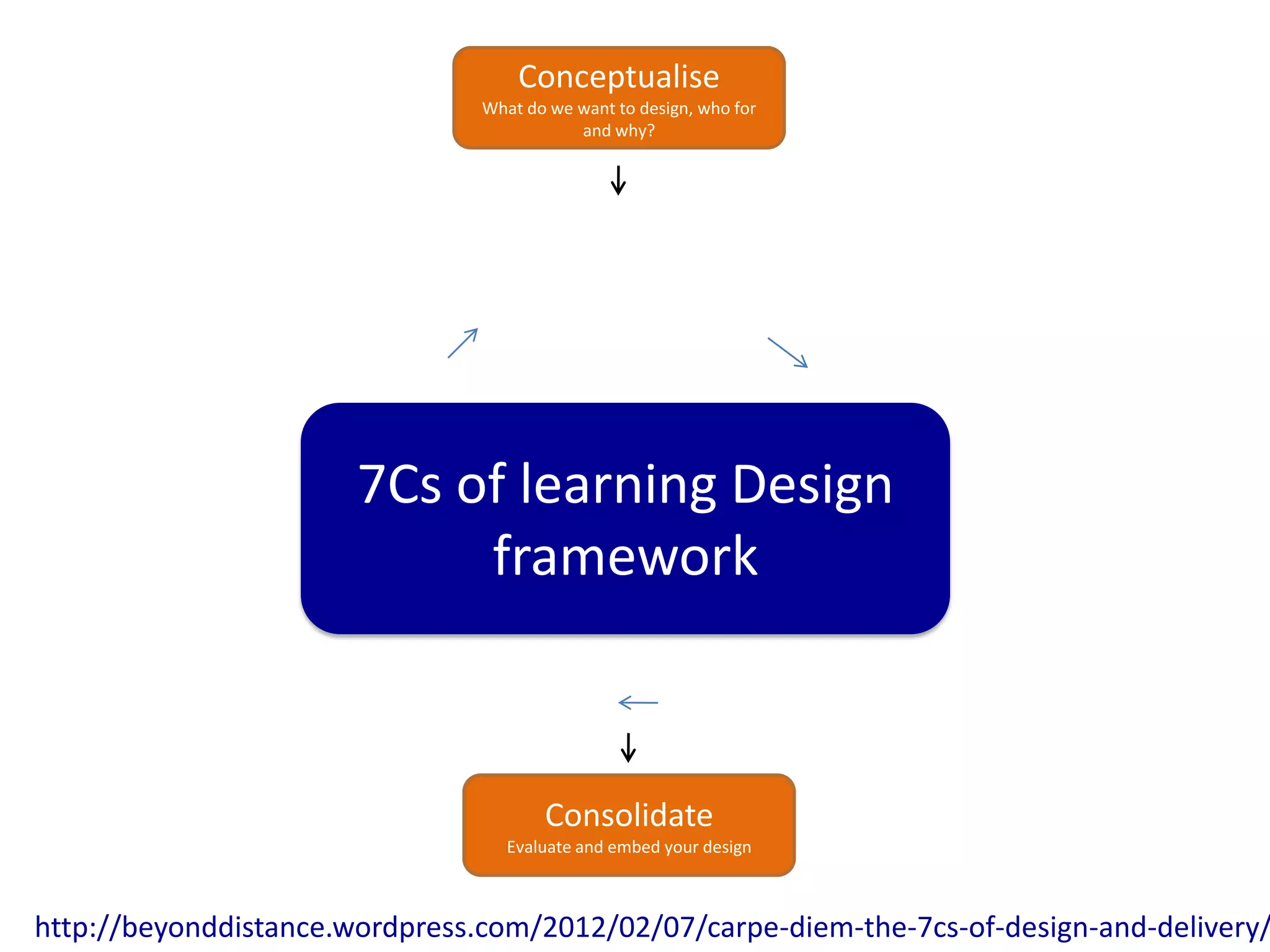
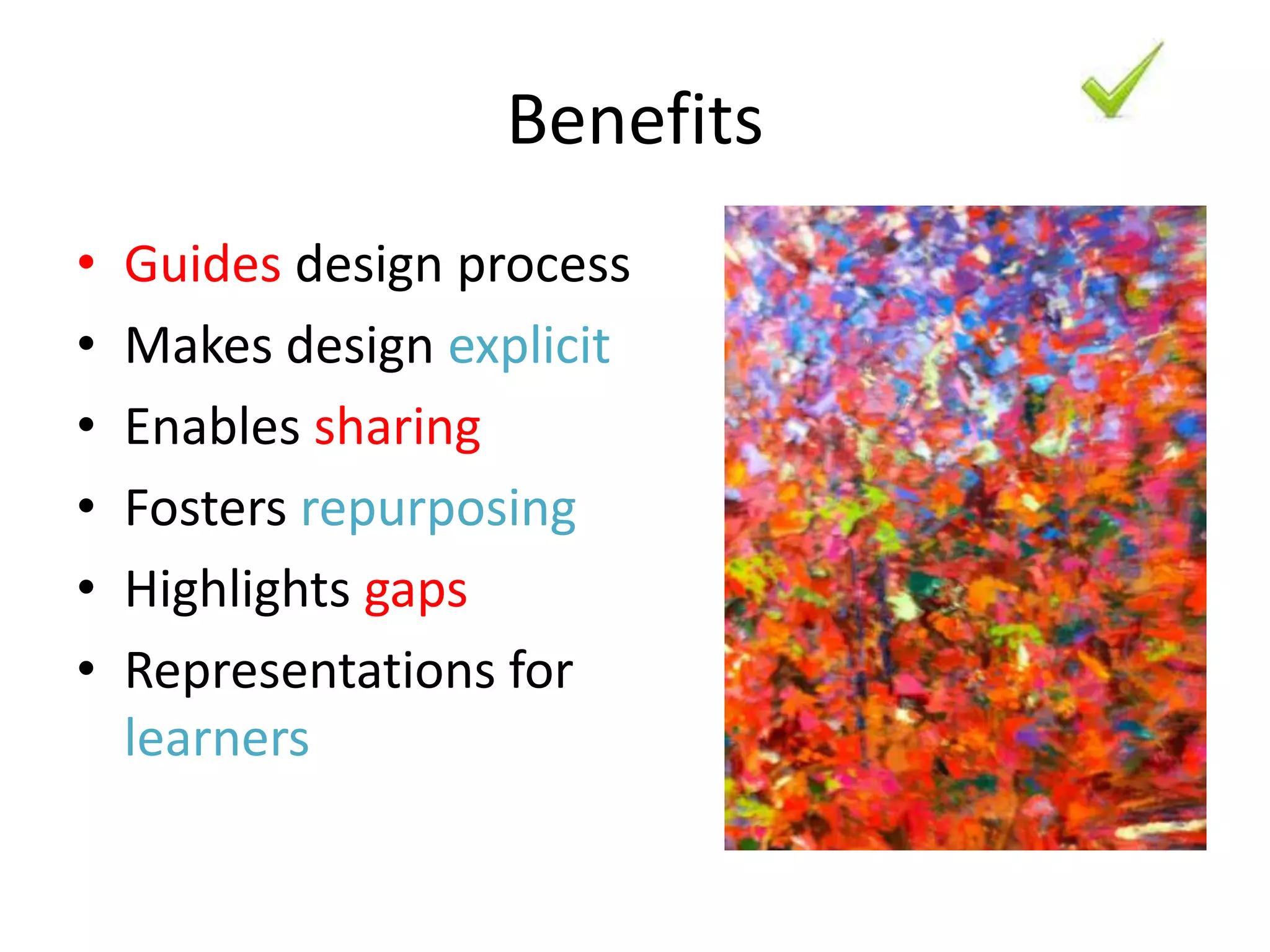
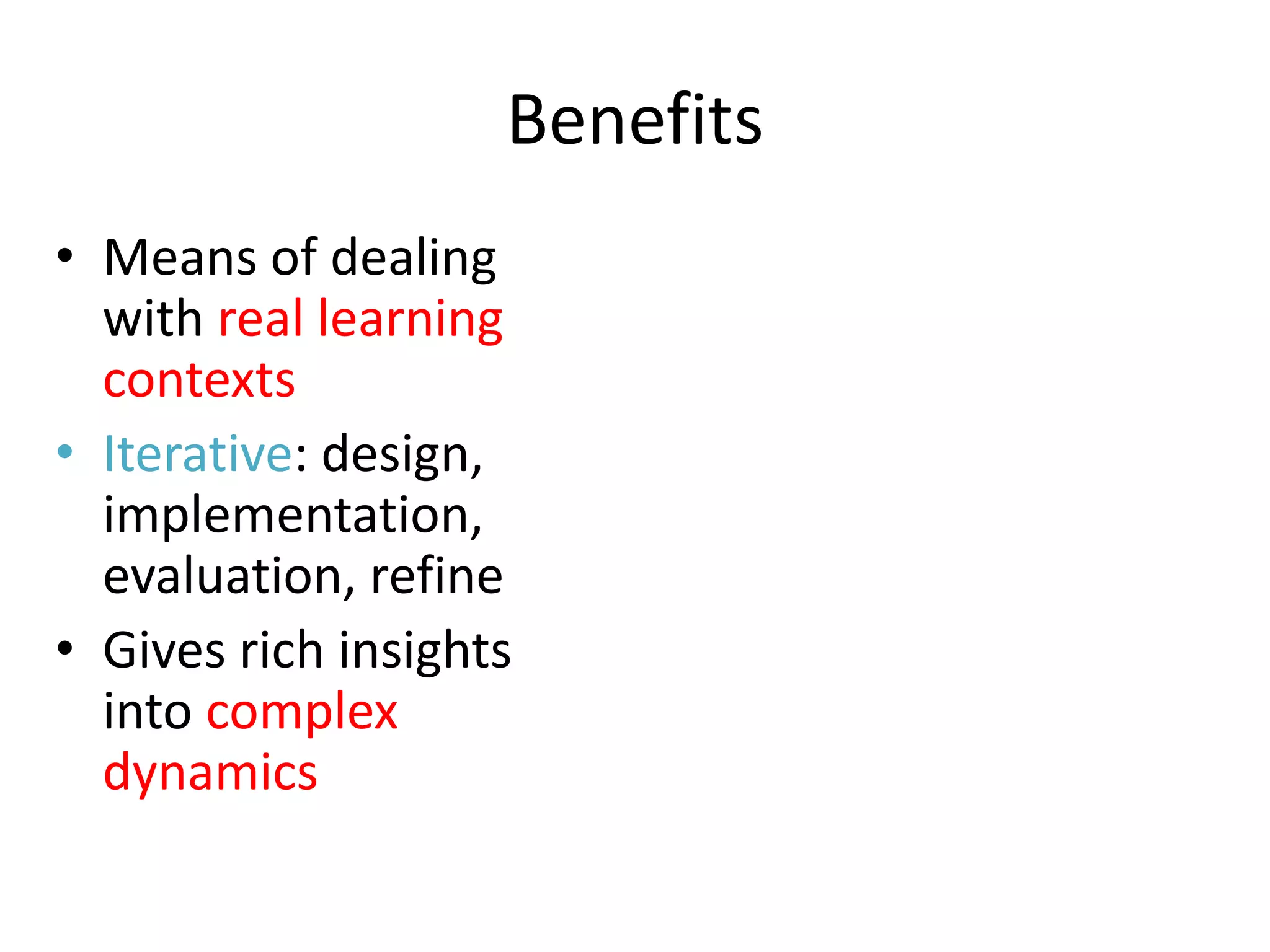
