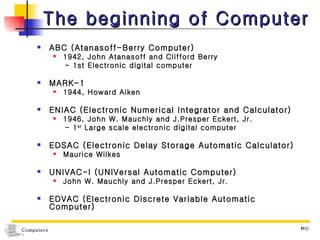
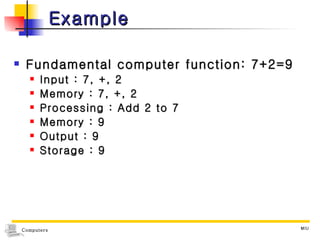
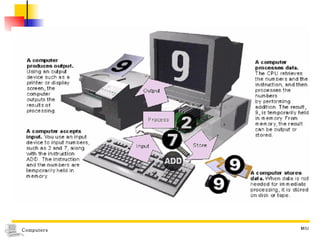
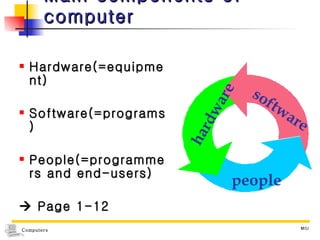
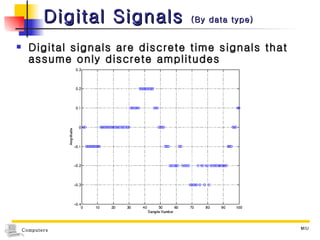
1) Computers accept input, process data, store data, and produce output based on concepts from John von Neumann's influential report. 2) Early computers included the ABC, ENIAC, EDVAC, and UNIVAC. The ENIAC was one of the first large-scale electronic digital computers built for military calculations. 3) Computers are now classified based on data type (digital, analog, hybrid), purpose (specialized, general), and processing capabilities (microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframes, supercomputers).