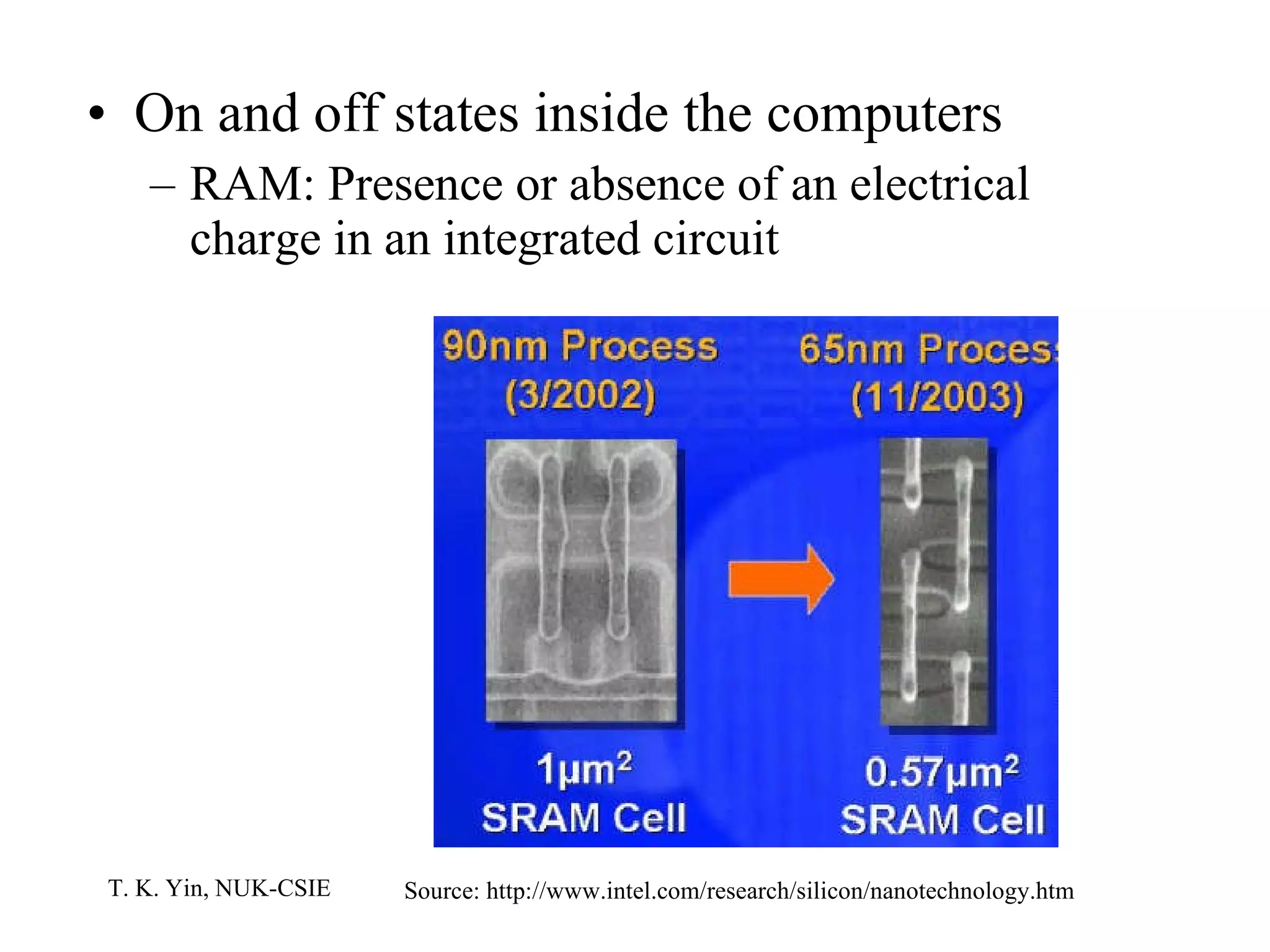
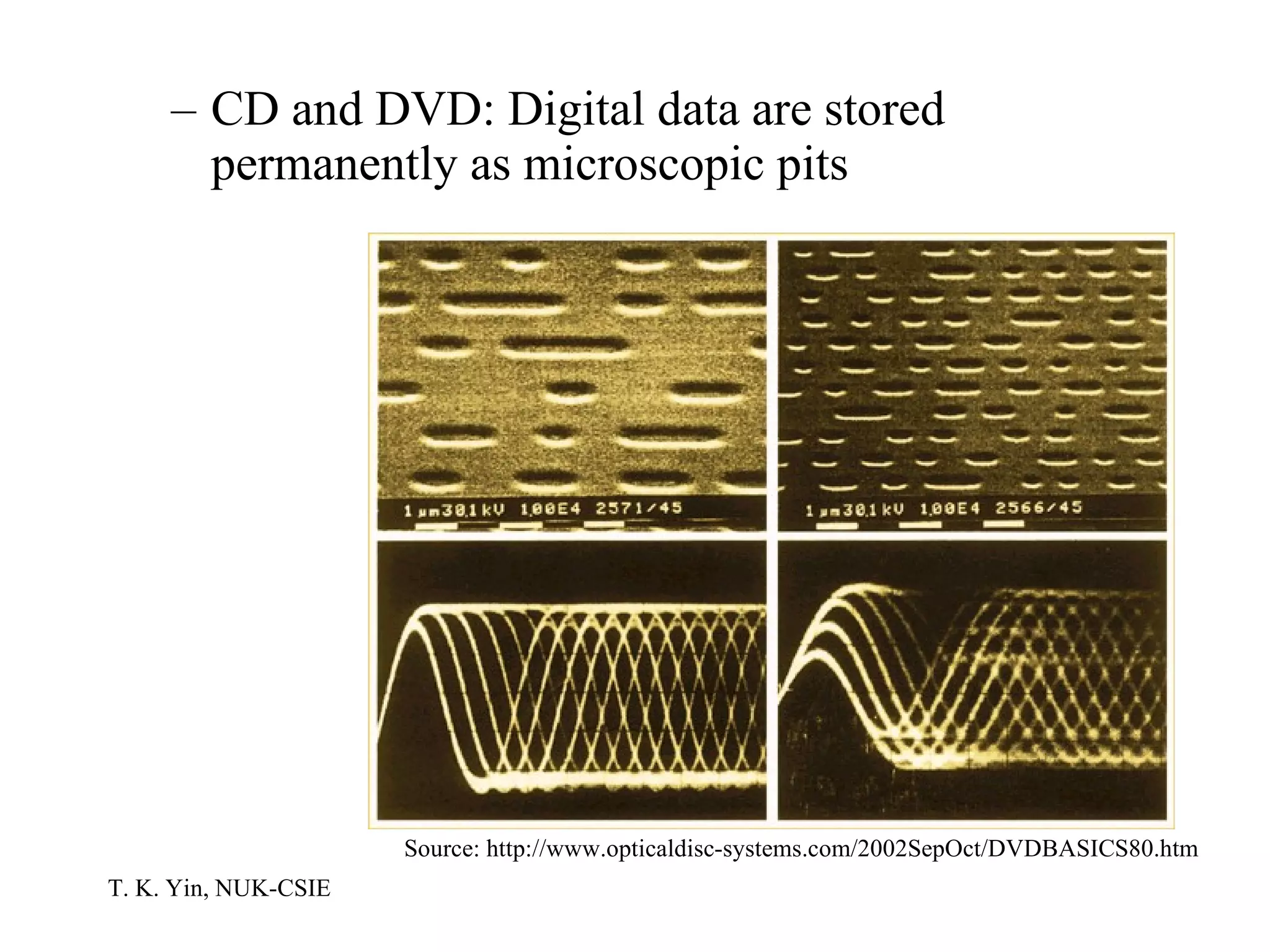
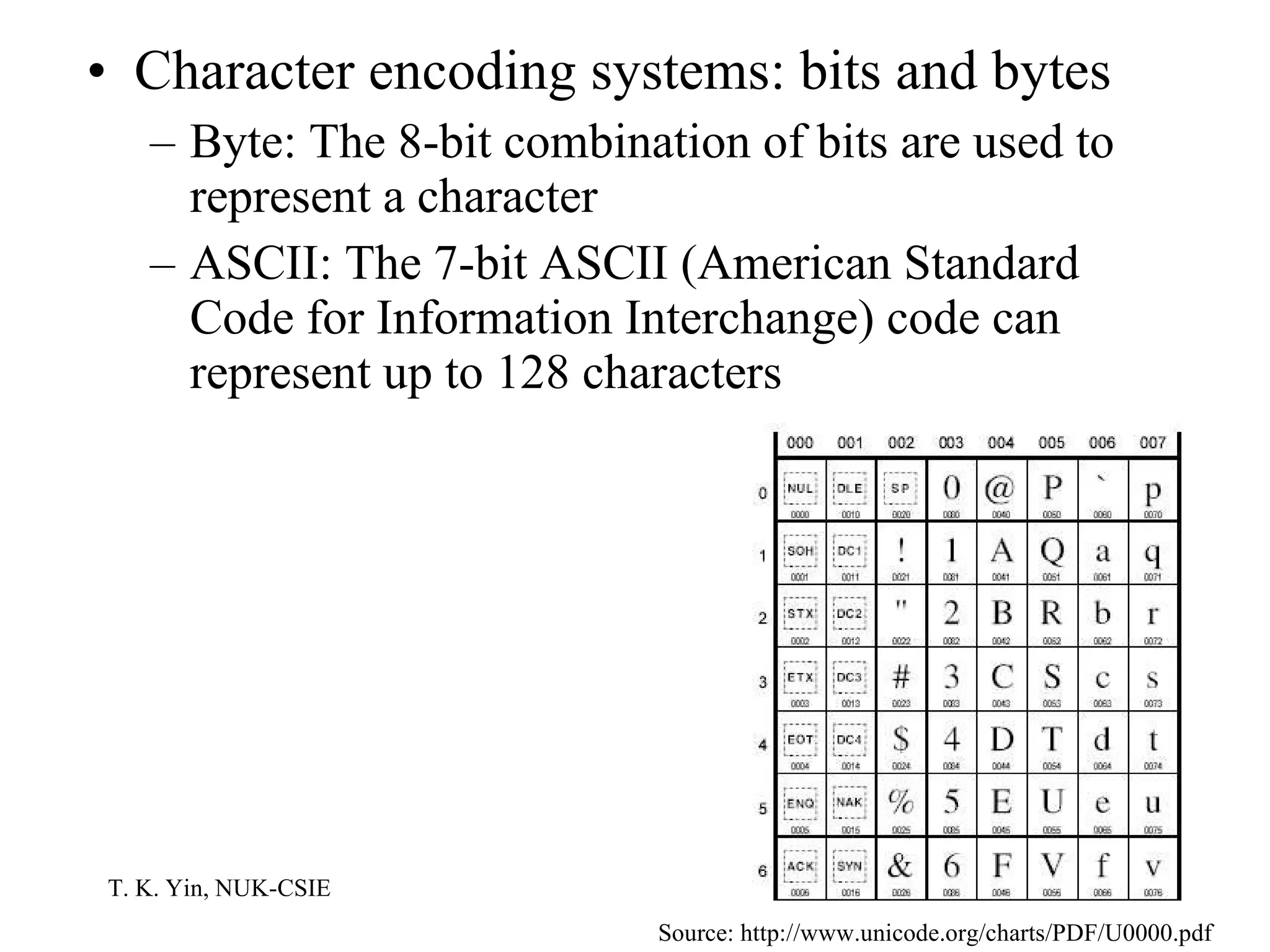
