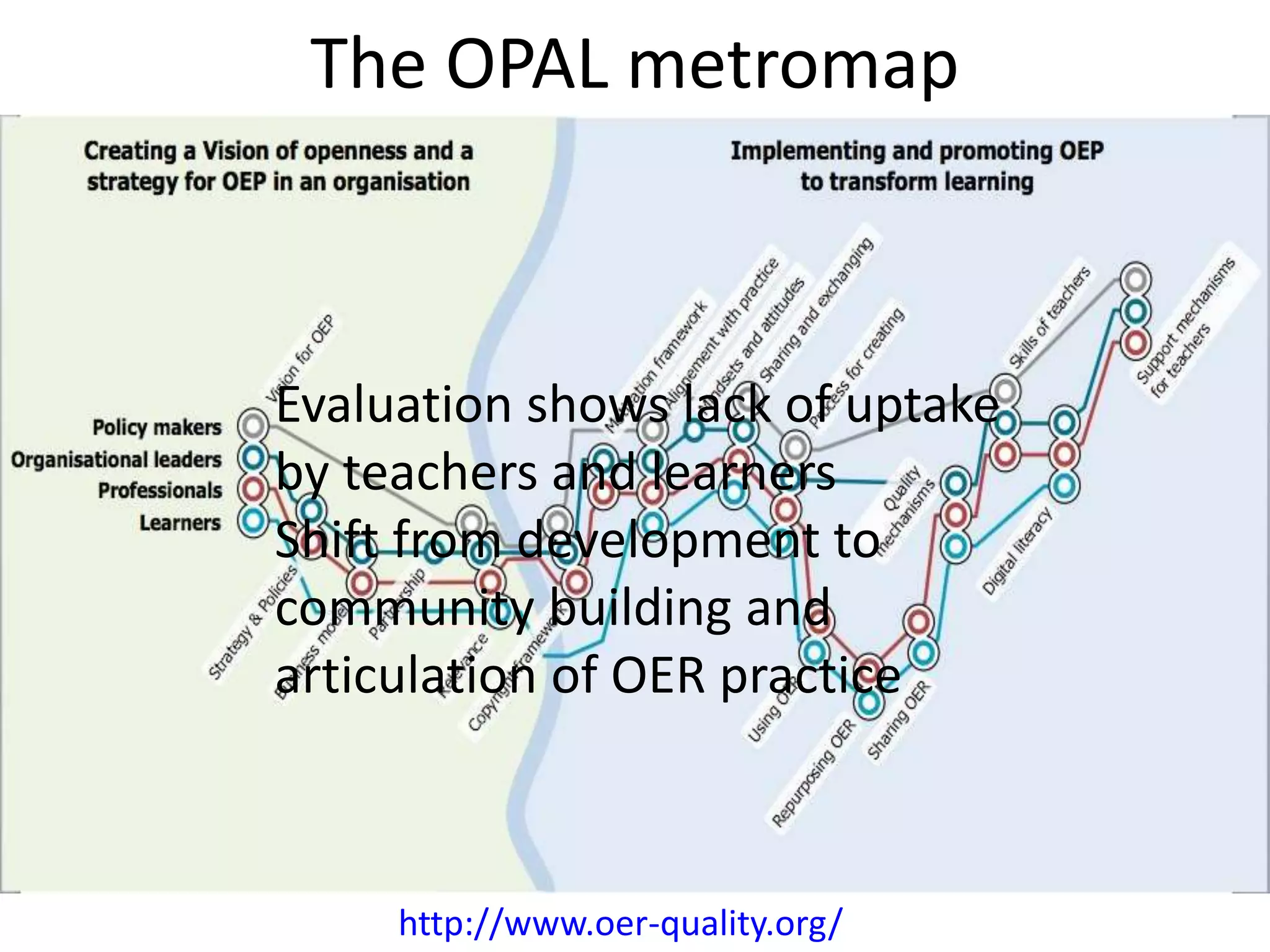
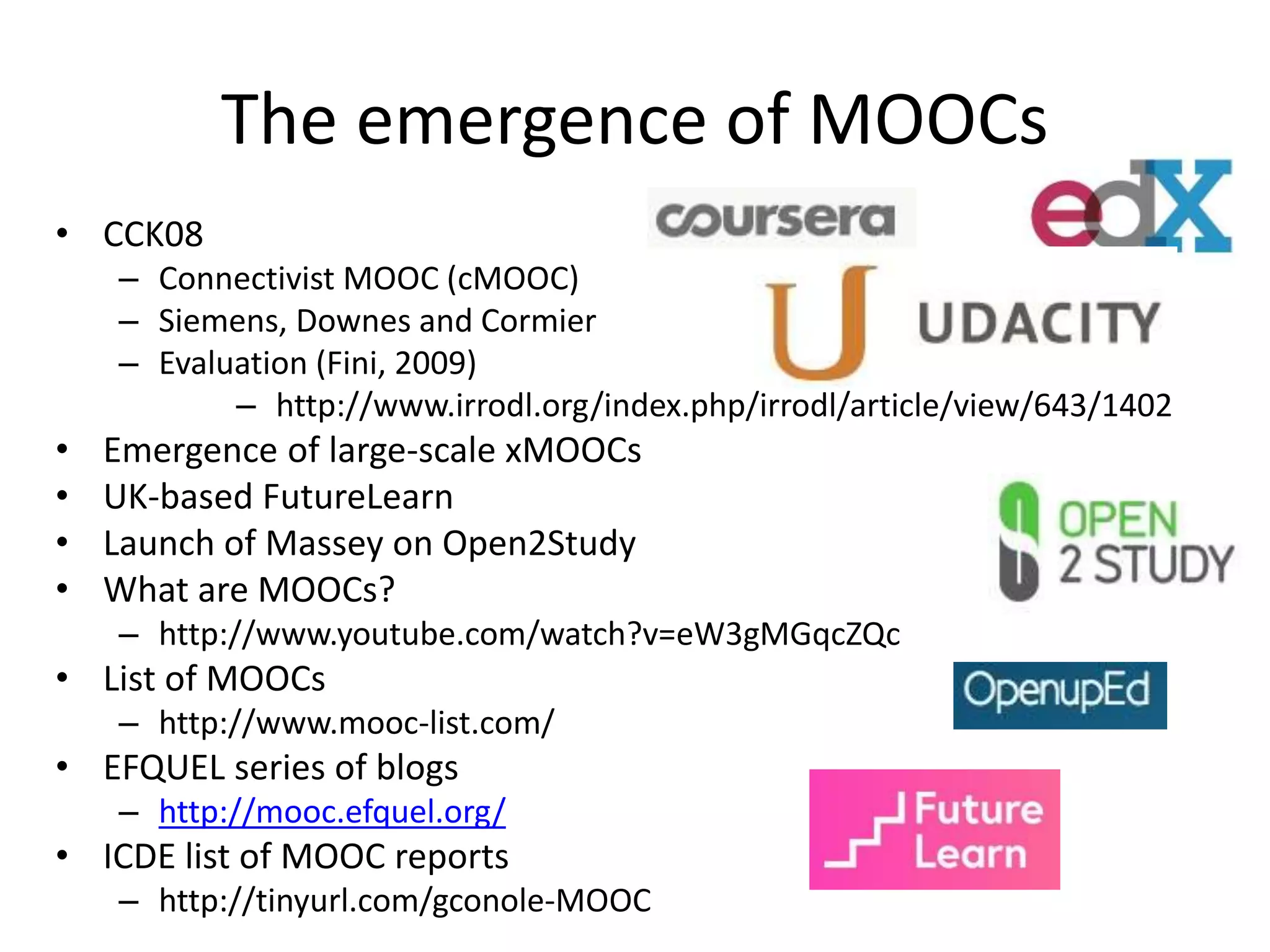
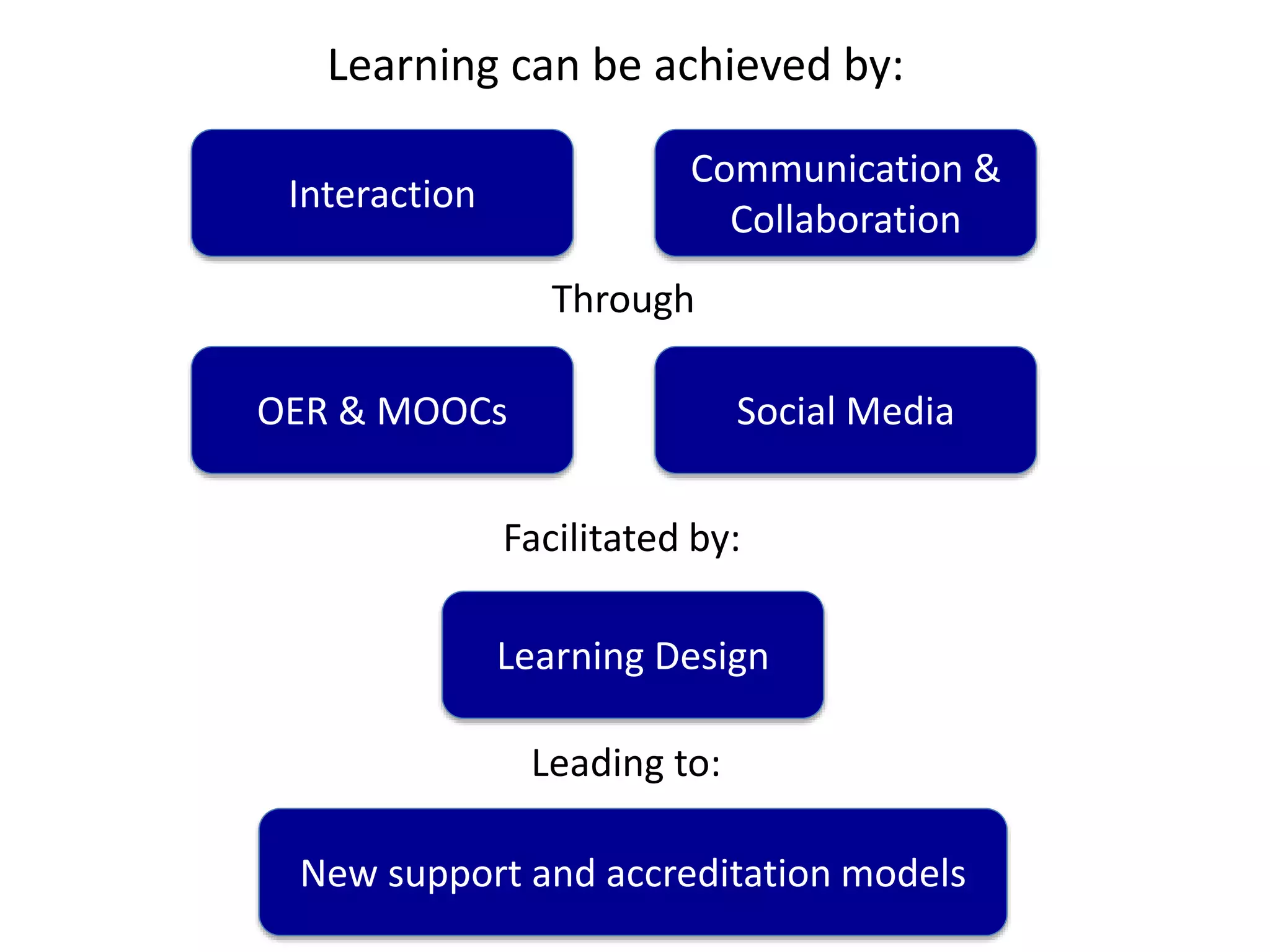
