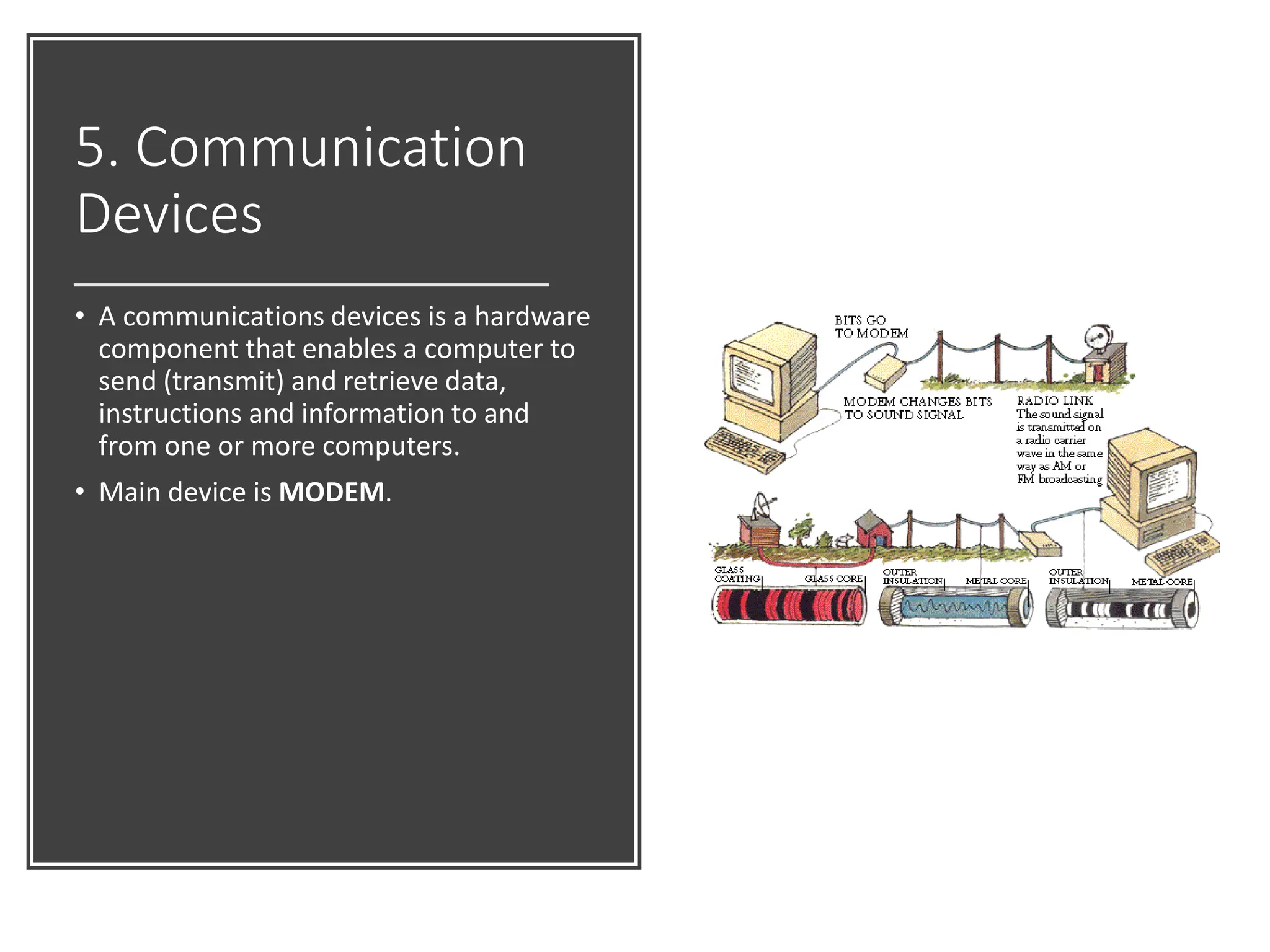
Chapter 2 of the document introduces multimedia technology with a focus on computer hardware, detailing the components vital for a powerful computer: speed, reliability, accuracy, storage, and communication. Key concepts include the information processing cycle, major hardware components including input/output devices, the system unit, memory types (volatile and non-volatile), and storage devices. Additionally, it outlines how the CPU interacts with memory and storage, and describes communication devices like modems that facilitate data transmission.