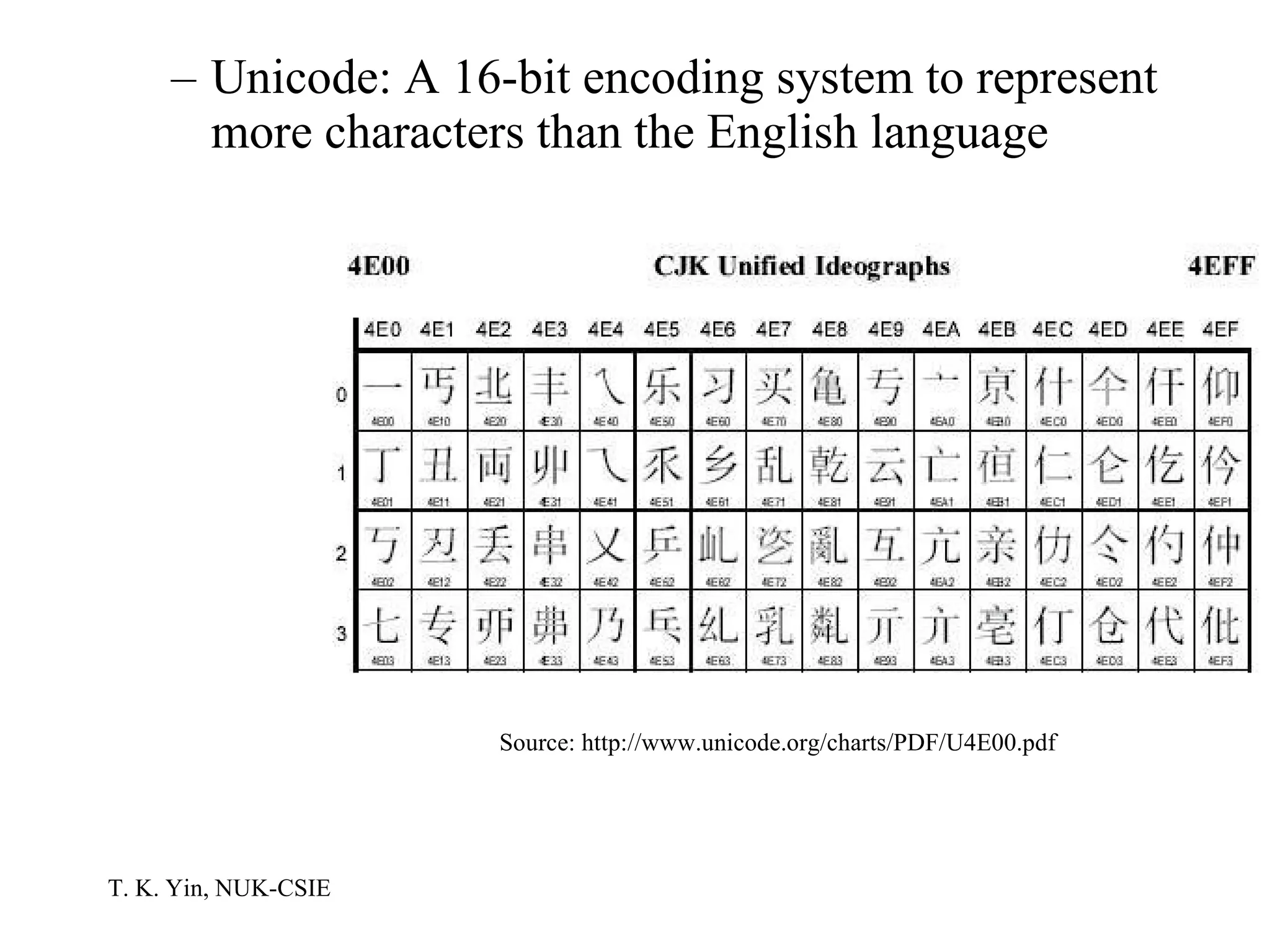
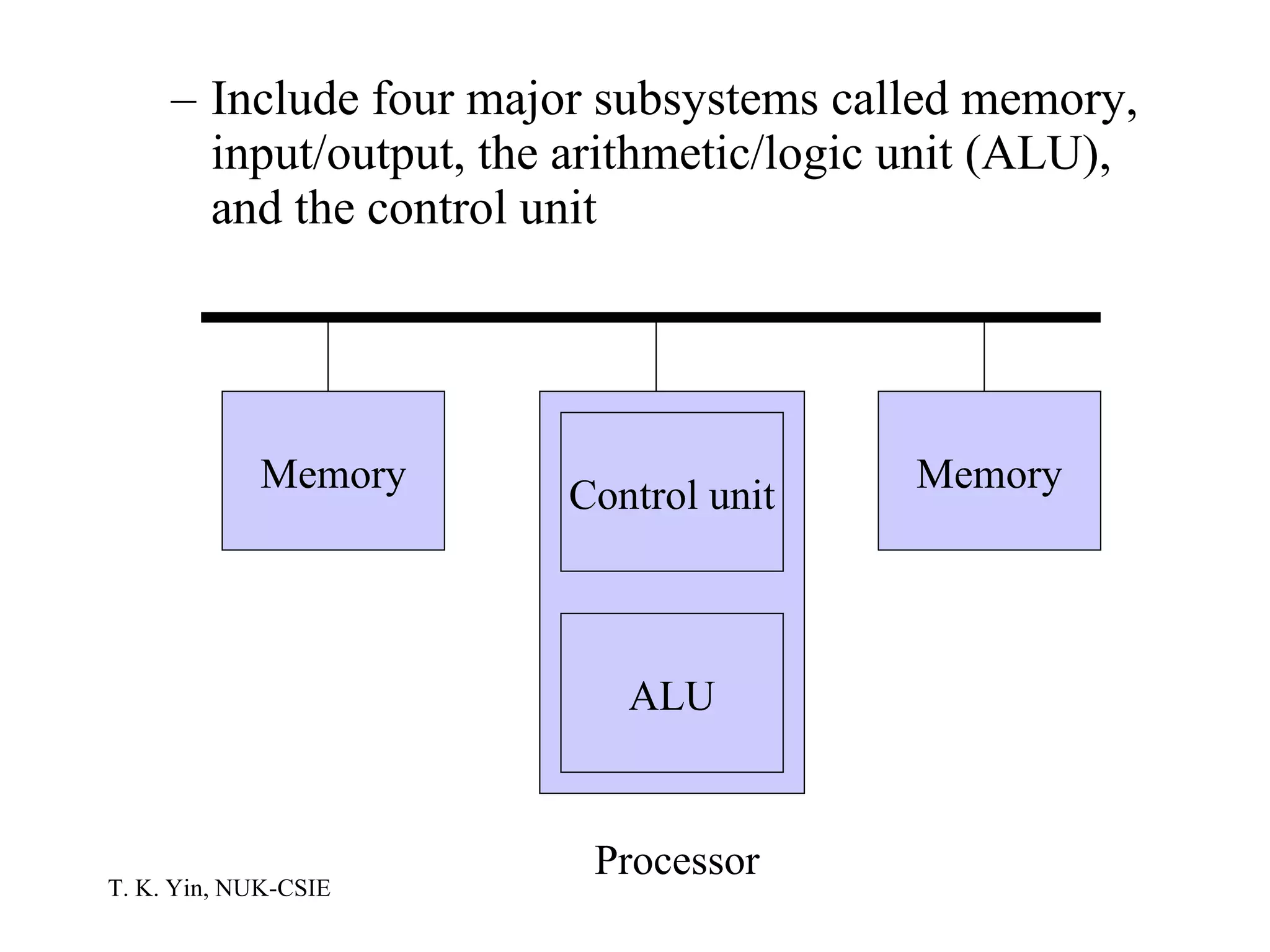
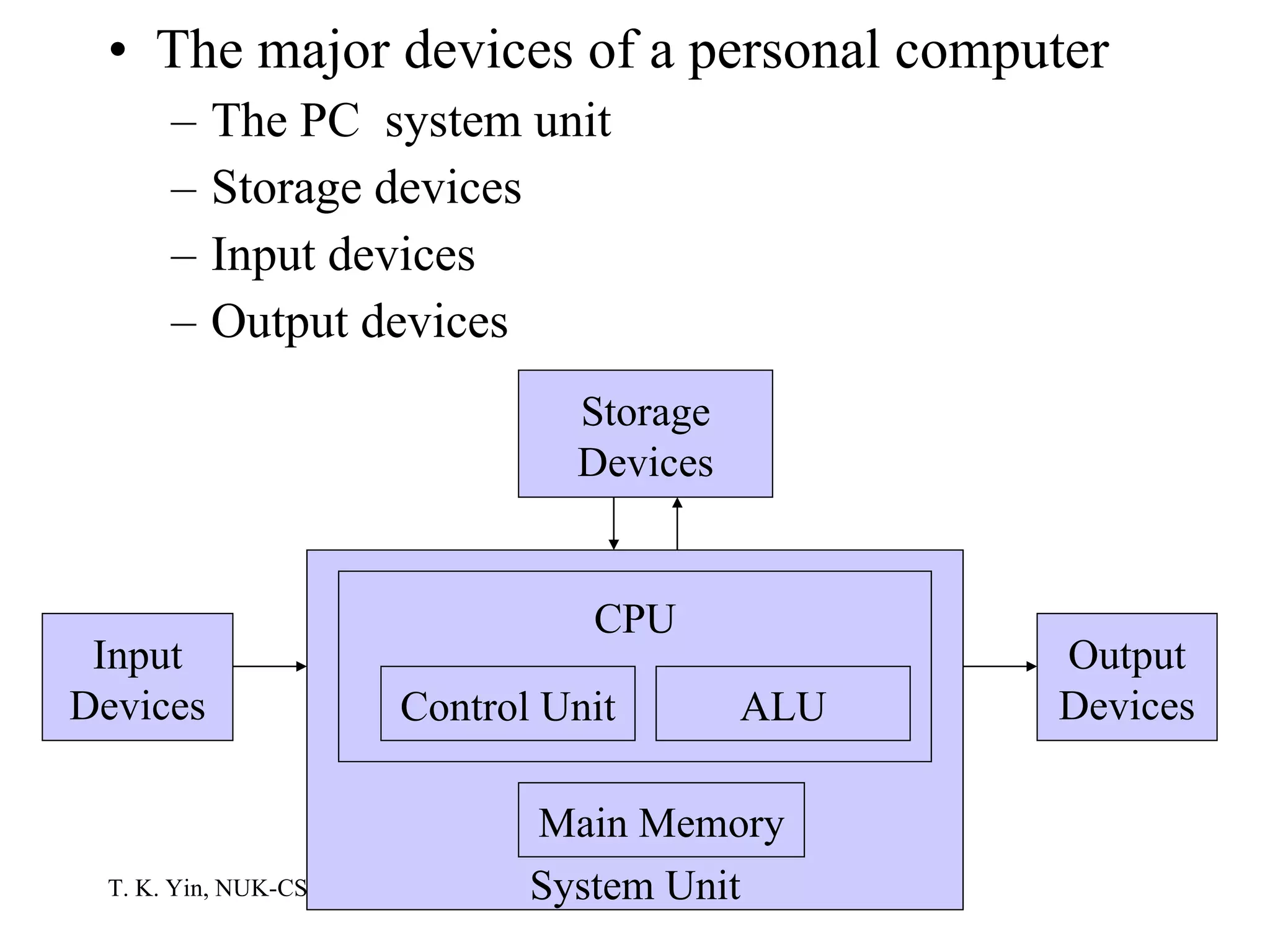
