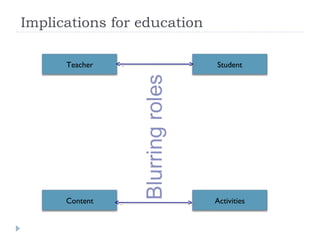
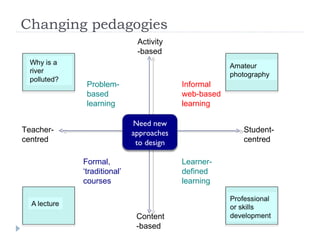
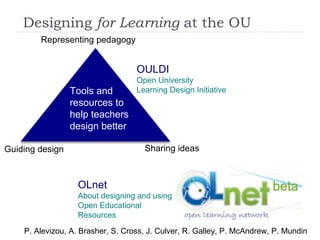
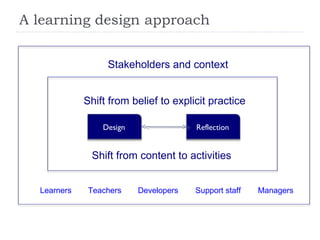
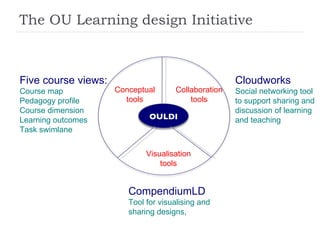
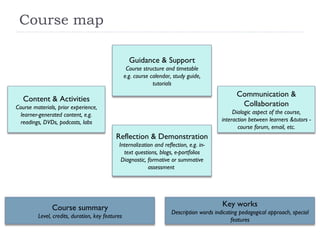
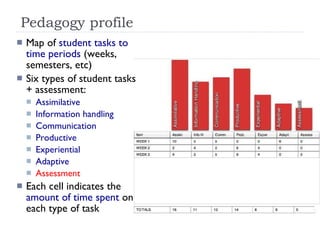
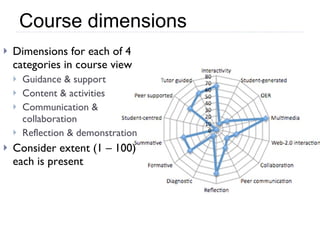
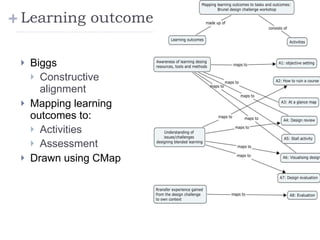
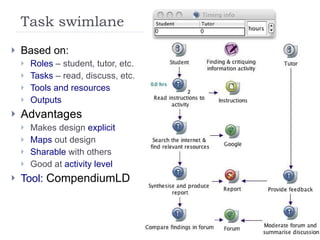
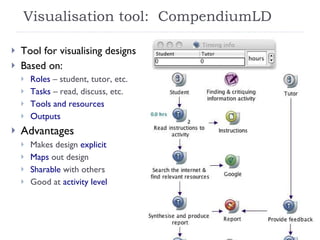
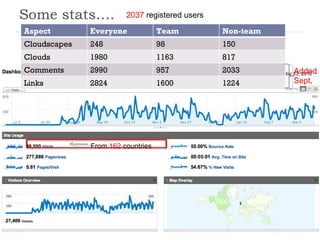
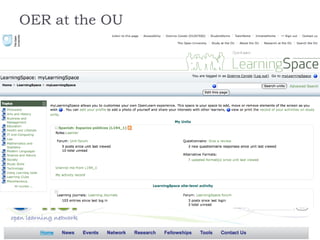
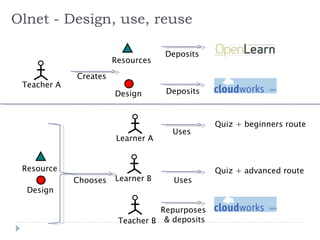
The document summarizes a presentation about innovations in learning and teaching given by Gráinne Conole at the International Arab Conference of e-technology in Kuwait. The presentation discusses how new technologies and the changing nature of learners requires new approaches to designing education. It provides an overview of tools like Web 2.0, open educational resources, and learning design initiatives at the Open University UK to design more interactive, collaborative and personalized learning experiences that develop important digital literacy skills.