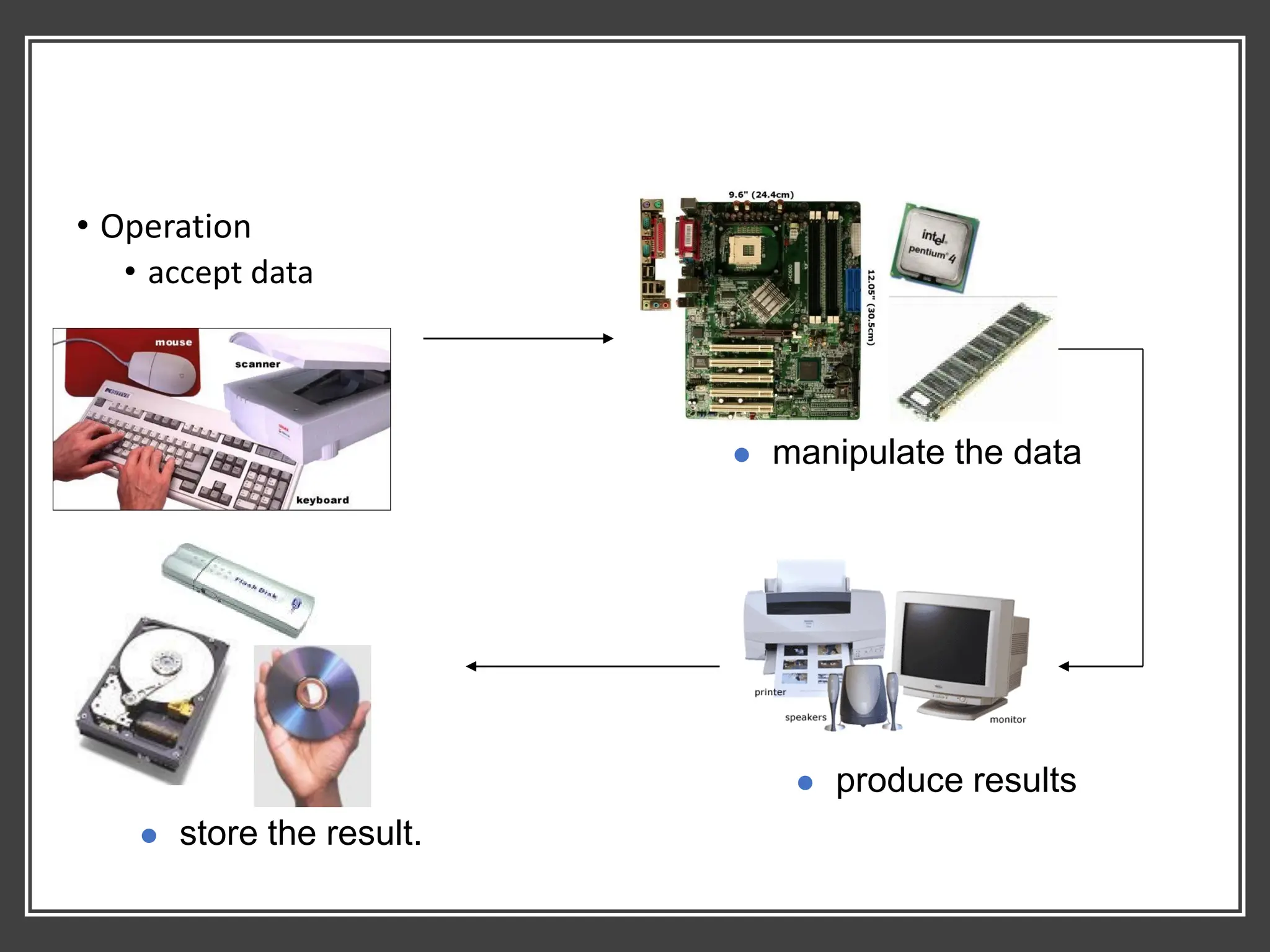



![3. System Unit
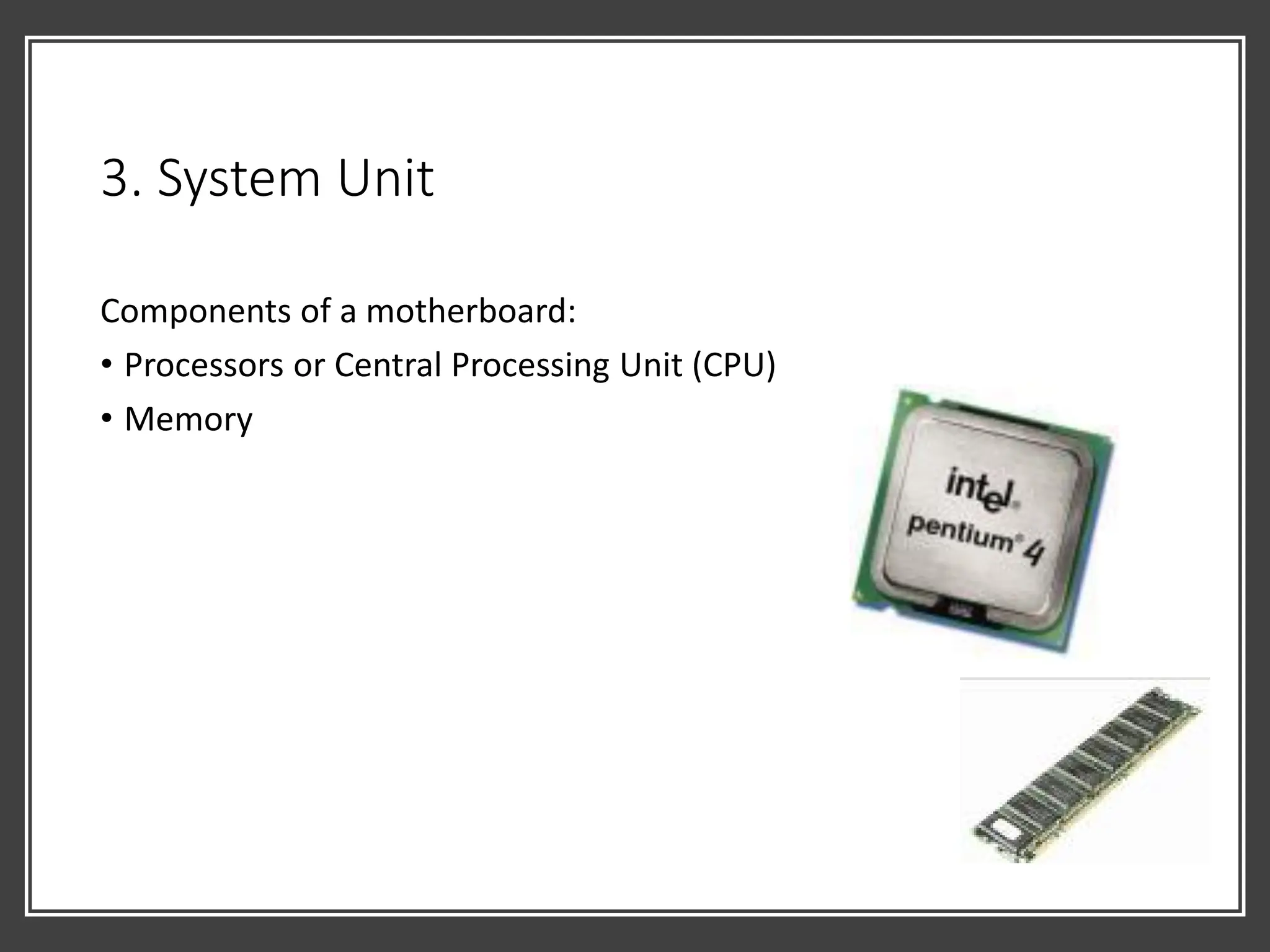
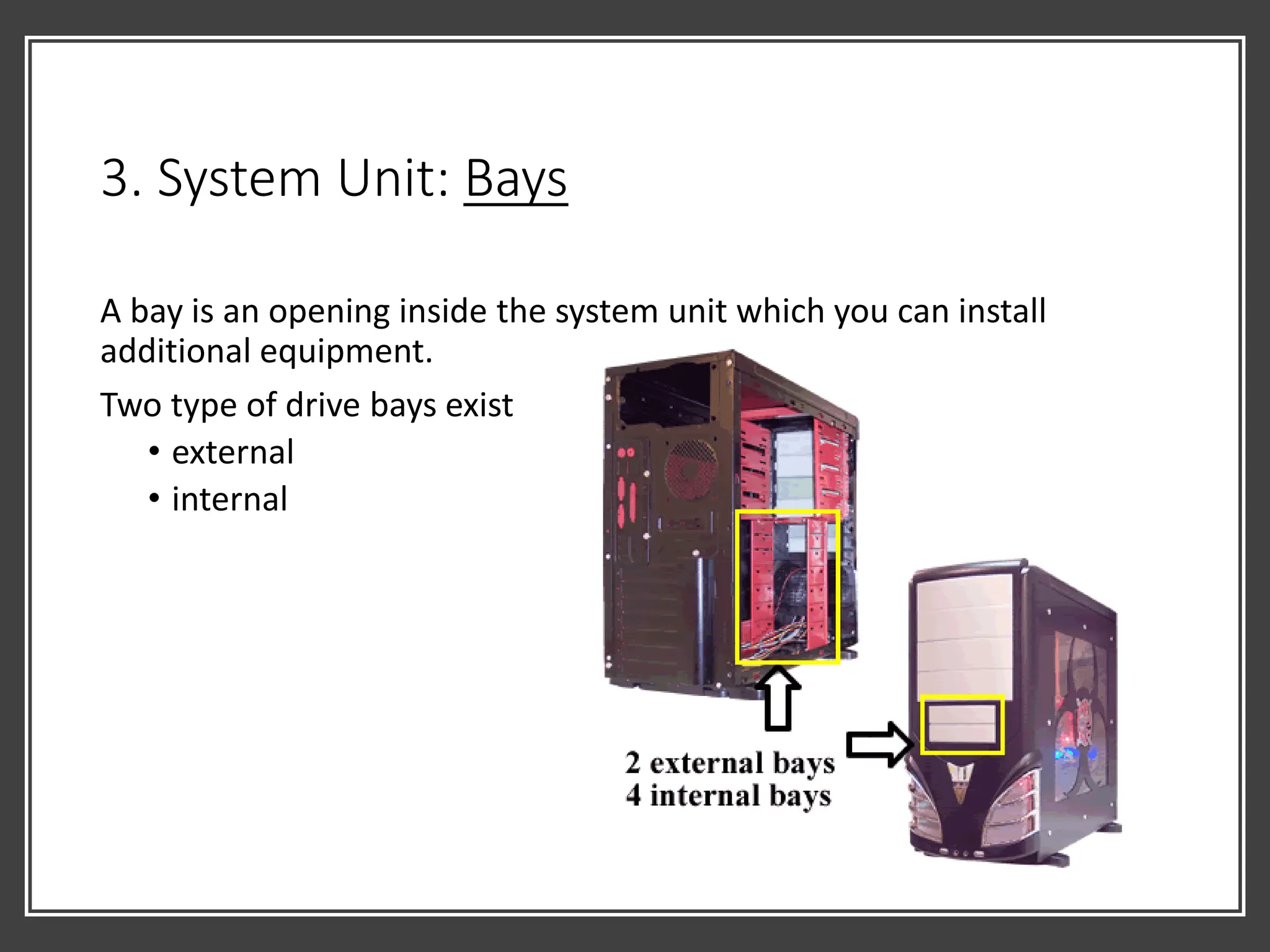
• Box like case that contains electronic components of the computer
that is used to process data. [1]
