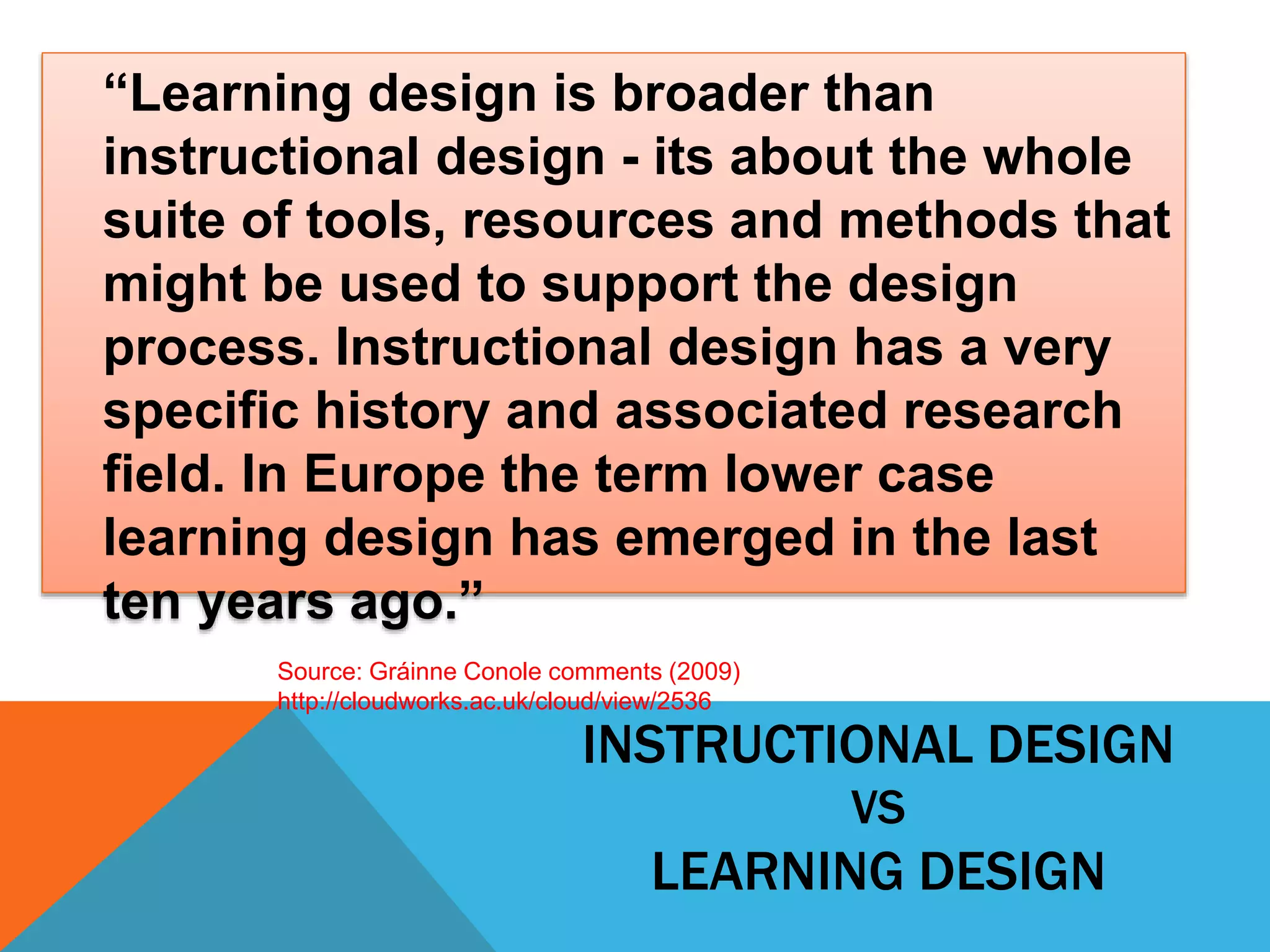
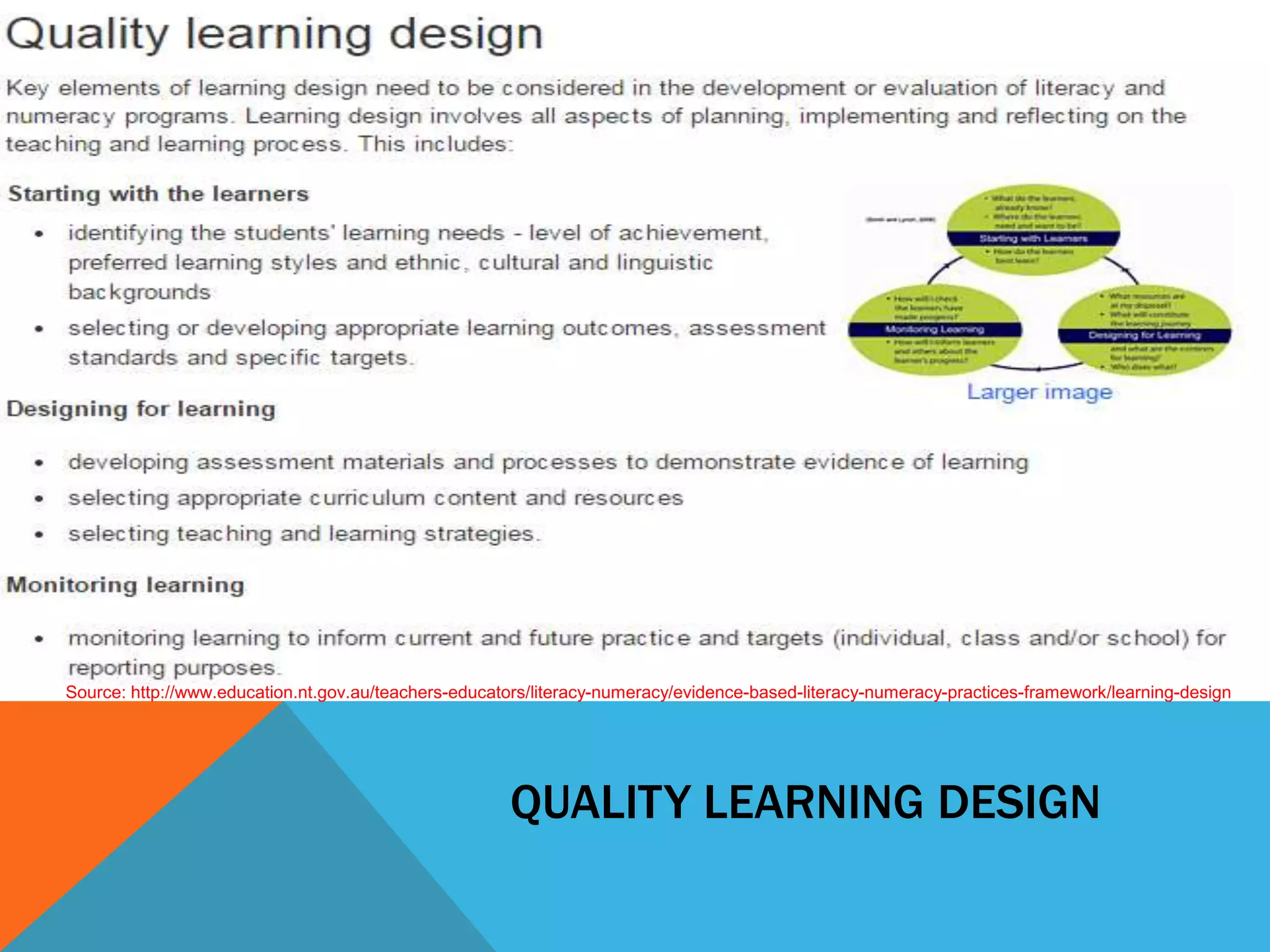
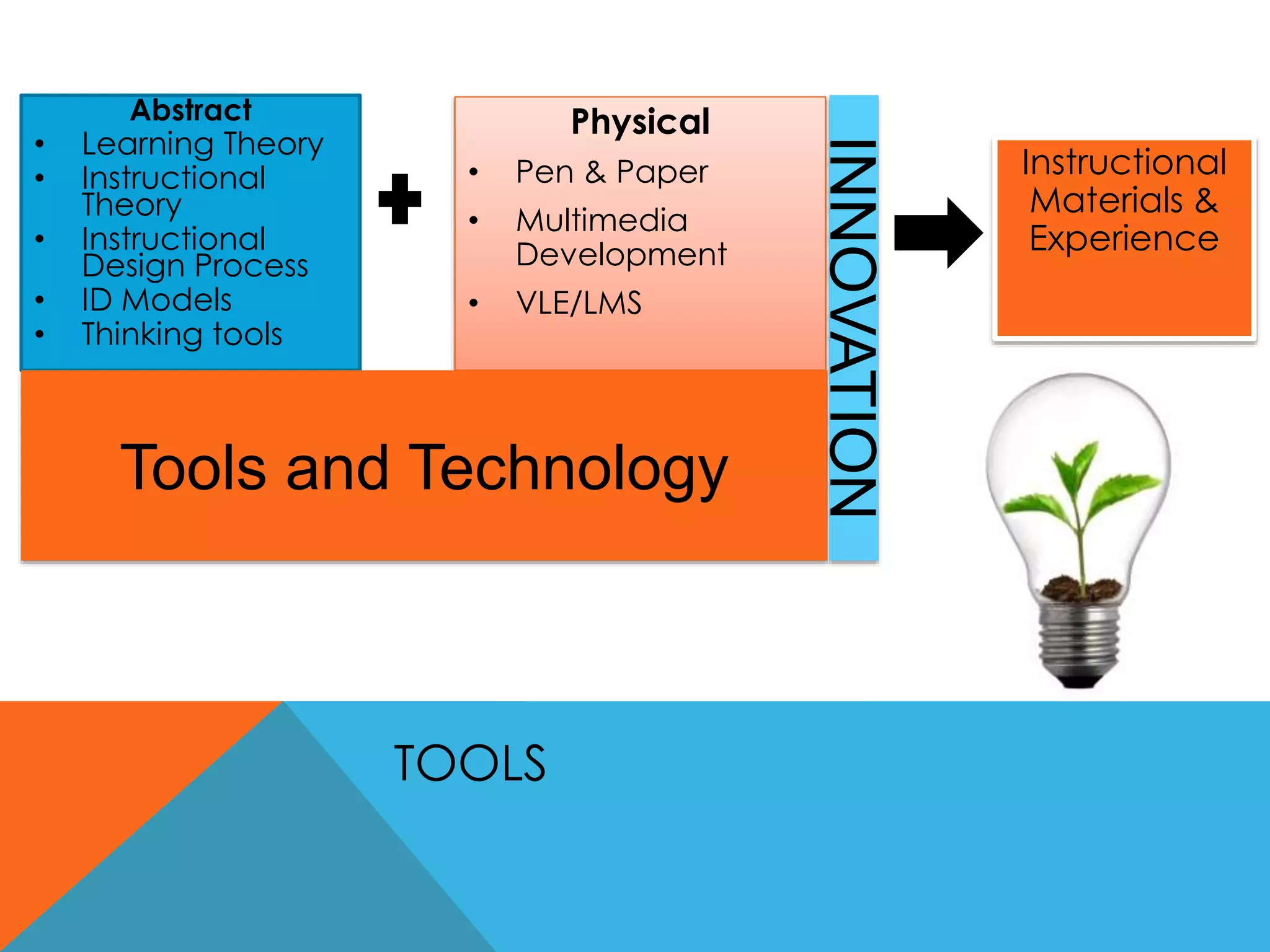