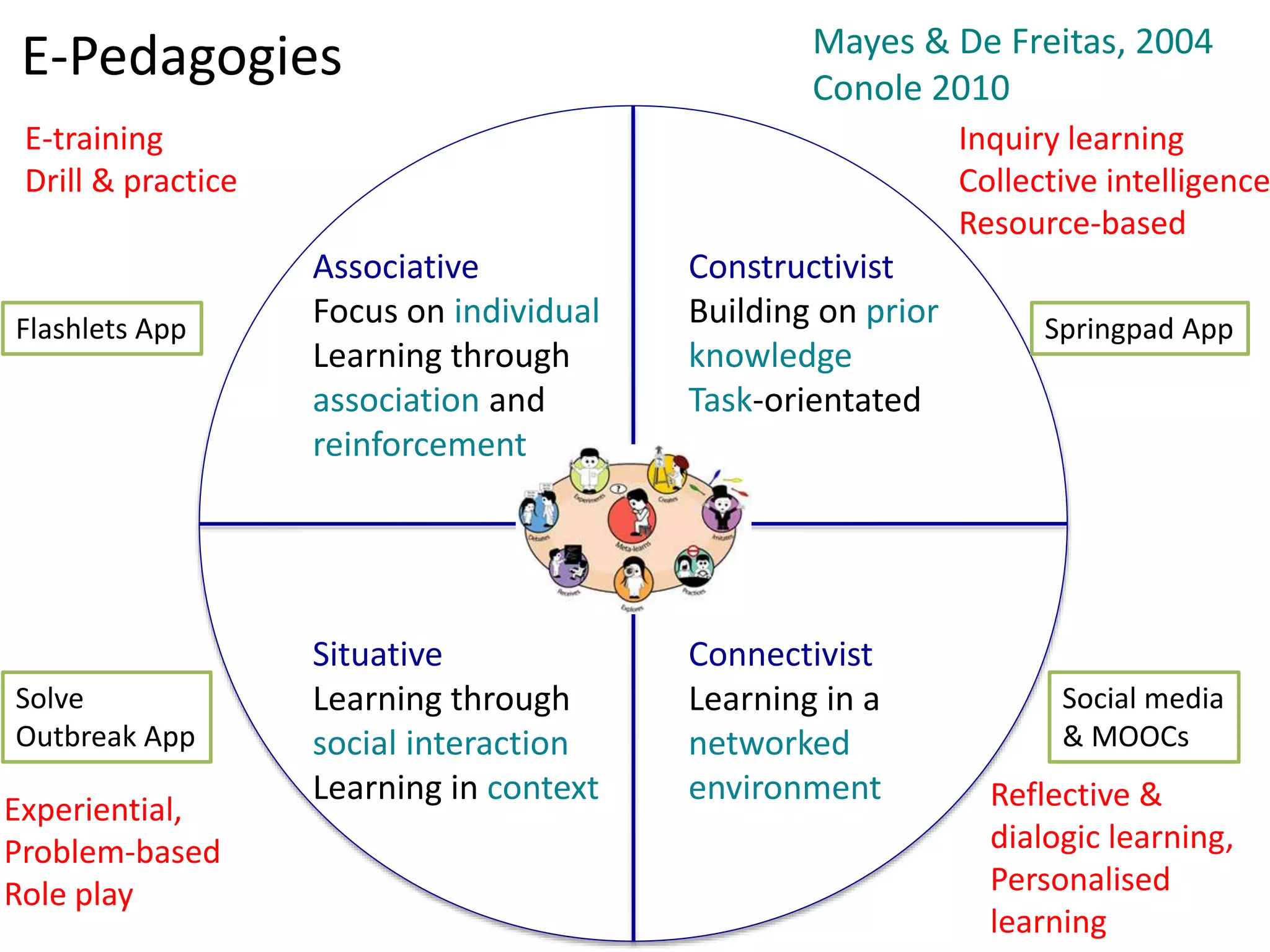
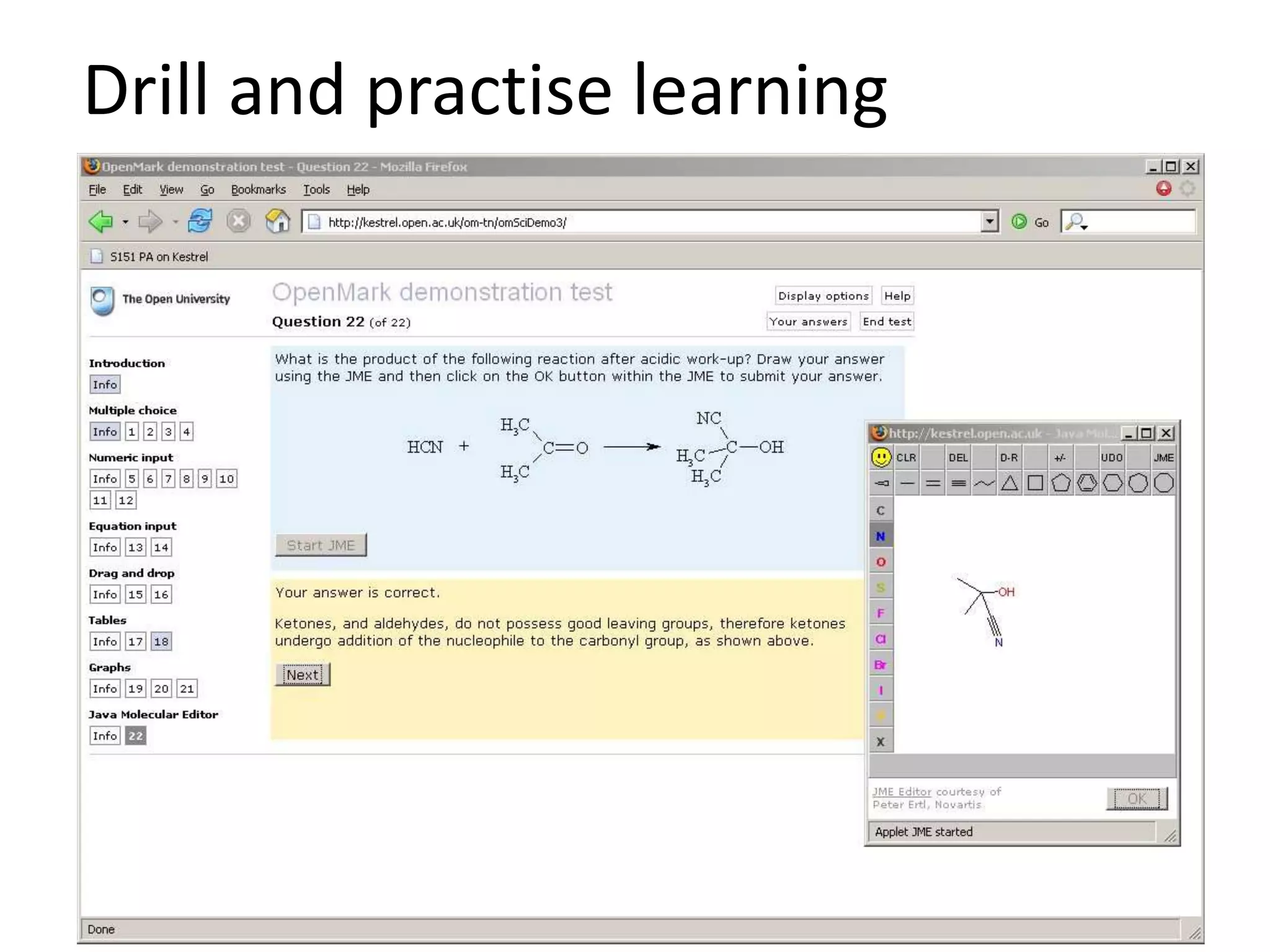
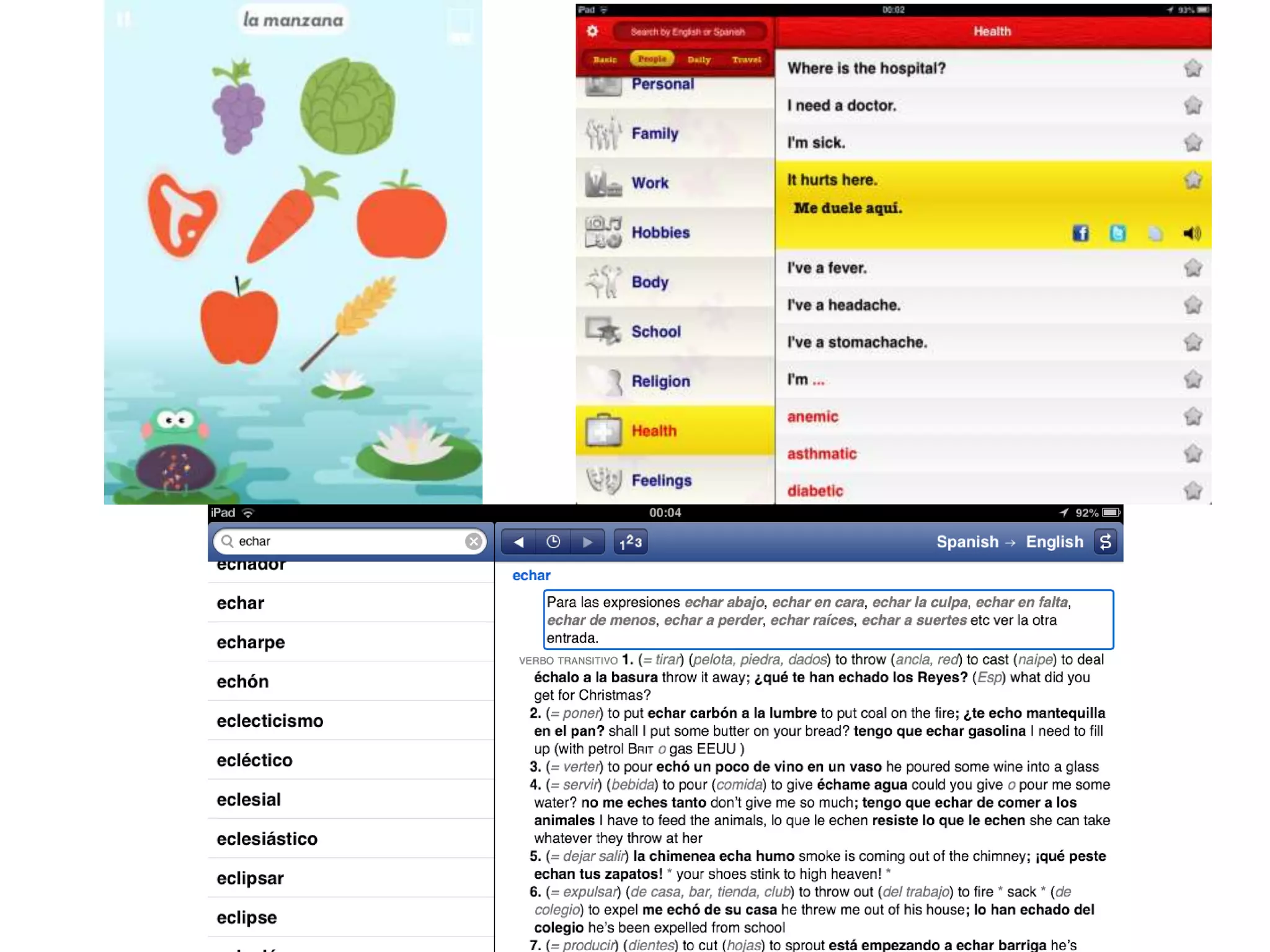
