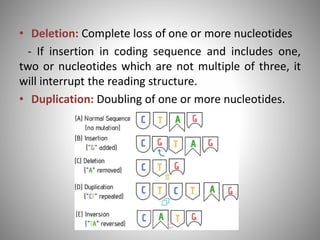
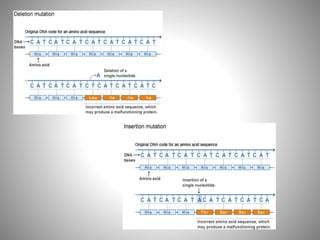
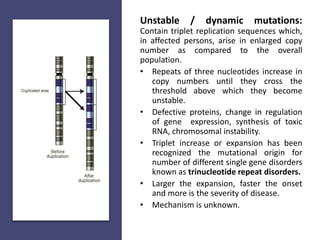
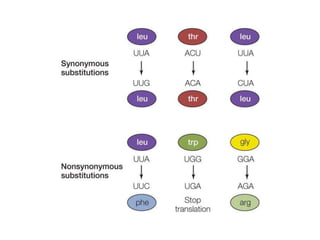
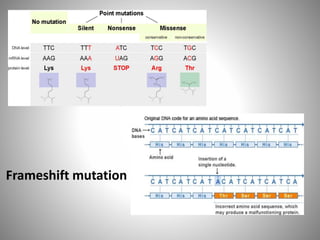
The document discusses the nature and types of mutations, highlighting their occurrence in somatic and germline cells and the potential for hereditary transmission. It categorizes mutations based on transmission stability, molecular alterations, effects on encoded proteins, and functional impacts, such as loss or gain of function. Examples of mutations include substitutions, insertions, deletions, and the implications of dynamic mutations related to genetic disorders.