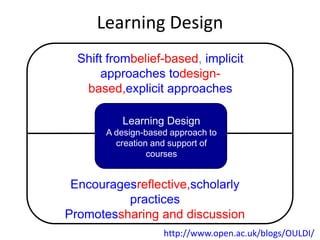
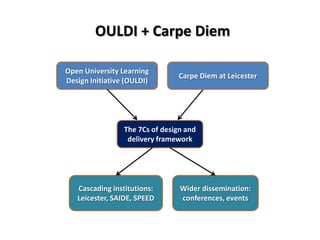
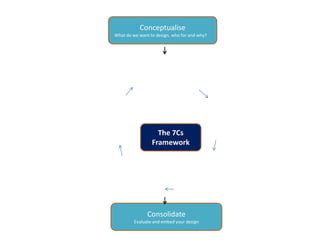
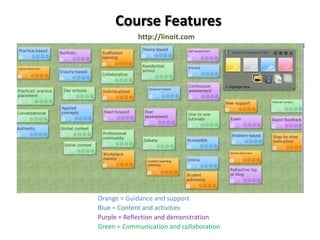
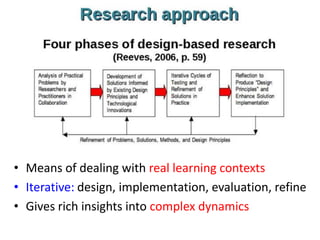
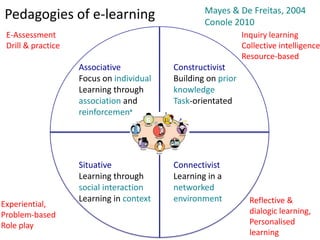
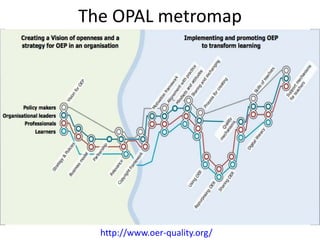
The document outlines Gráinne Conole's presentation on design thinking, learning design, and creativity. It discusses technological trends in learning like mobile learning, games-based learning, and the Internet of things. It then covers learning design frameworks like the 7Cs model and socio-cultural perspectives on design. Finally, it discusses approaches like design-based research and e-pedagogies that integrate technology and pedagogy for learning.