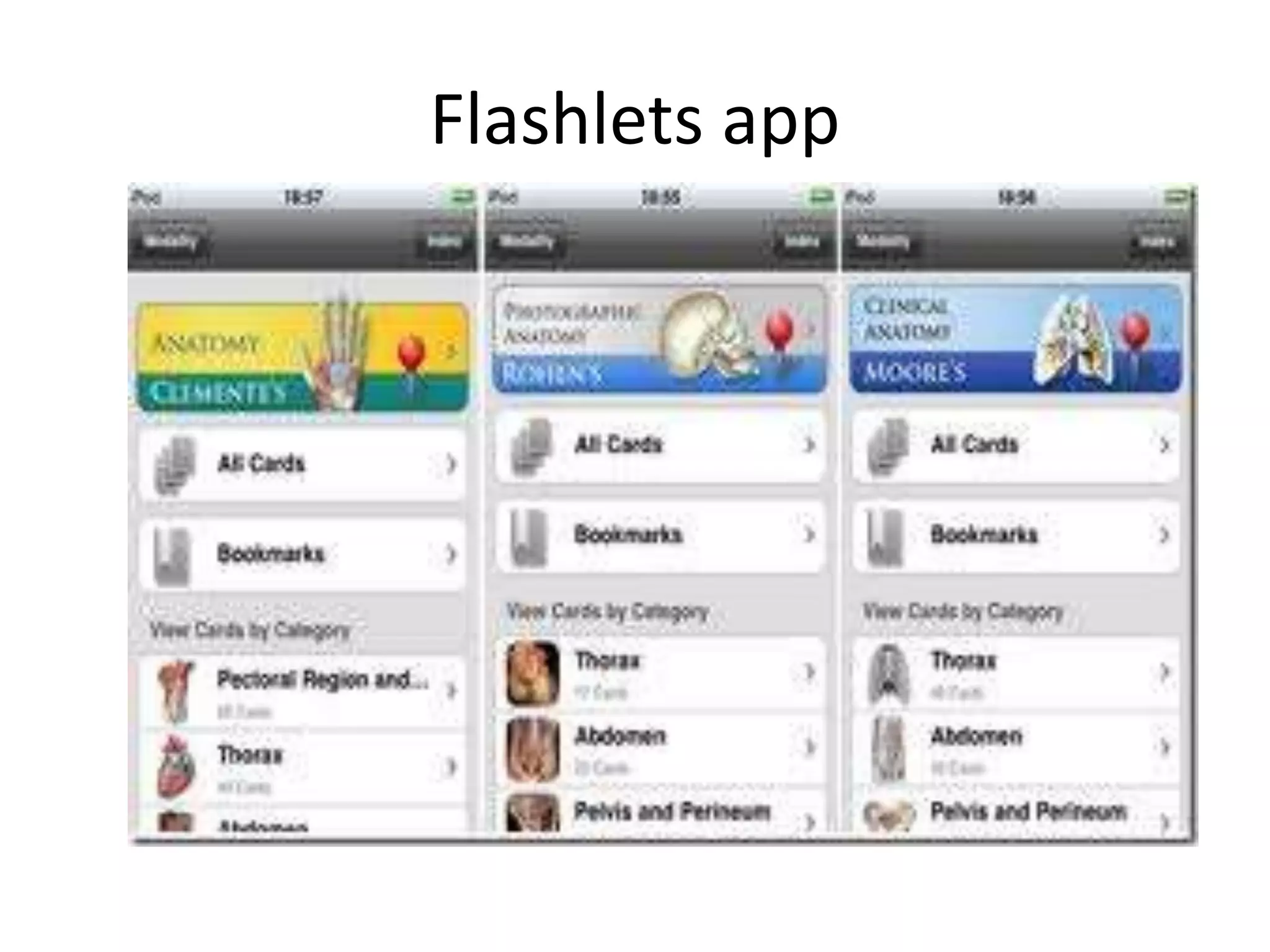
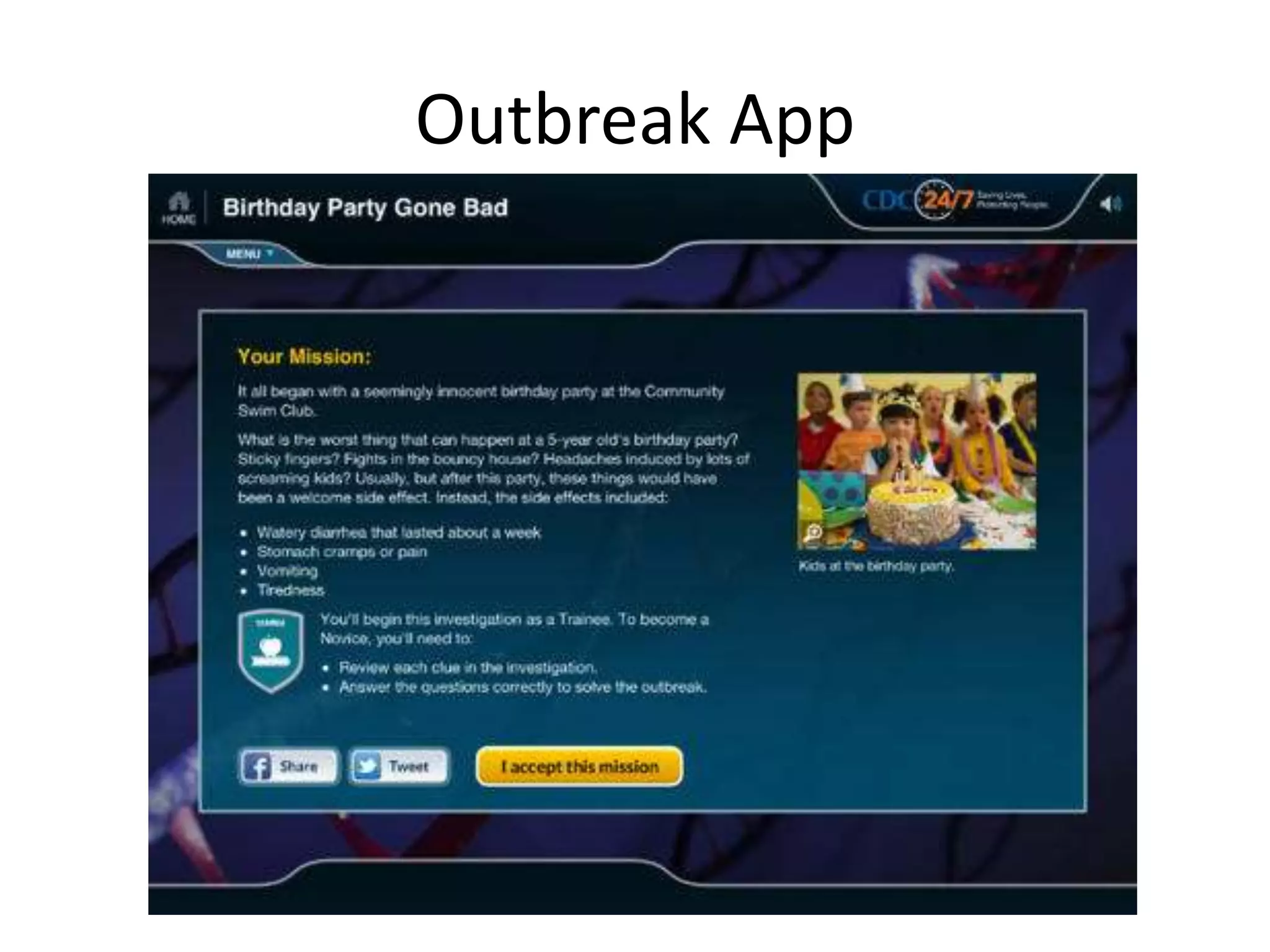
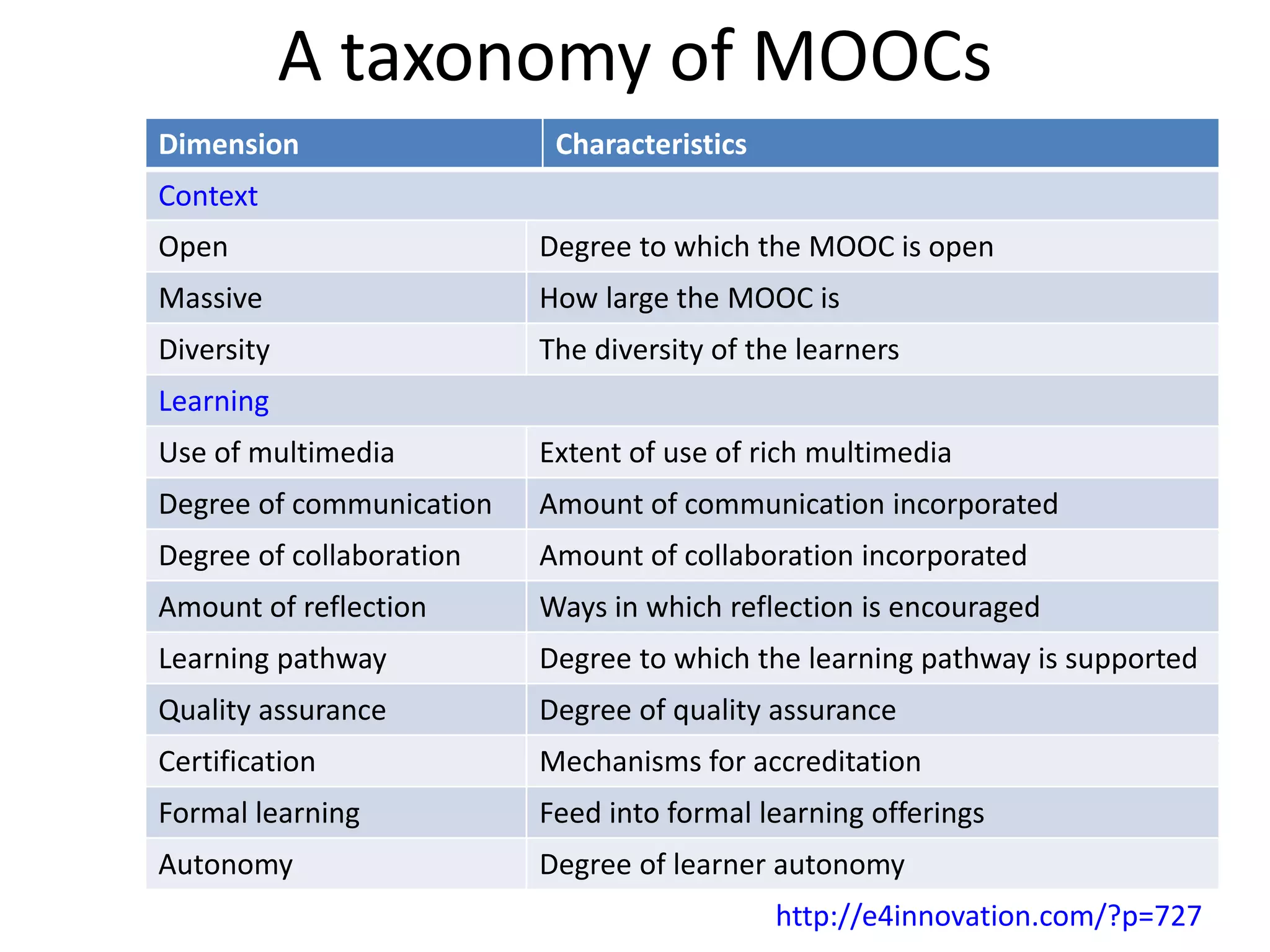
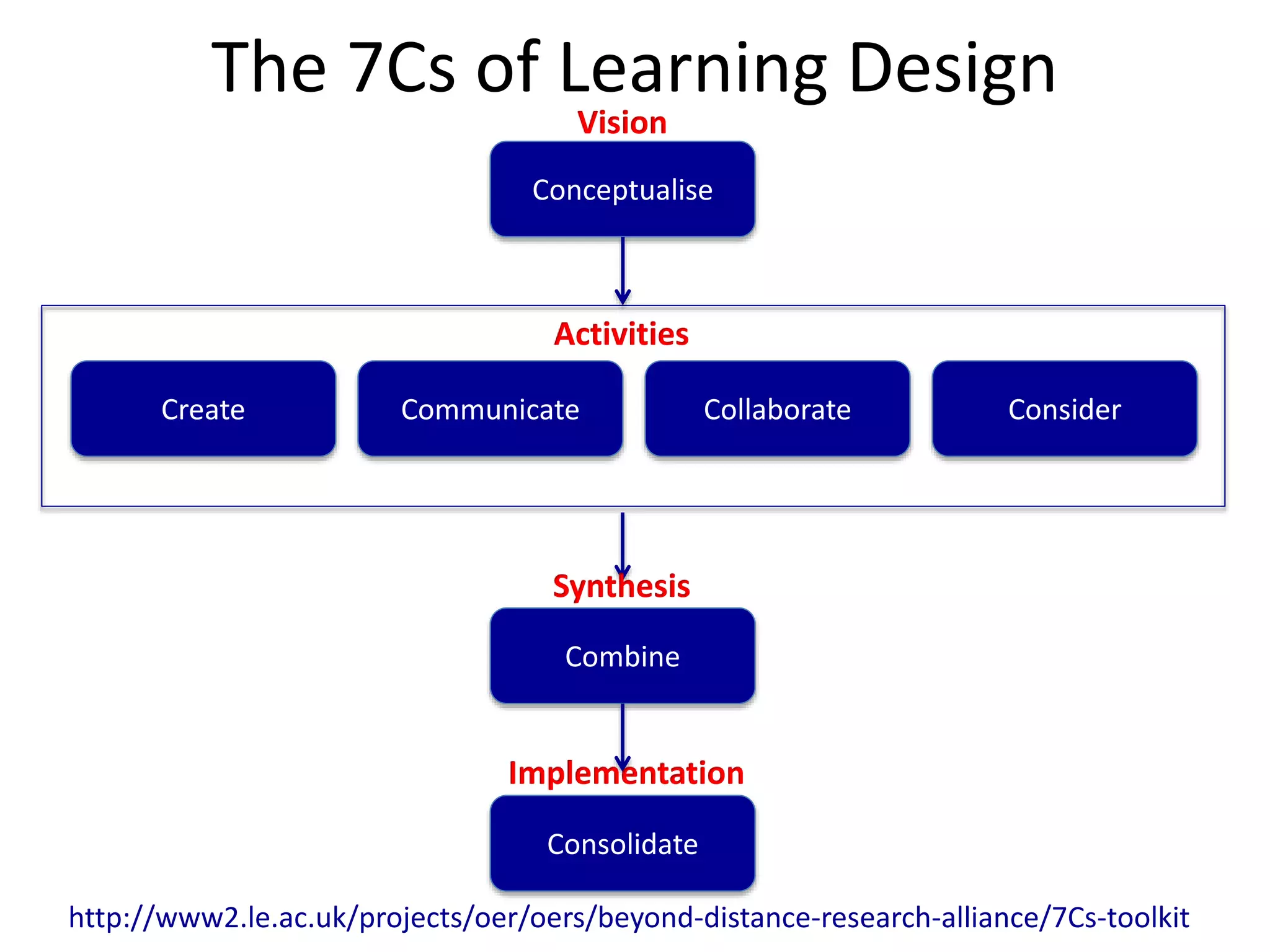