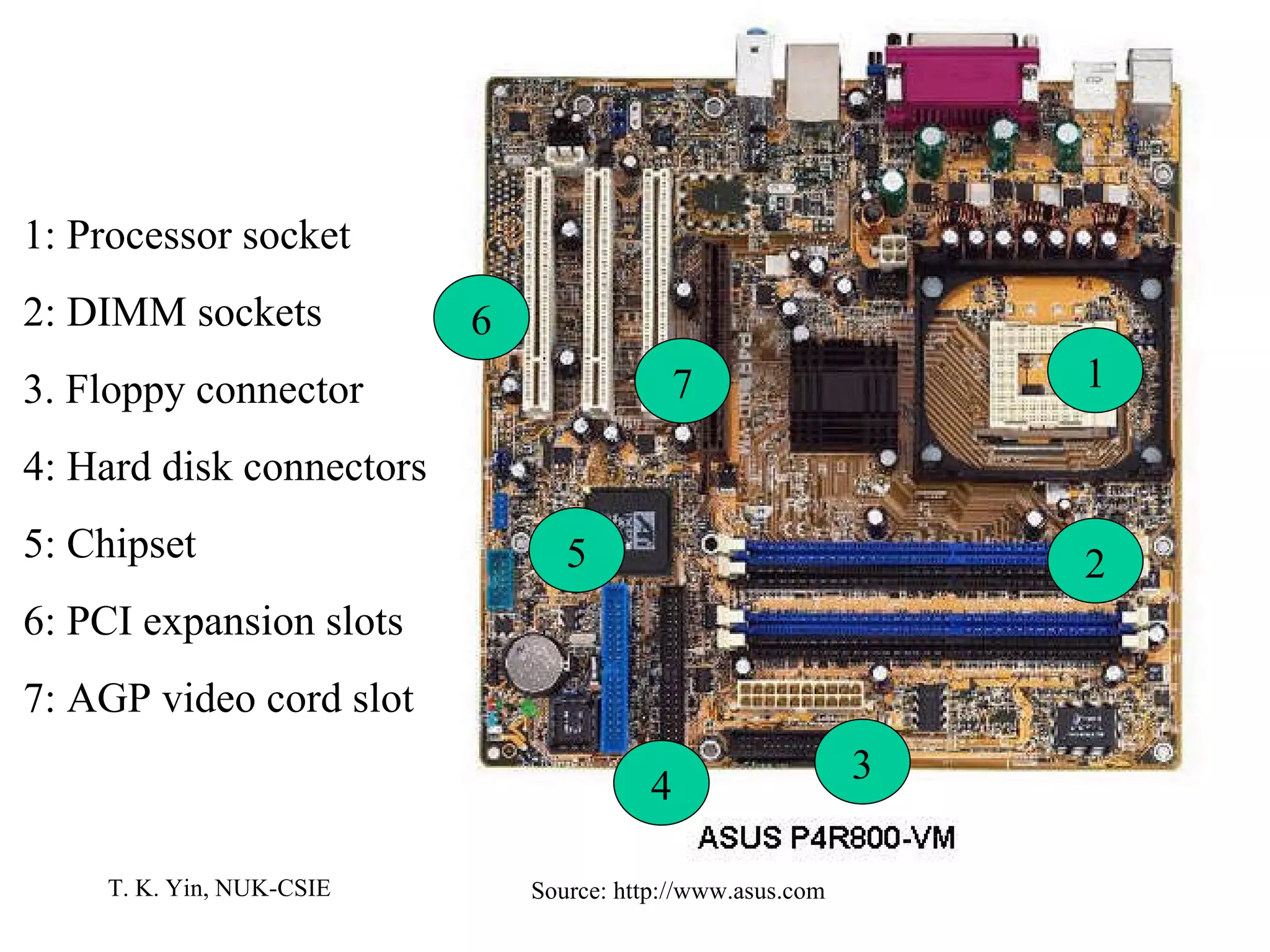
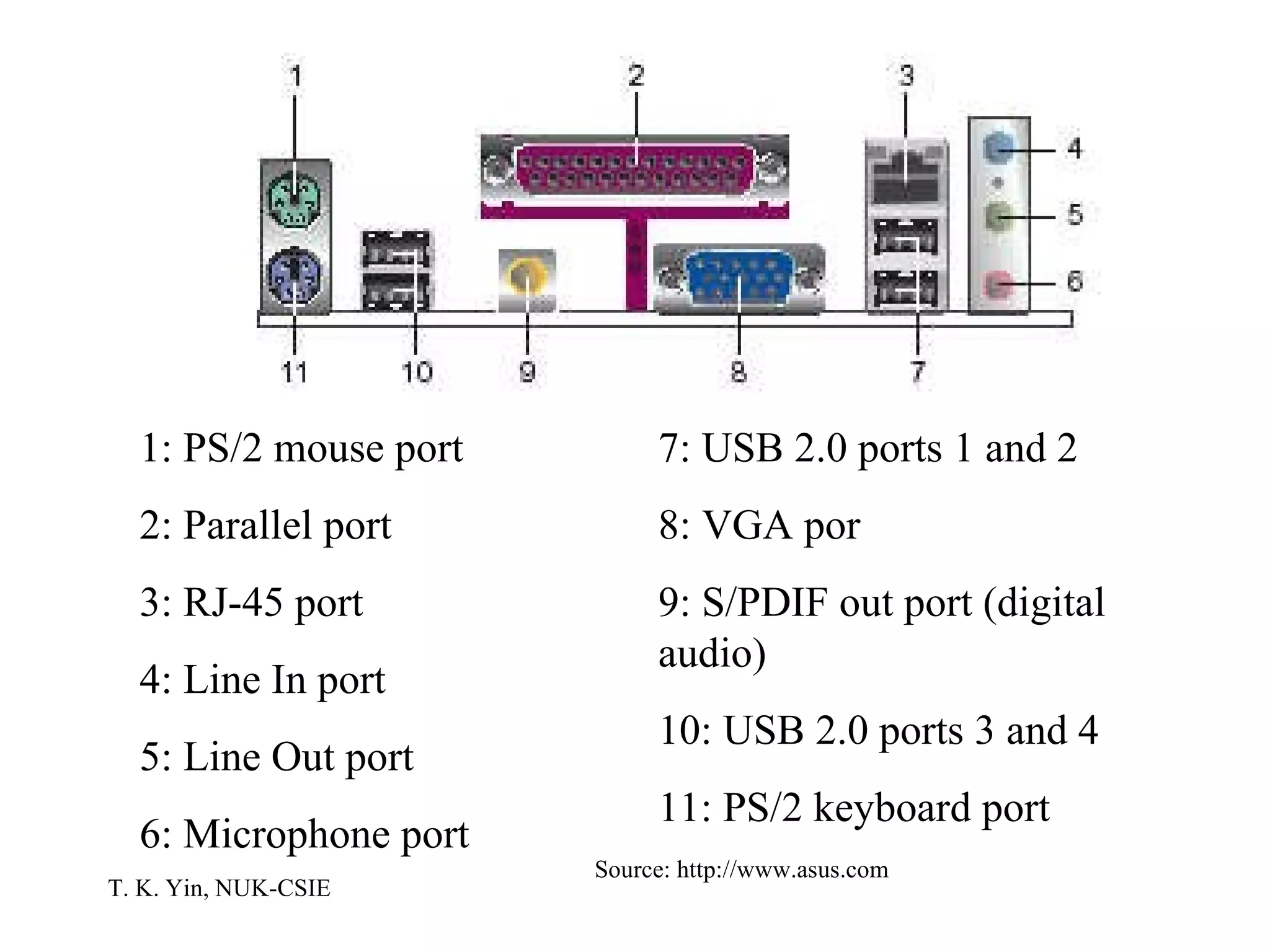
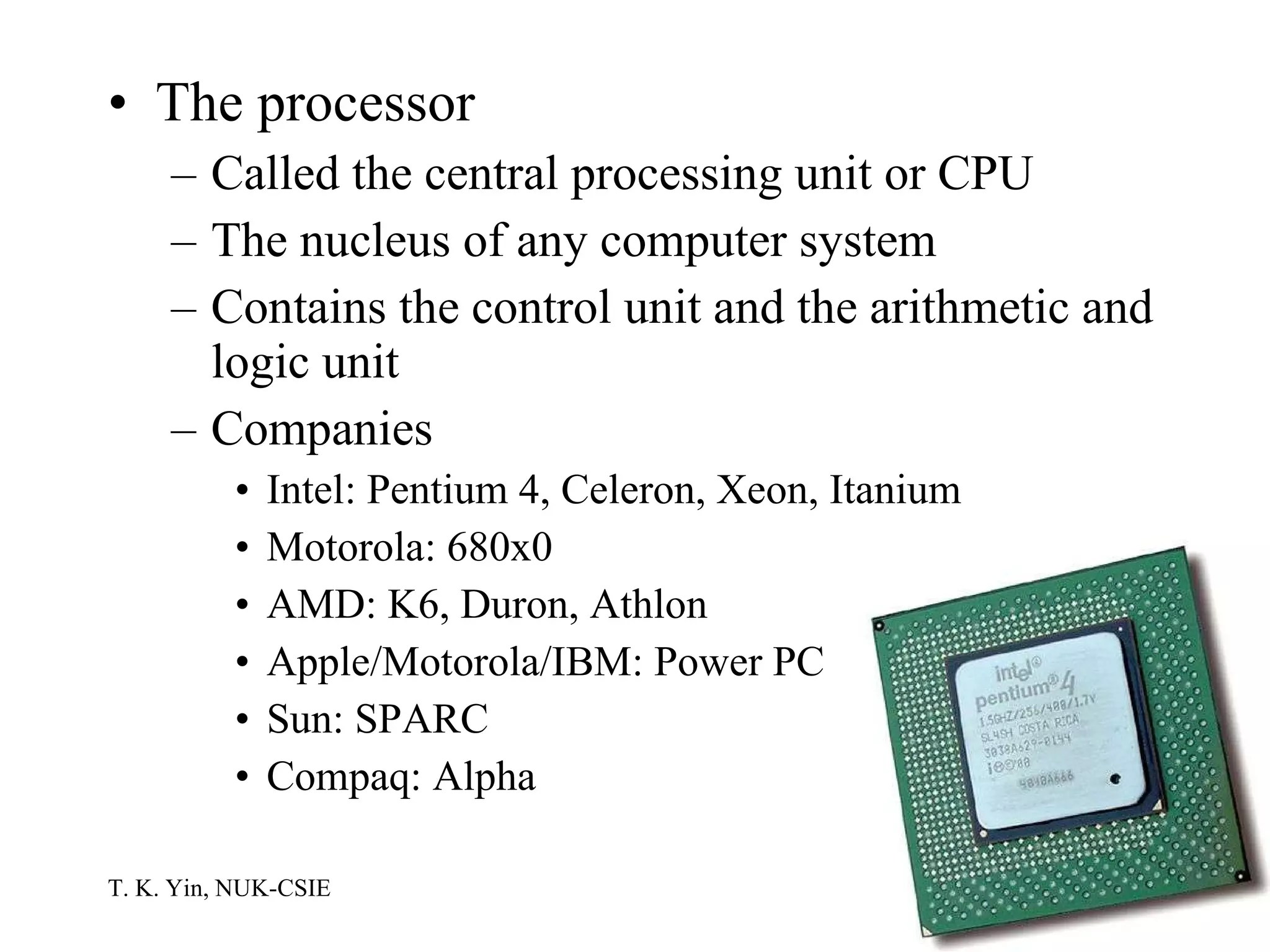
