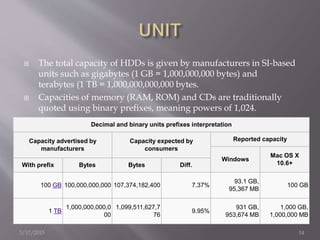
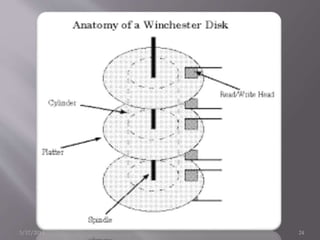
This document provides information about different types of storage devices used in computers. It discusses magnetic storage devices like floppy disks and hard disks, which use magnetism to store binary data. Optical storage devices like CDs and DVDs use lasers to read and write data to reflective surfaces. Solid state storage devices like flash drives store data electronically without moving parts. Hard disk drives are described in more detail, including how data is stored by magnetizing metal platters and read with magnetic read/write heads. Performance is measured by data rate and seek time. Popular hard drive manufacturers are also listed.