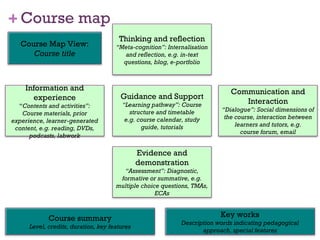
Gráinne Conole presented a holistic, student-centered approach to learning design using new technologies. She discussed how technologies are changing the learning landscape and learner expectations. Conole proposed learning design as a conceptual framework and tools like CompendiumLD and Cloudworks to help educators design for learning and share ideas. Her vision emphasizes flexible, experiential learning that blurs boundaries between formal and informal learning through open educational resources and new digital spaces.