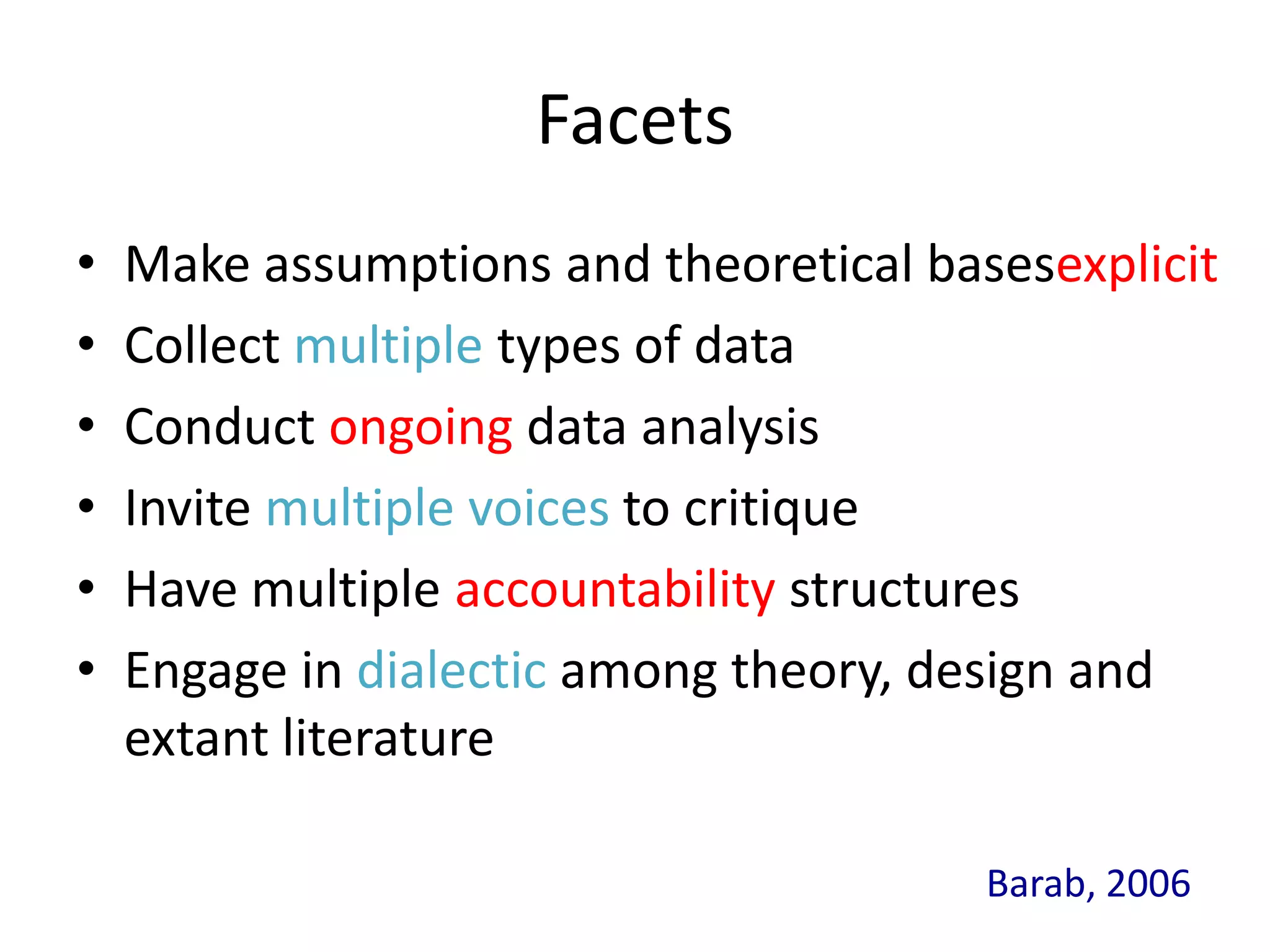
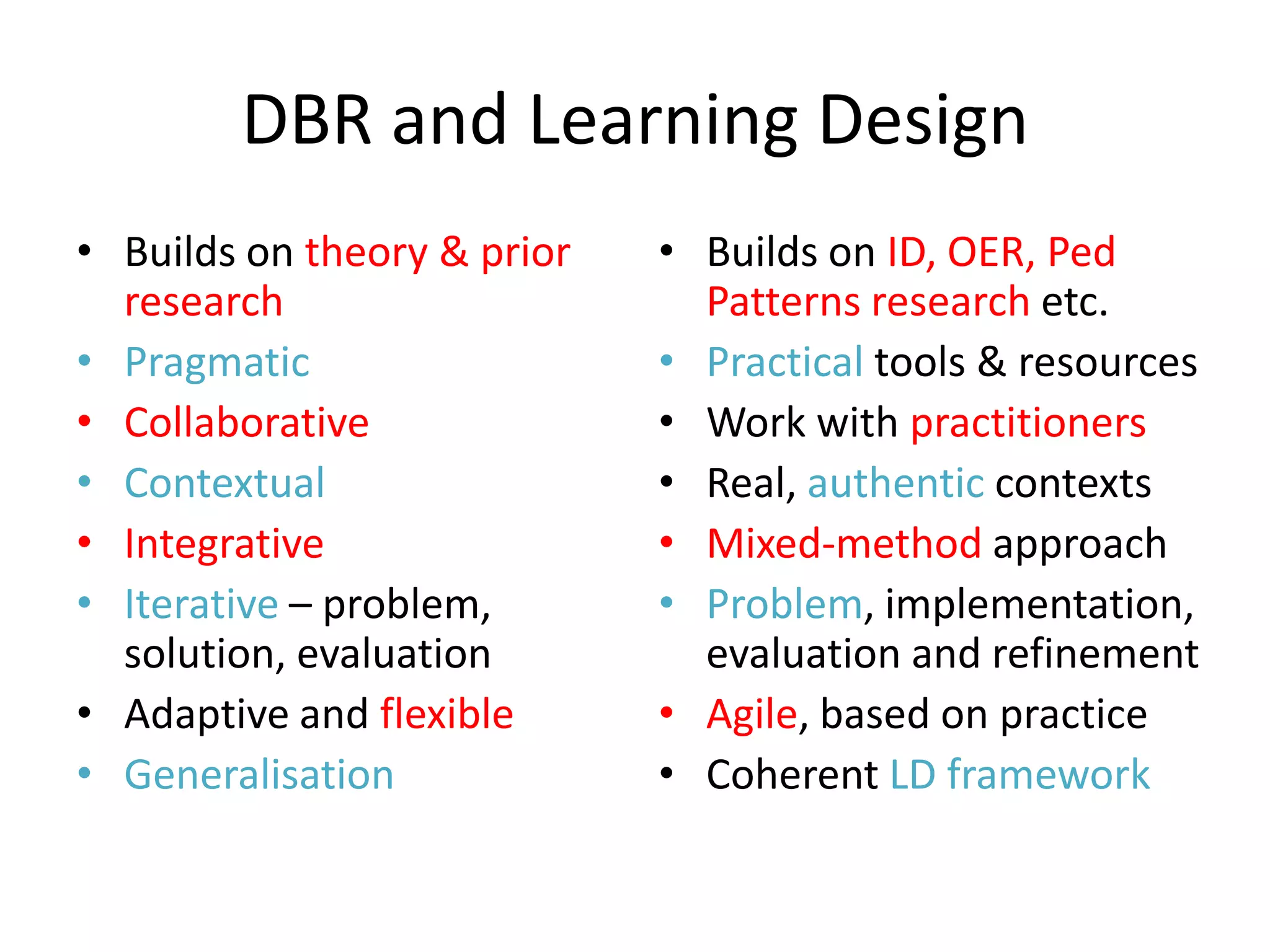
