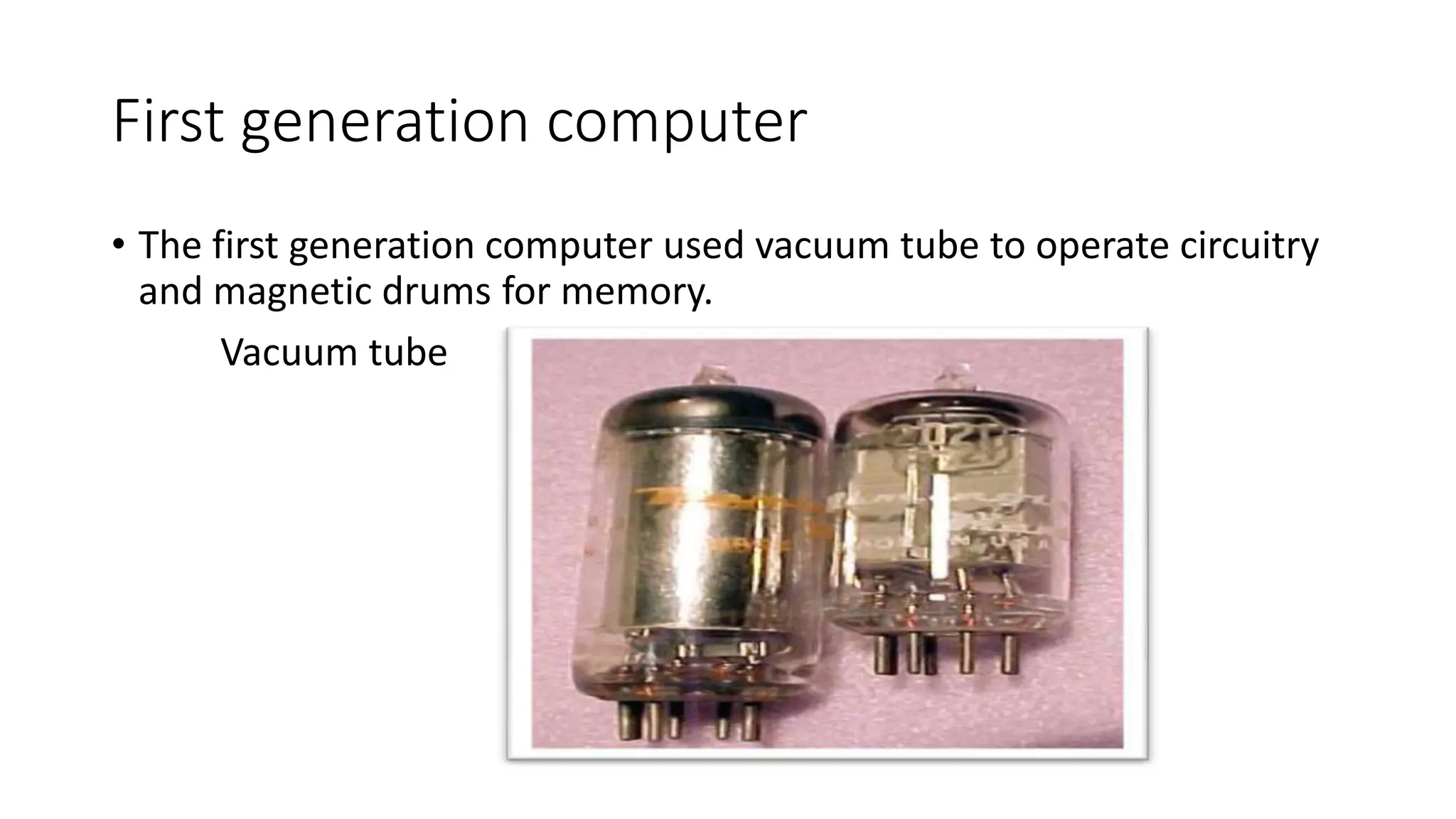
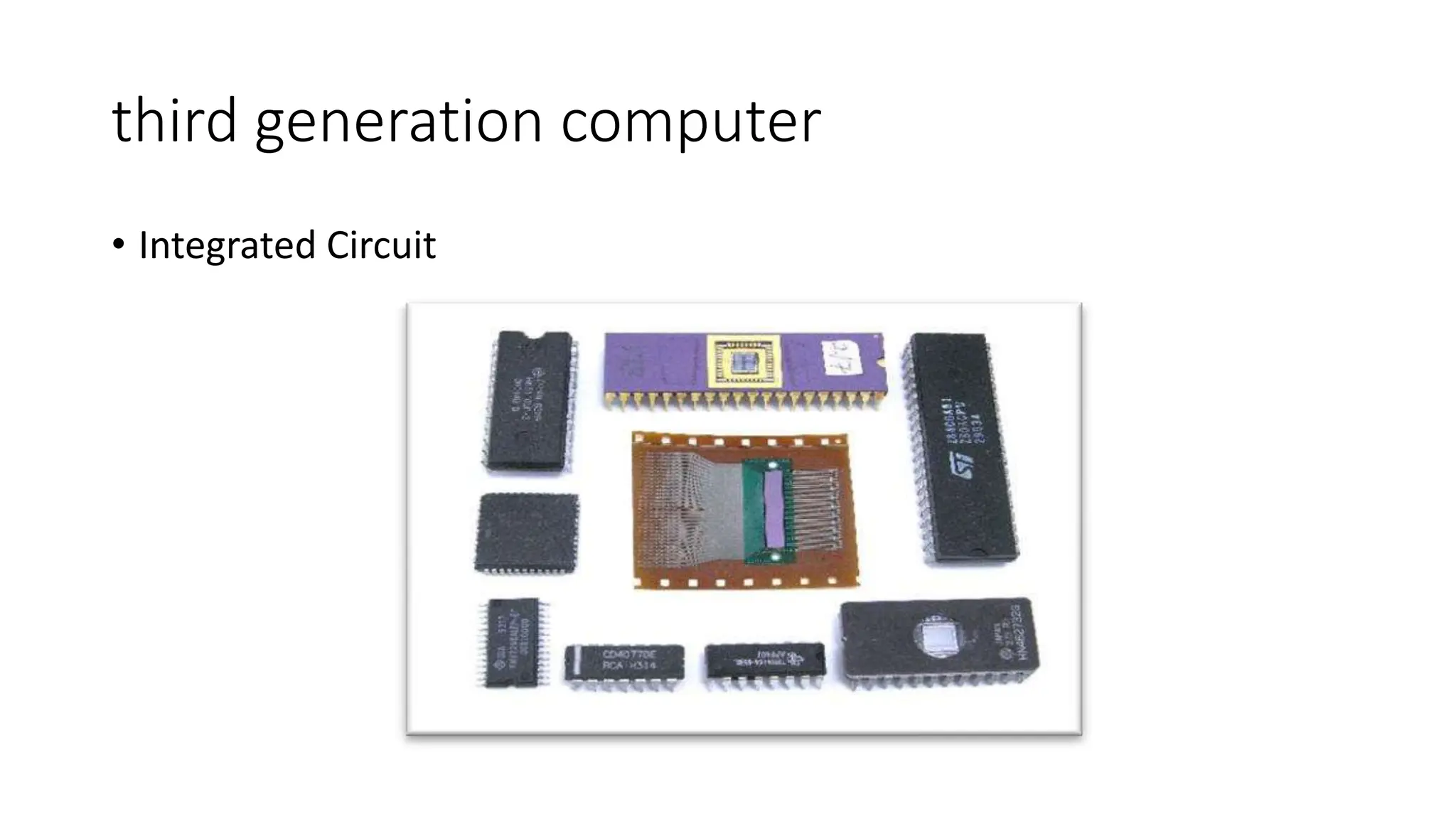
The document outlines the history of computers across five generations, detailing their evolution from vacuum tube-based machines in the first generation to modern devices utilizing artificial intelligence in the fifth generation. Each generation introduced significant improvements in size, speed, efficiency, and user interaction methods. Current advancements focus on AI development, aiming for devices capable of natural language processing and self-learning.