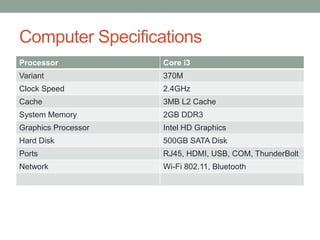
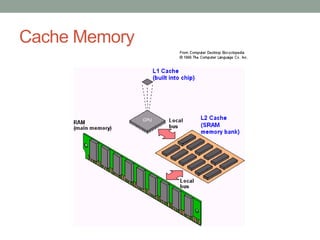
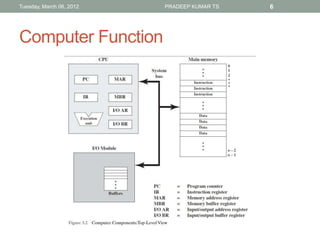
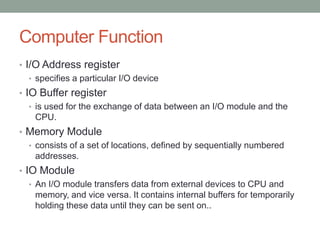
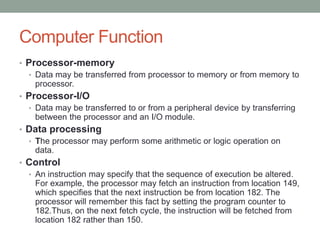
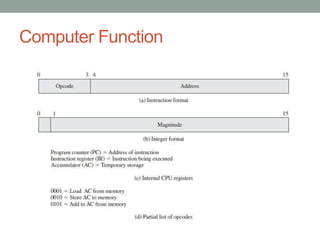
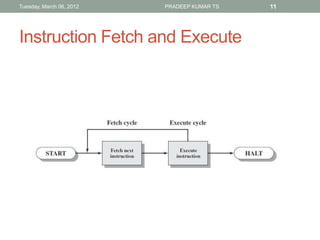
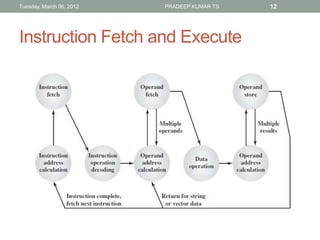
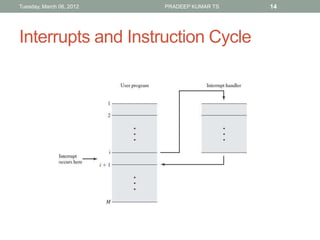
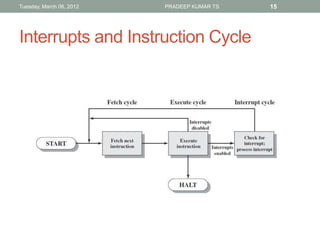
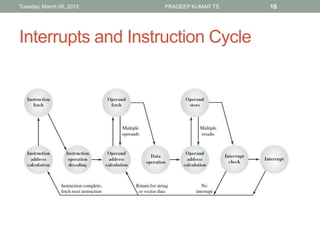
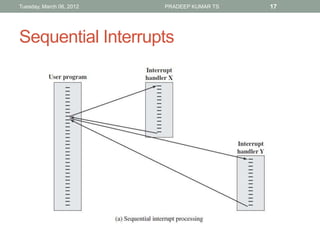
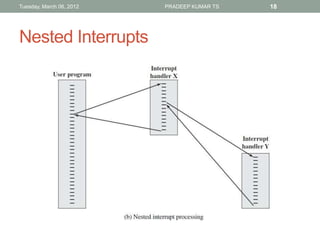
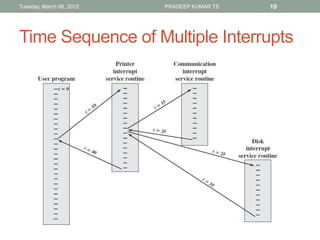
The document describes the basic functions and components of a computer. It discusses the processor, memory, input/output modules, and how they interact. It also covers the fetch-execute cycle, how interrupts work, and how the computer handles multiple interrupts.