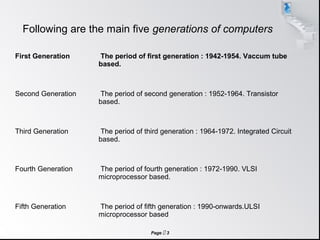
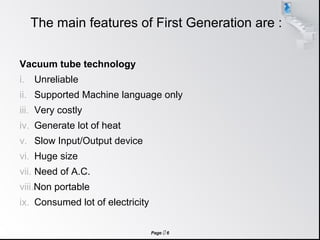
The document outlines the five generations of computers, detailing their technology, time periods, and characteristics. From the vacuum tube-based first generation to the ultra large scale integration technology of the fifth generation, it highlights key advancements and features that define each era. The evolution reflects major improvements in reliability, cost, size, power consumption, and the introduction of artificial intelligence.