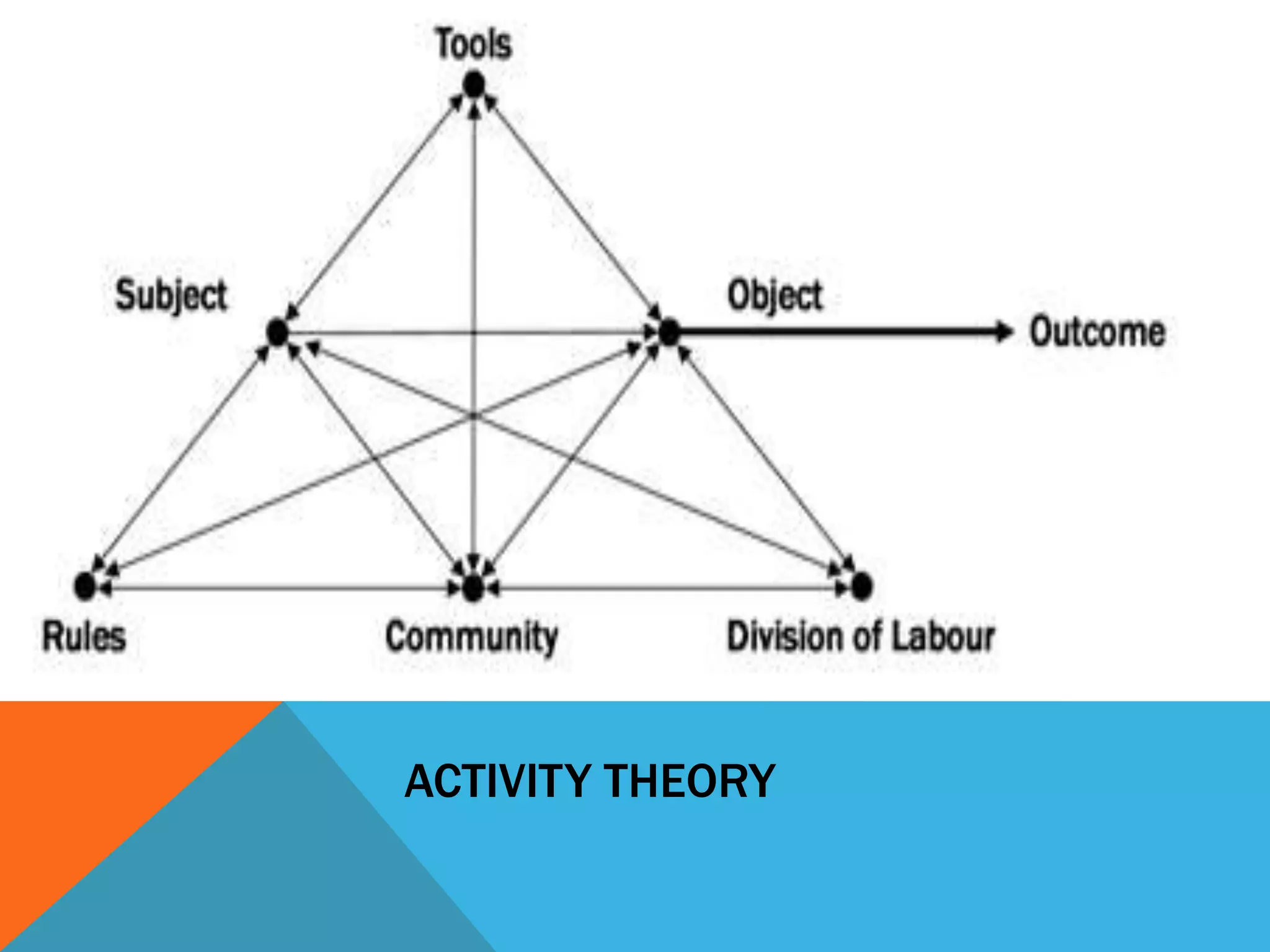
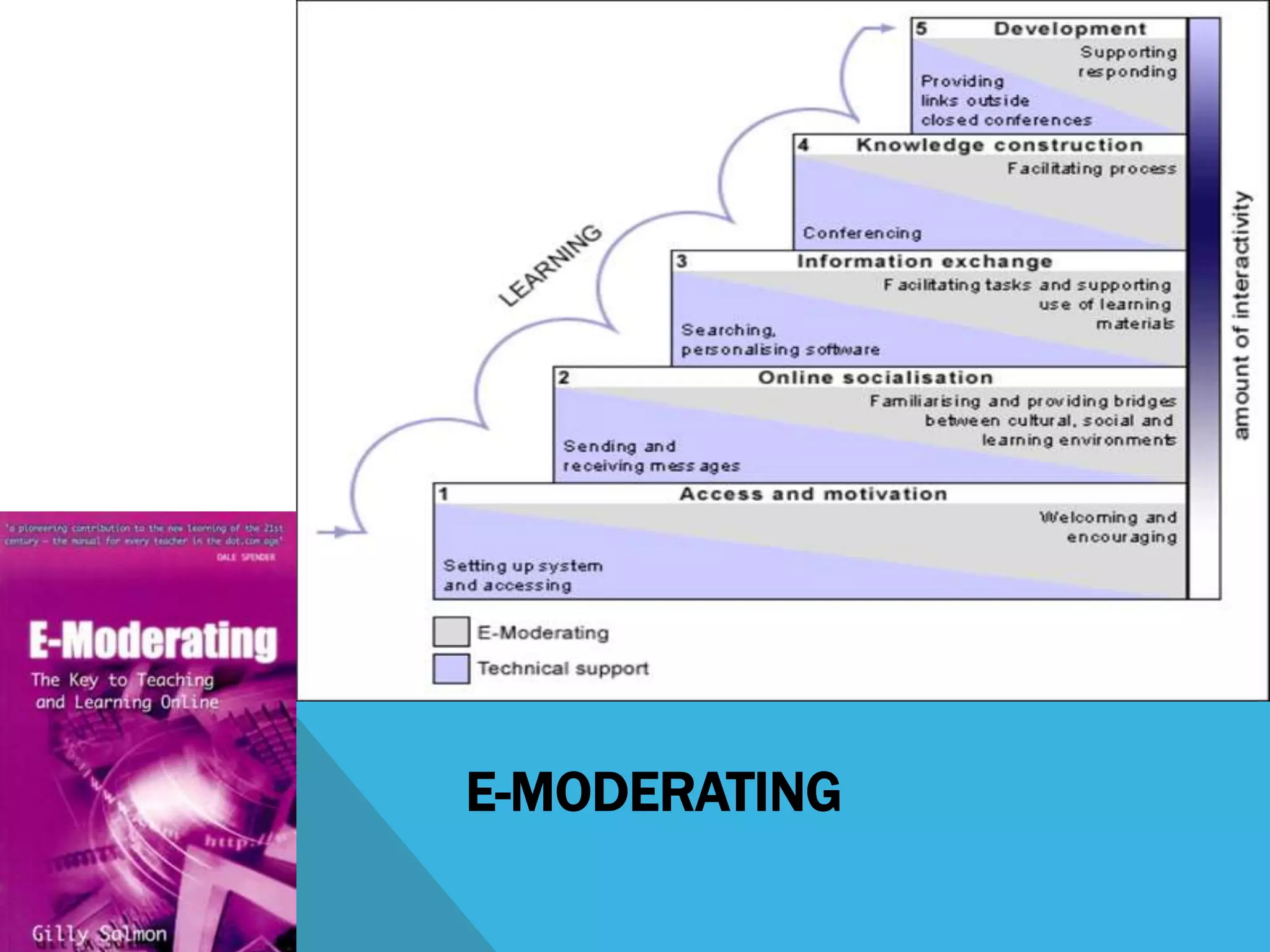
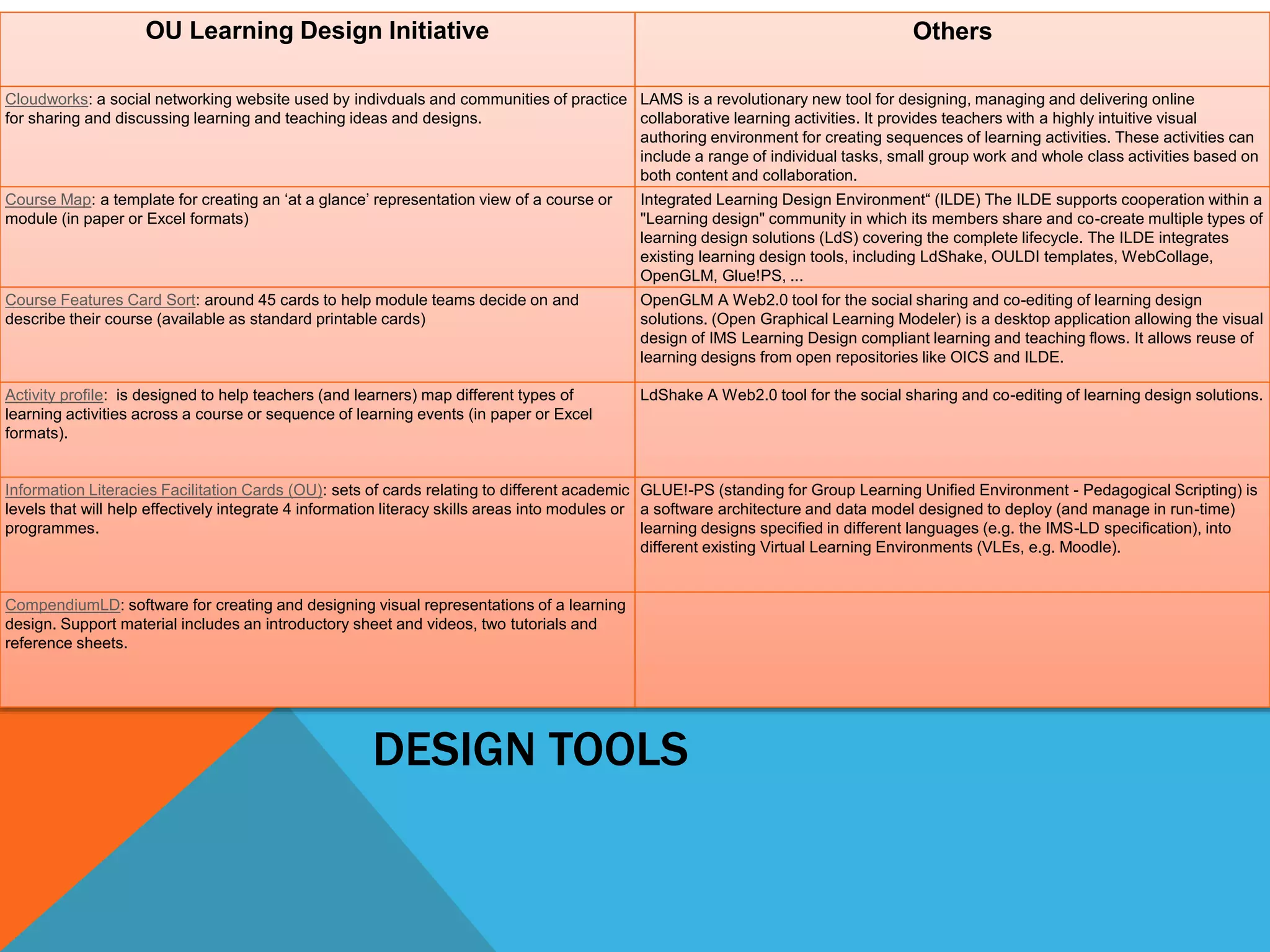
