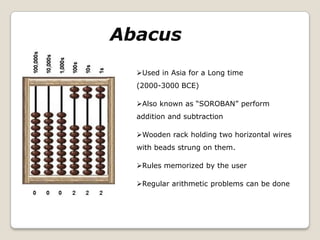
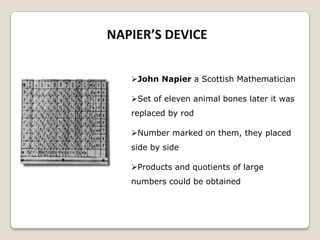
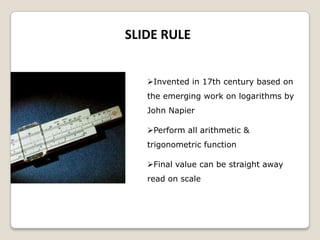
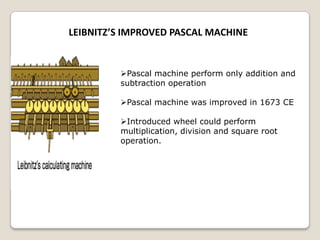
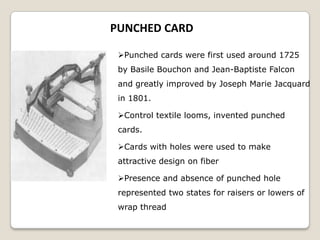
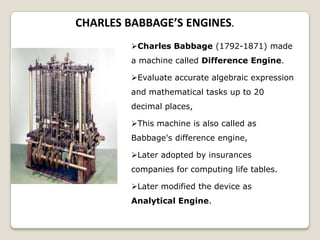
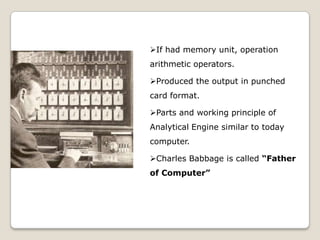
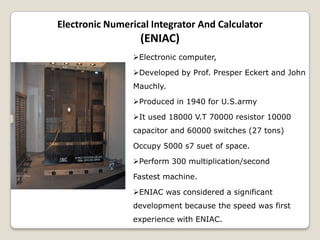
The document summarizes the evolution of computers from ancient counting devices like the abacus to modern computers. It describes early mechanical calculating devices developed by Napier, Pascal, and Leibniz. Punched cards were introduced in the 18th century to control looms. Babbage designed analytical engines in the 1800s but they were never completed. The first digital computers like ENIAC, EDVAC, EDSAC and UNIVAC used vacuum tubes. The microprocessor was invented in 1969, leading to personal computers in the 1970s. Modern computers integrate all components into a single chip called a system on chip.