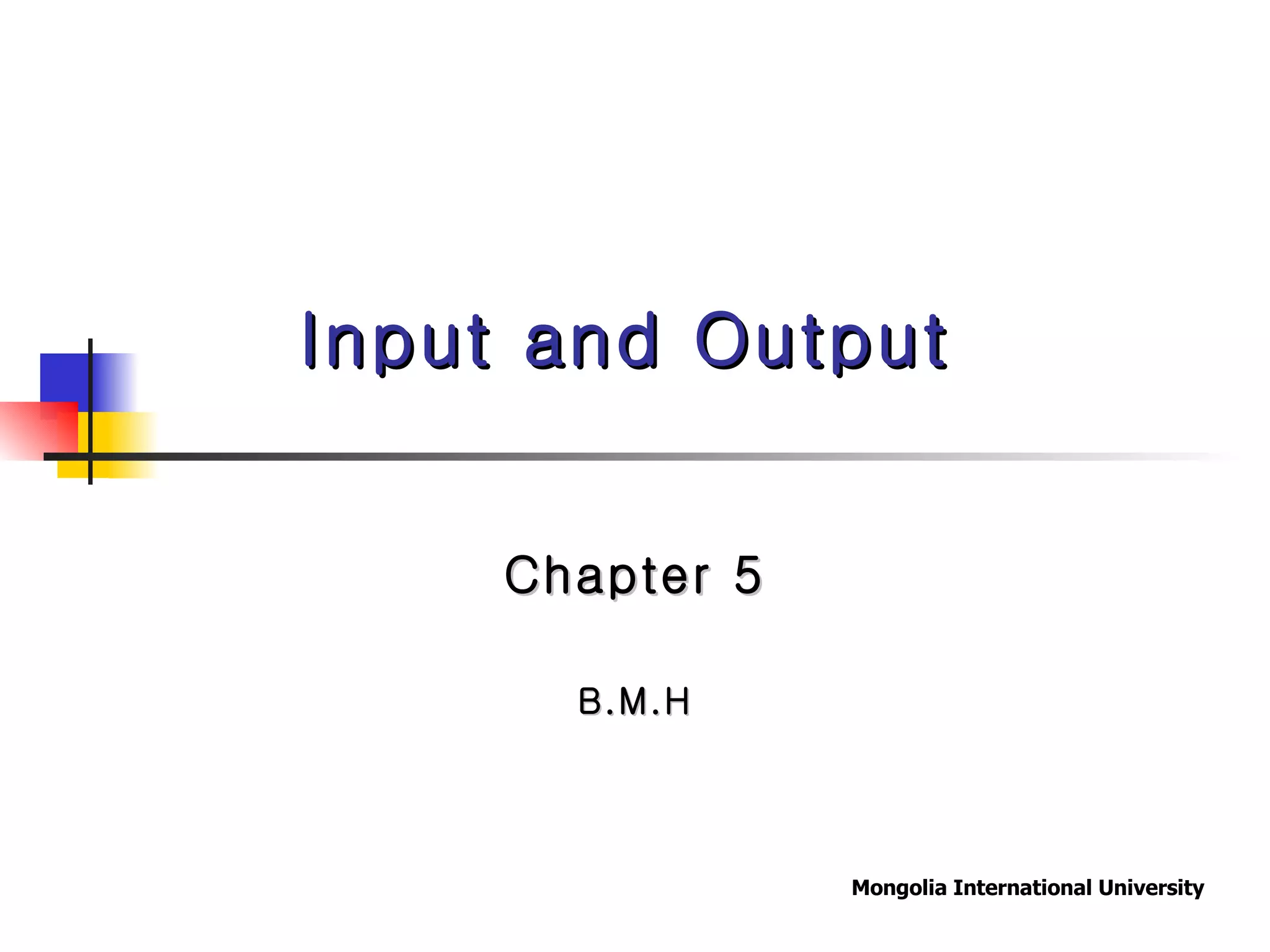
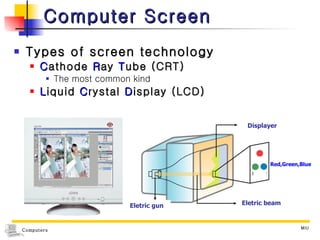
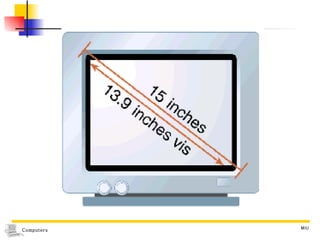
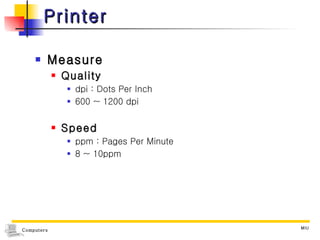
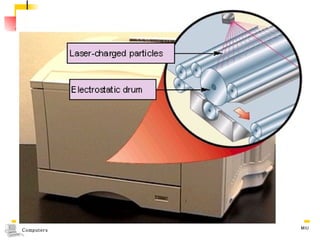
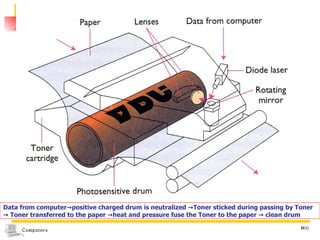
The document summarizes different types of computer output devices and technologies. It discusses cathode ray tube (CRT) and liquid crystal display (LCD) computer screens, including resolution standards. It also covers impact and non-impact printers such as dot matrix, laser, and inkjet printers. Additionally, it mentions voice output using speech synthesis, as well as music output and sounds through speakers, sound cards, and MIDI interfaces.