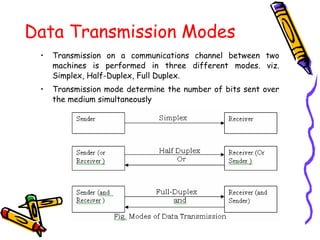
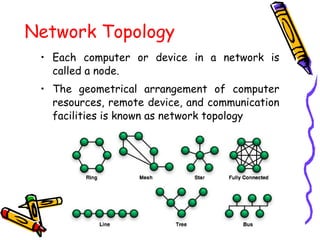
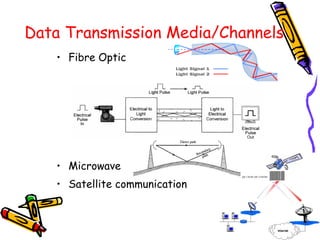
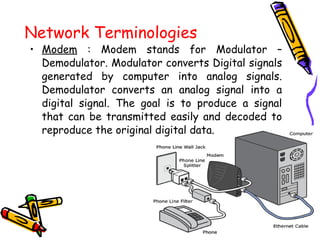
This document discusses computer networks and networking concepts. It defines a computer network and describes the main objectives of sharing information and resources. It discusses different types of networks like LAN, WAN, MAN and wireless networks. It also covers various networking terminologies like bandwidth, protocols, multiplexing, and network devices like hubs, switches, routers and gateways. Finally, it discusses different data transmission media and modes used in computer networks.