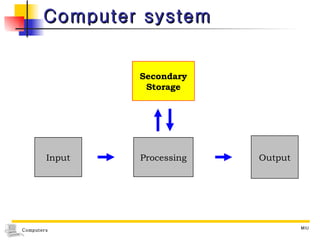
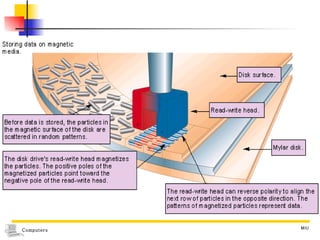
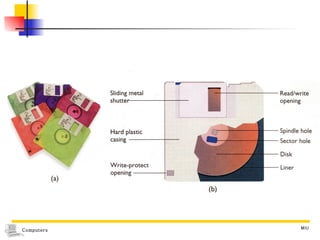
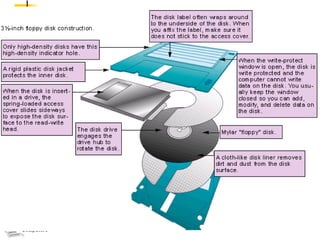
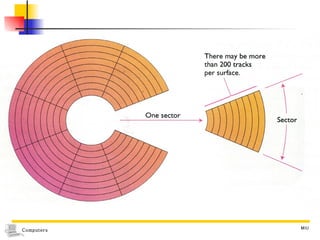
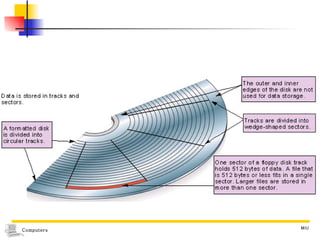
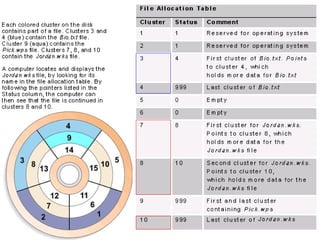
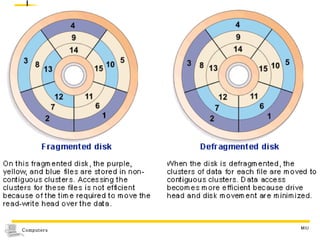
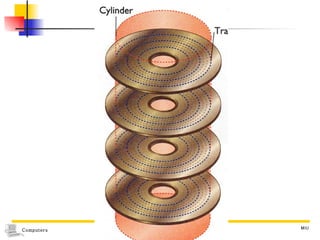
The document discusses different types of secondary storage used in computer systems, focusing on magnetic disk storage. It describes diskettes and hard disks, the basic components and technologies used. Diskettes are flexible and store 1.44 MB or less, while hard disks are rigid platters that can store hundreds of gigabytes. Hard disks assemble multiple platters and use read/write heads to access and transfer data via tracks and sectors.