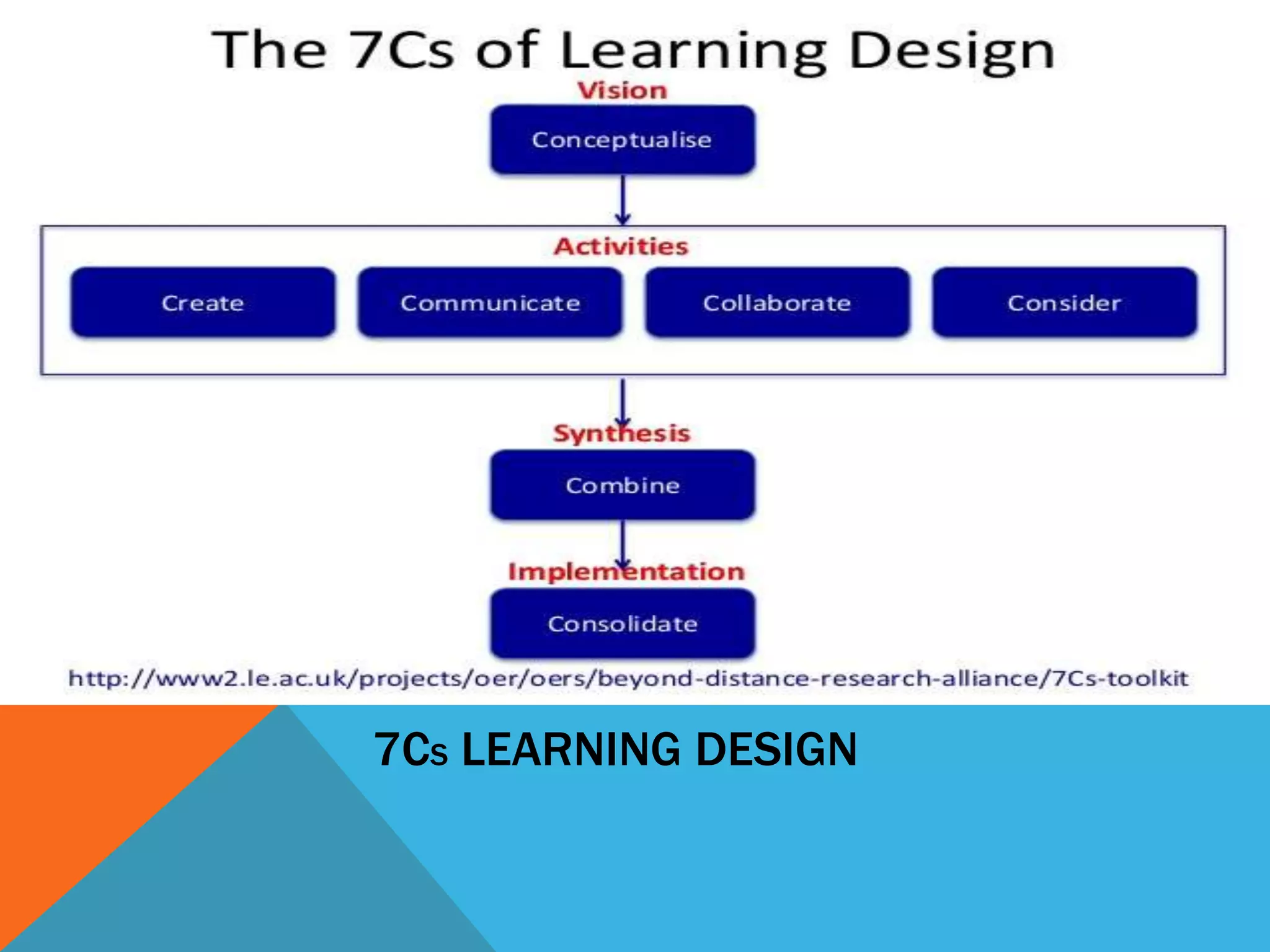
This document discusses learning design and instructional design. It provides definitions of learning design from various sources, which emphasize the planning and structuring of learning experiences and activities. The document also discusses elements of learning design like objectives, environment, and assessment. It compares learning design and instructional design, and presents different models and tools that can be used for design, including ADDIE, Merrill's principles, and Bloom's taxonomy. Finally, it addresses some common myths around design and the roles of facilitators.