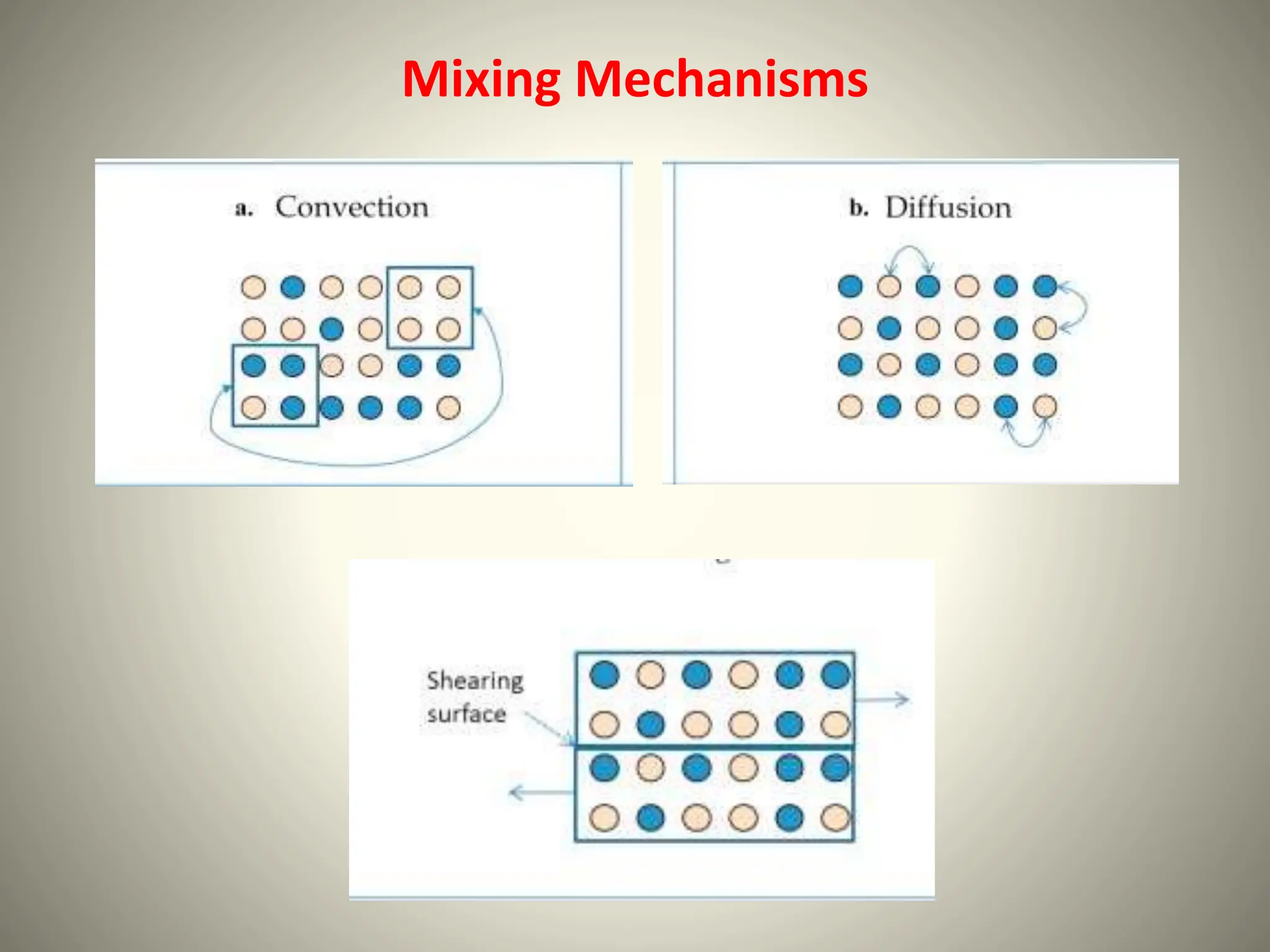
This document discusses the mixing processes of liquids and solids in pharmaceuticals, detailing the differences in mechanisms, energy requirements, and factors affecting efficiency. It covers various mixing techniques, including wet and dry mixing, and the use of different types of mixers like twin shell blenders and planetary mixers. Additionally, it explains the interparticle interactions and forces involved in achieving effective mixing, along with specific applications in pharmaceutical formulations.