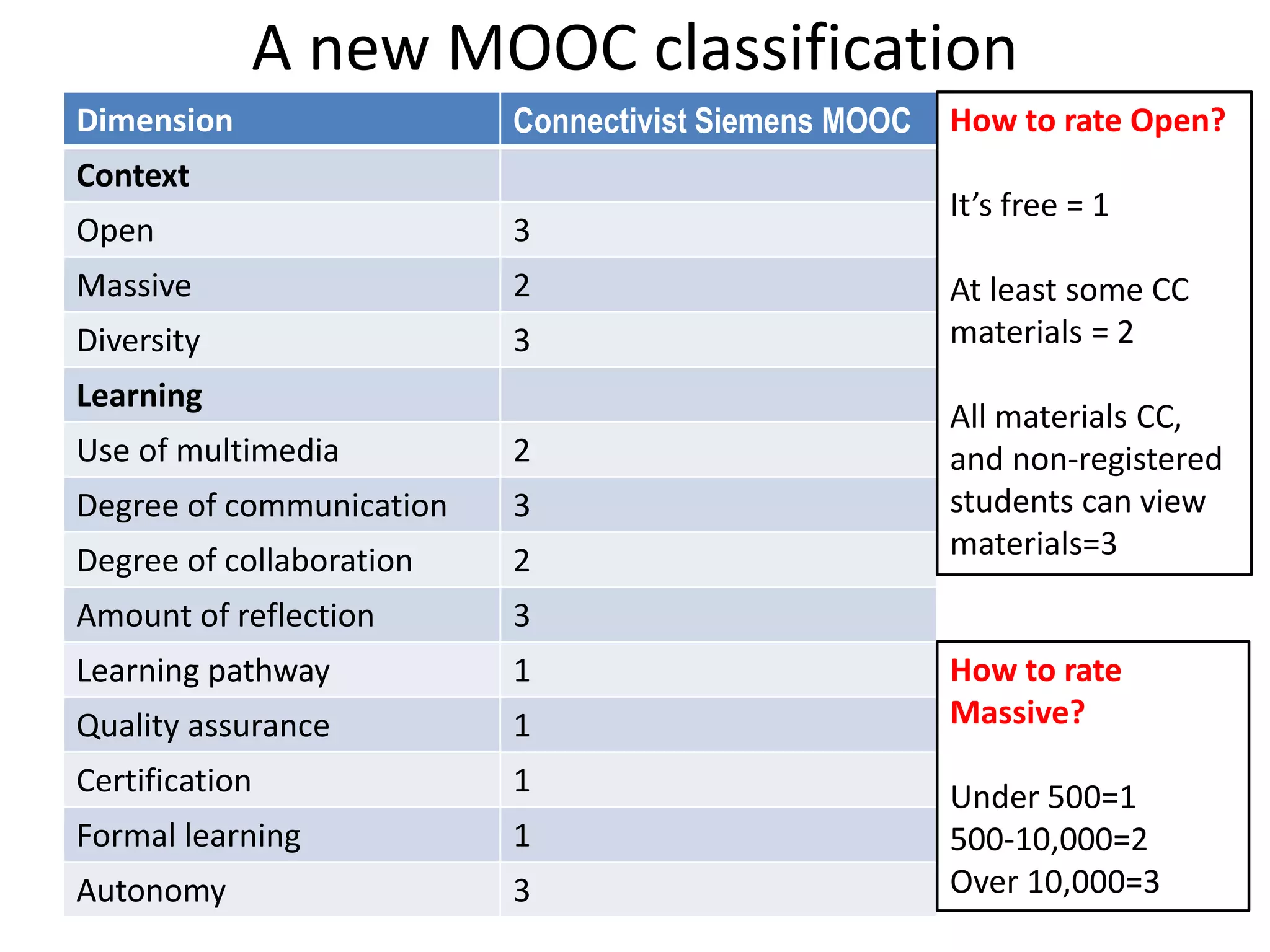
The document discusses the pedagogy and classification of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), outlining their evolution, the role of Open Educational Resources (OER), and the challenges associated with high dropout rates and low teacher engagement. It details various pedagogical approaches, characteristics of different MOOC types, and the impact of social media on learning experiences. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for innovative teaching strategies and business models to adapt to the disruptive nature of MOOCs within traditional education systems.