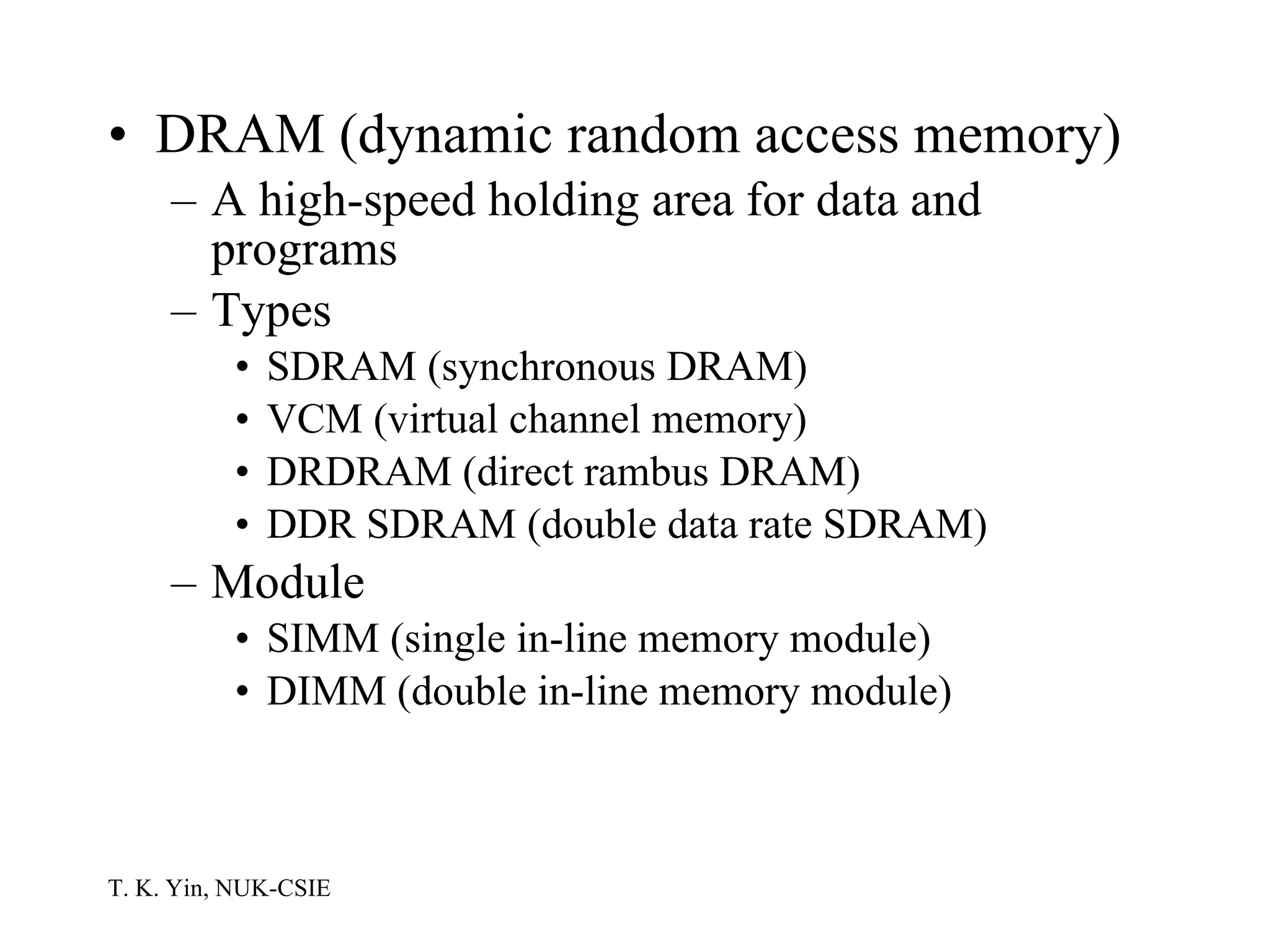
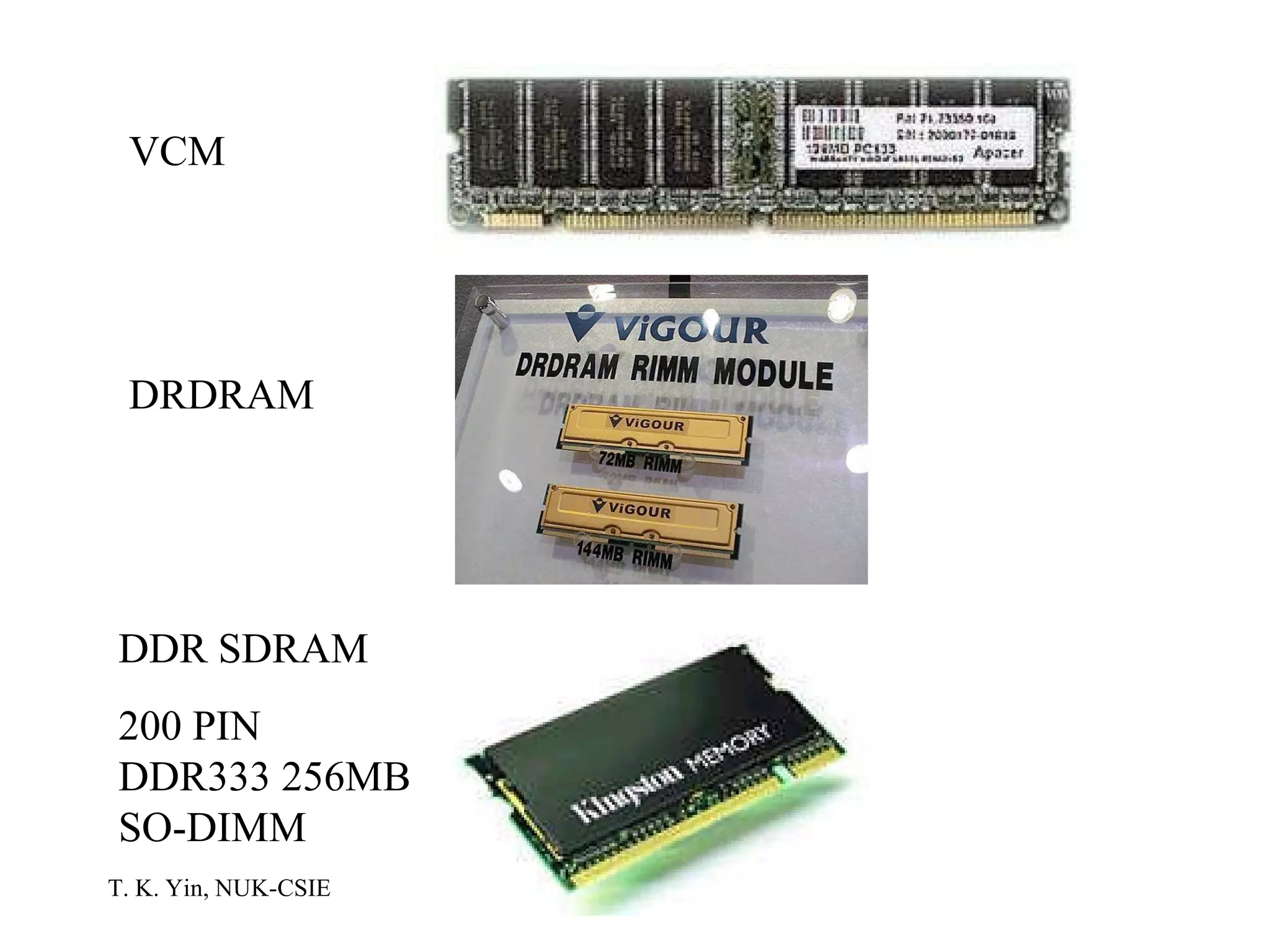
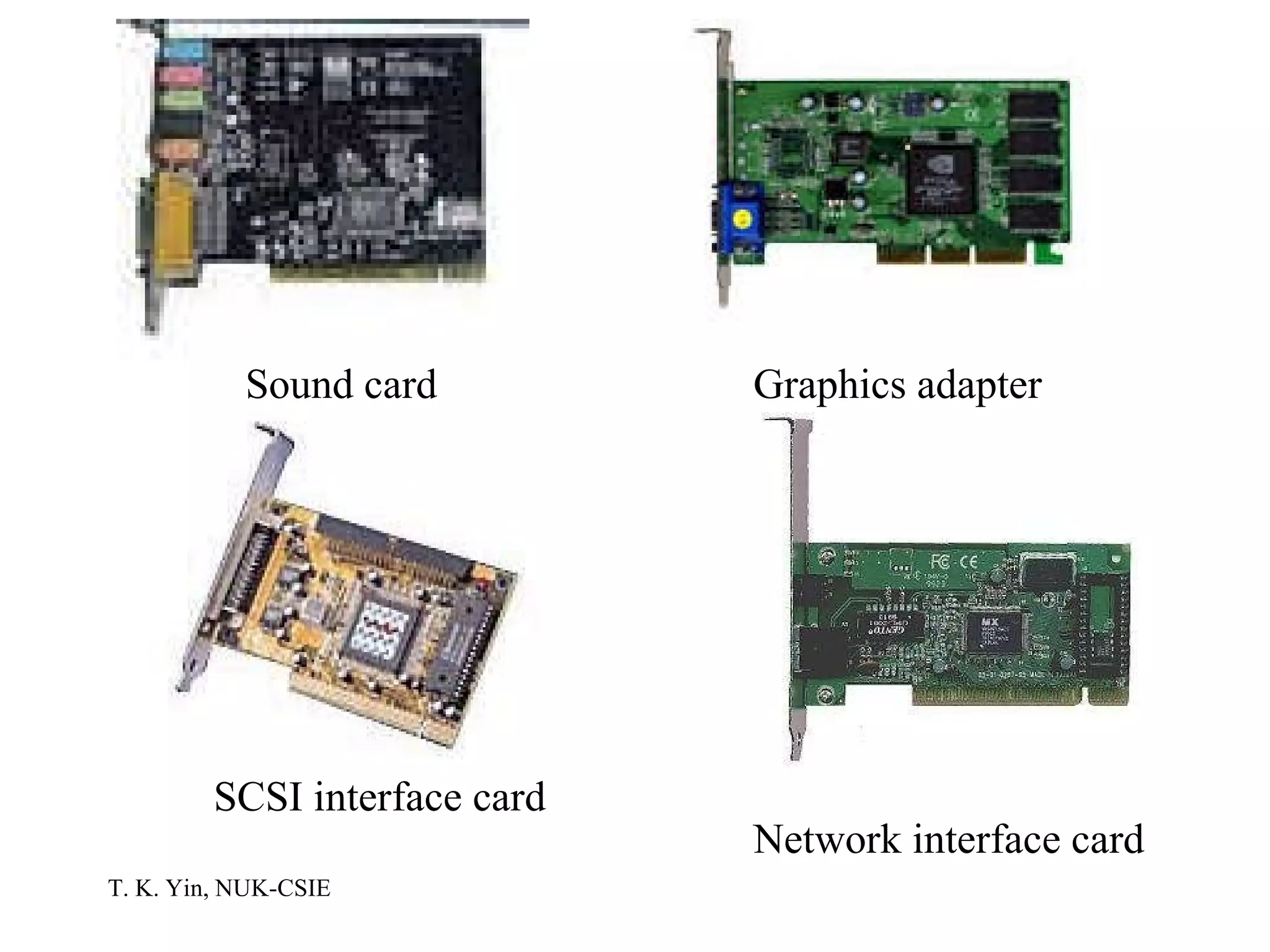
The document provides an overview of computer hardware and software components. It describes how a computer system consists of hardware, software, and data. The hardware includes components like the central processing unit, memory, storage devices, input/output ports, and peripheral devices. Software includes operating systems and programs. Data is the raw information input and output of the computer. Key components like CPUs, memory types, storage media, ports, expansion boards, and input/output devices are explained.