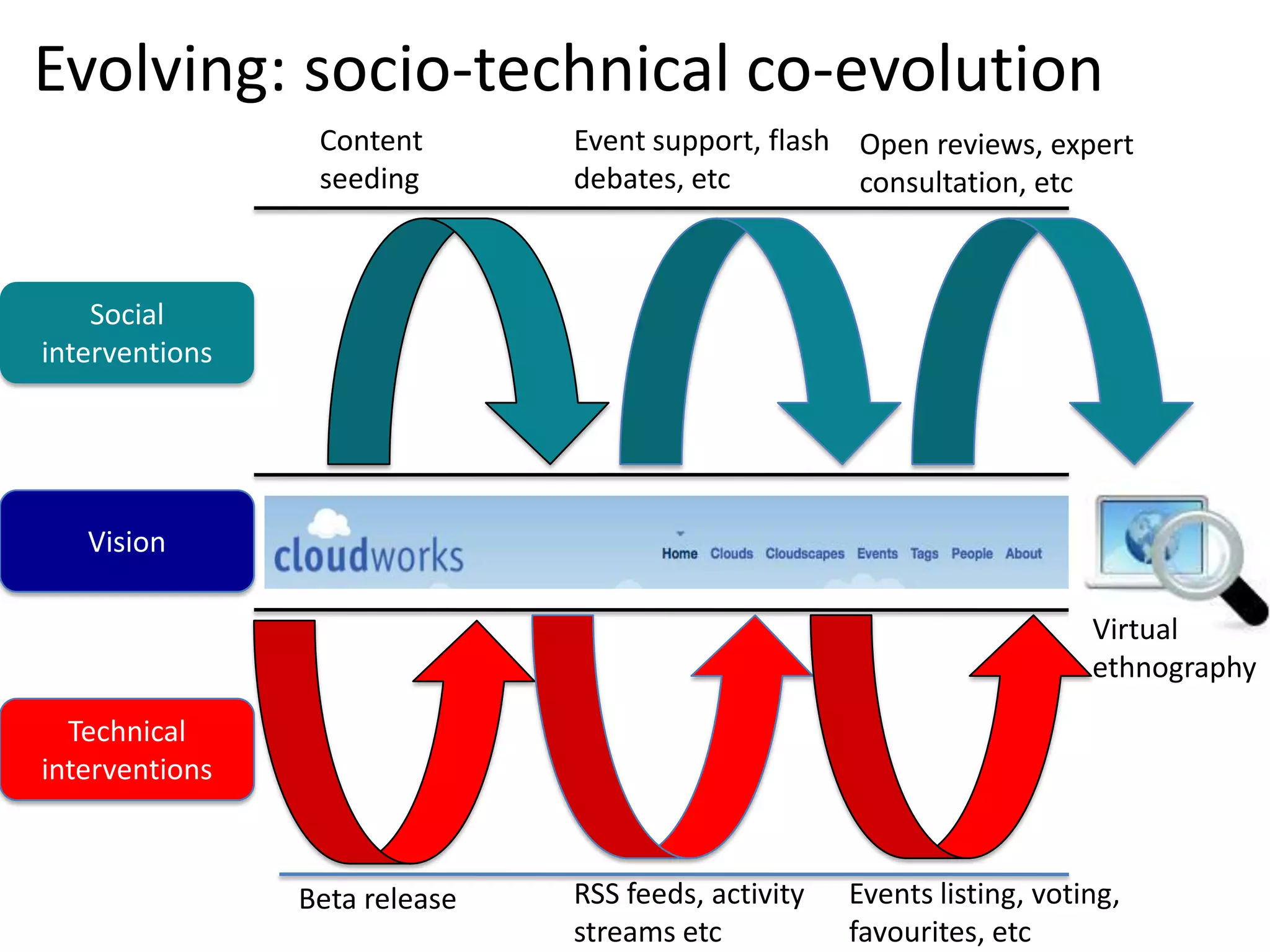
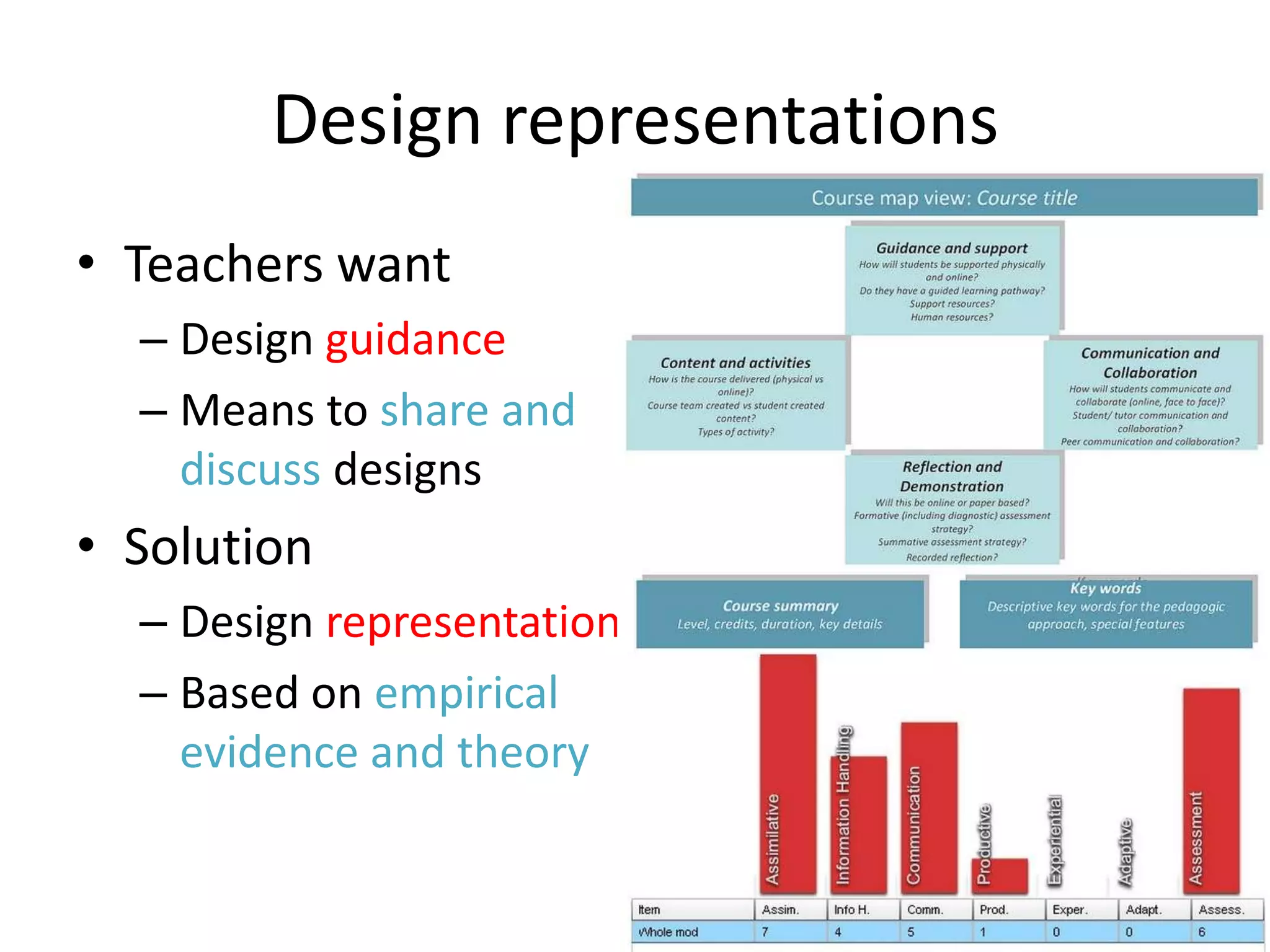
Design-based research in technology-enhanced learning (TEL) aims to improve educational practice through iterative design, development, and implementation of interventions in real-world contexts. It involves collaboration between researchers and practitioners and leads to contextually sensitive design principles. The methodology is systematic but flexible, and builds on learning design frameworks to make the design process explicit and enable sharing of best practices.