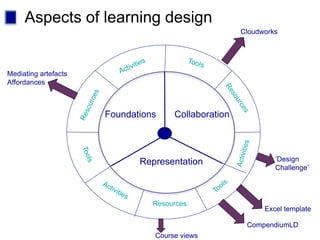
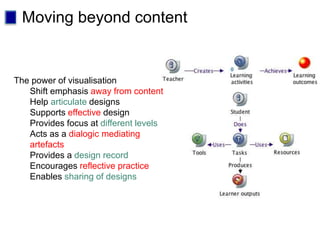
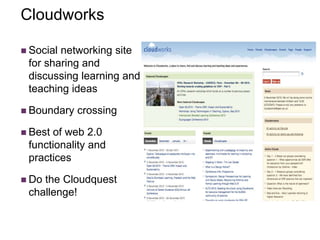
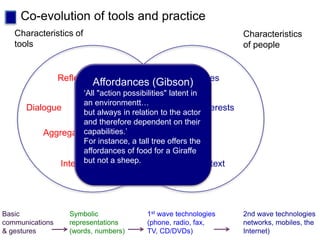
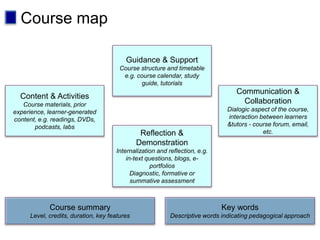
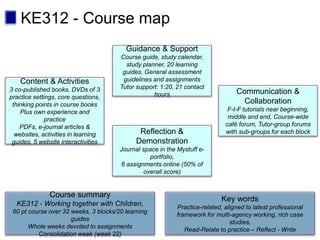
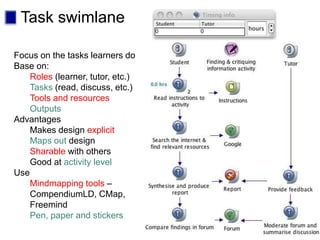
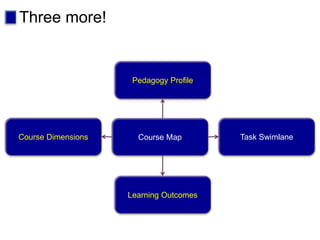
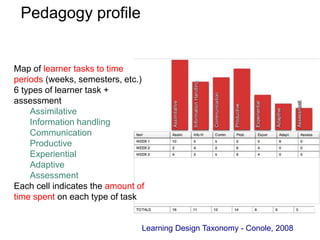
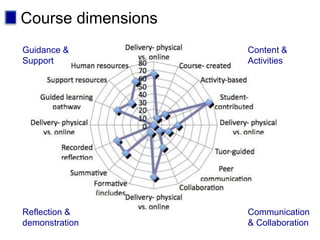
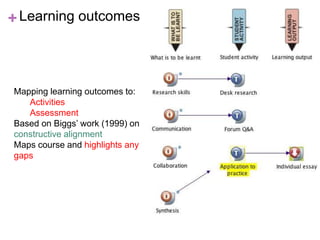
This document discusses new approaches to learning design and visualization. It emphasizes shifting from implicit to explicit and design-based approaches. Various tools are presented for visualizing course design, including course maps, pedagogy profiles, learning activities diagrams, and learning outcome maps. These tools make the design explicit, enable sharing of designs, and encourage reflective practice. Workshops and Cloudworks are presented as ways to collaborate and discuss designs.