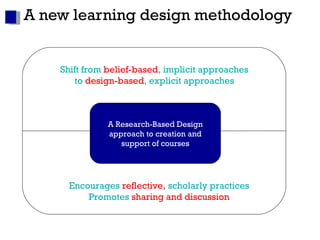
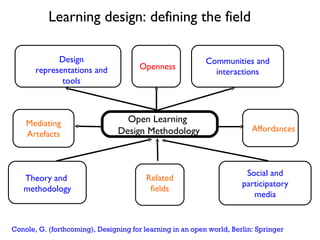
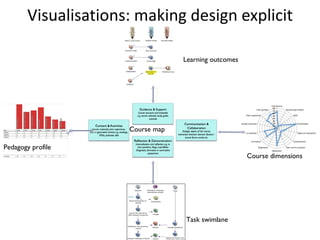
The document discusses learning design as a field of research and practice. It defines learning design as a methodology for making the learning design process more explicit and shareable. It outlines how learning design encourages reflective practices, promotes sharing of designs, and shifts approaches from implicit to explicit. Visual tools and collaboration allow designers to represent and discuss their learning designs.
![Designing for learning: The state of the art in learning design Gráinne Conole University of Leicester, [email_address] Learning Design Seminar, Online Educa, 1/12/11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conoleldseminar-111130075655-phpapp01/85/Conole-ld-seminar-1-320.jpg)













![Conole, G. (forthcoming), Designing for learning in an open world, Berlin: Springer Chapters on dropbox: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conoleldseminar-111130075655-phpapp01/85/Conole-ld-seminar-21-320.jpg)