• Usually is part of or is connected to a circuit board called
MOTHERBOARD. [2]
• Electronic components attached to motherboard – cards, processors,
memory chip. [3]
[1] [2] [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture02multimediatechnologypart1-240531030029-eda4e5b4/75/Multimedia-Chapter-2-Multimedia-Technology-Part-1-pdf-11-2048.jpg)

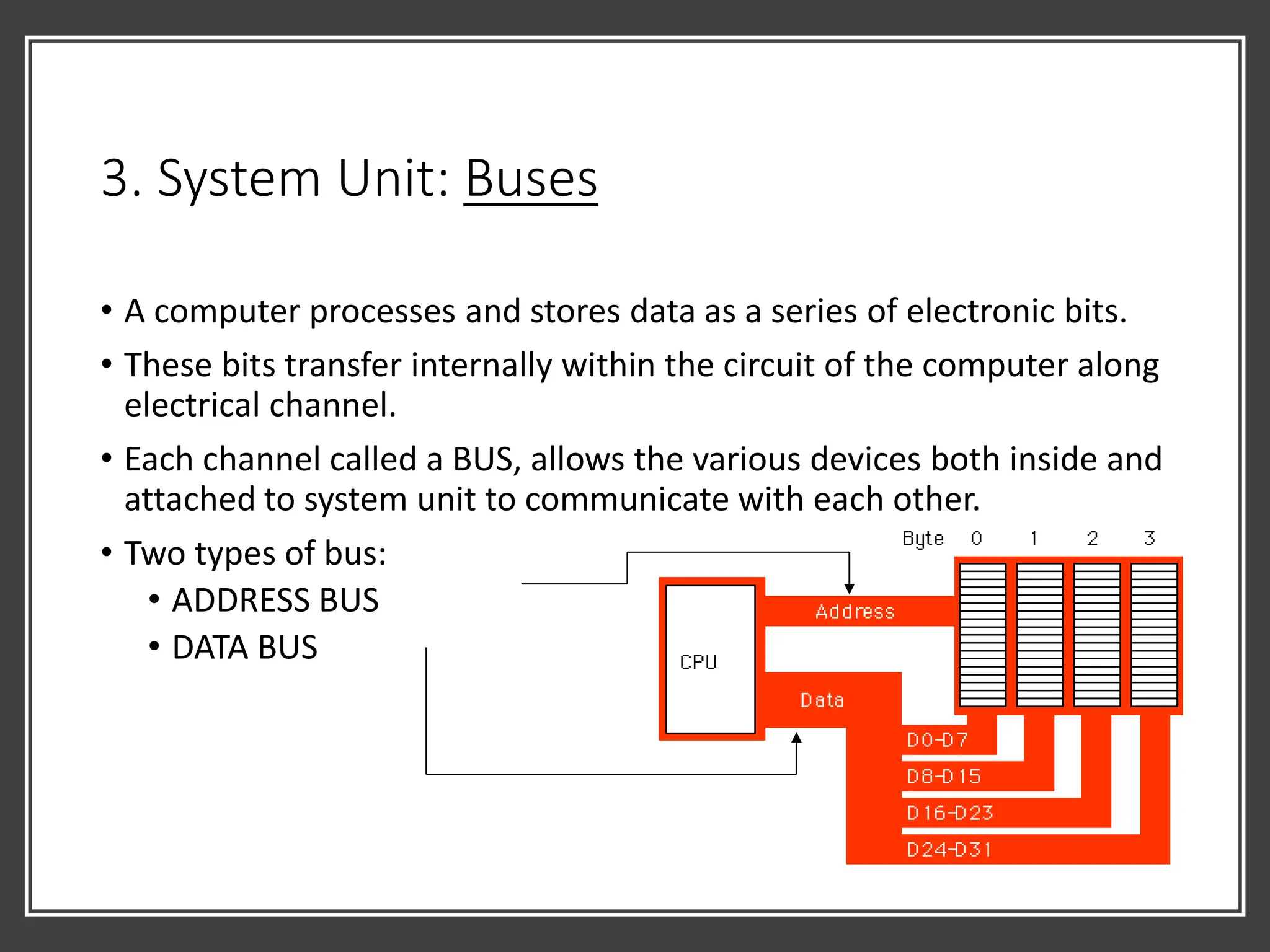


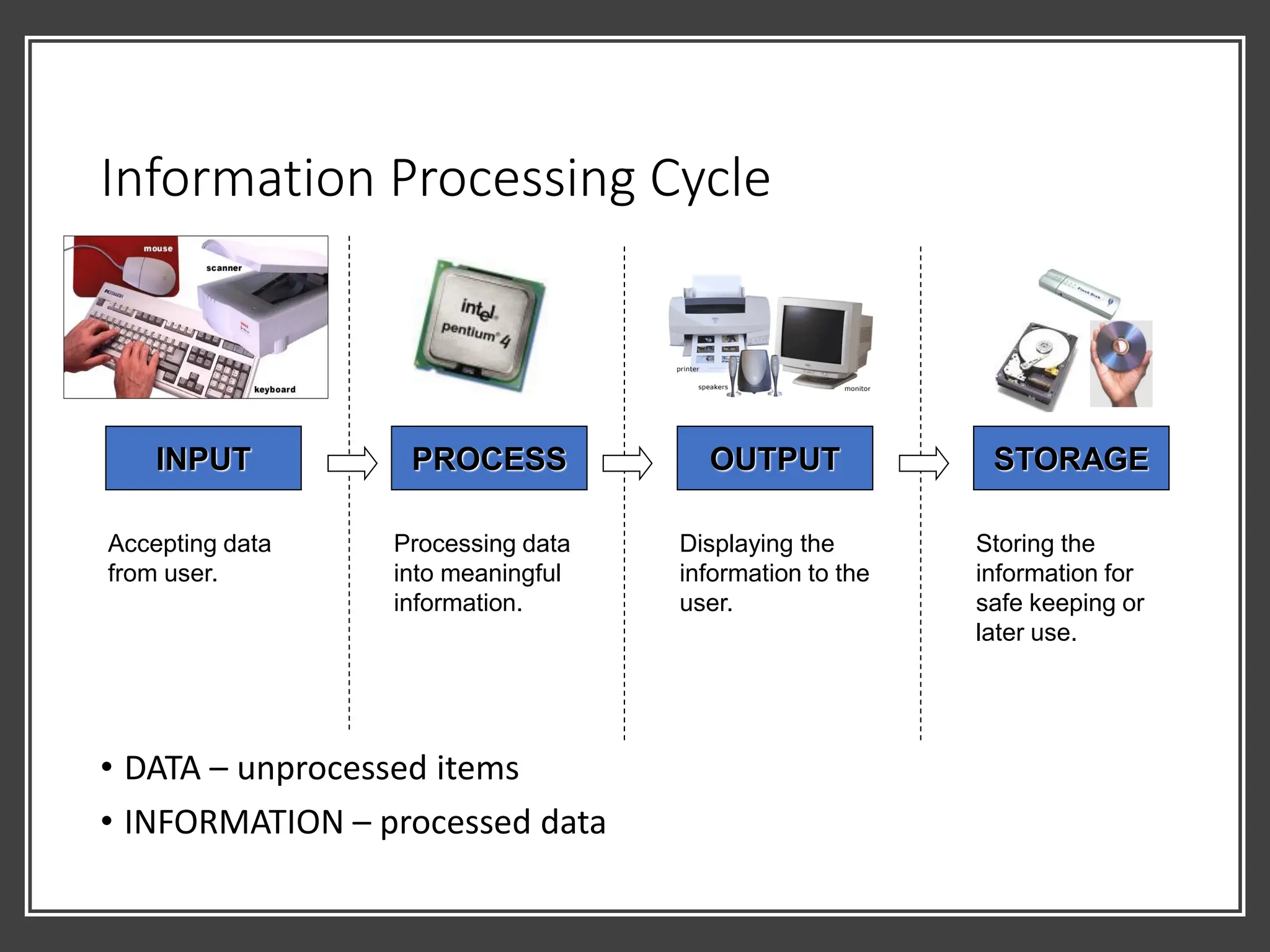
![Relationship between CPU, Bus, Memory,
Storage
• Each time a process needs to be done,the CPU will take it from the
storage media and bring it into the RAM. [1]
⚫ The process is done in the
RAM [2]
⚫ When the SAVE button is
pressed, the processed
information will be sent into
the storage media [3] for
permanent storage.
⚫ CPU assigns each data a unique address.
⚫ Each time a data needed to be accessed,
its address is called so that the data can
be fetched.
⚫ Every data is sent through the bus. [4]
2 1
3
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture02multimediatechnologypart1-240531030029-eda4e5b4/75/Multimedia-Chapter-2-Multimedia-Technology-Part-1-pdf-36-2048.jpg)