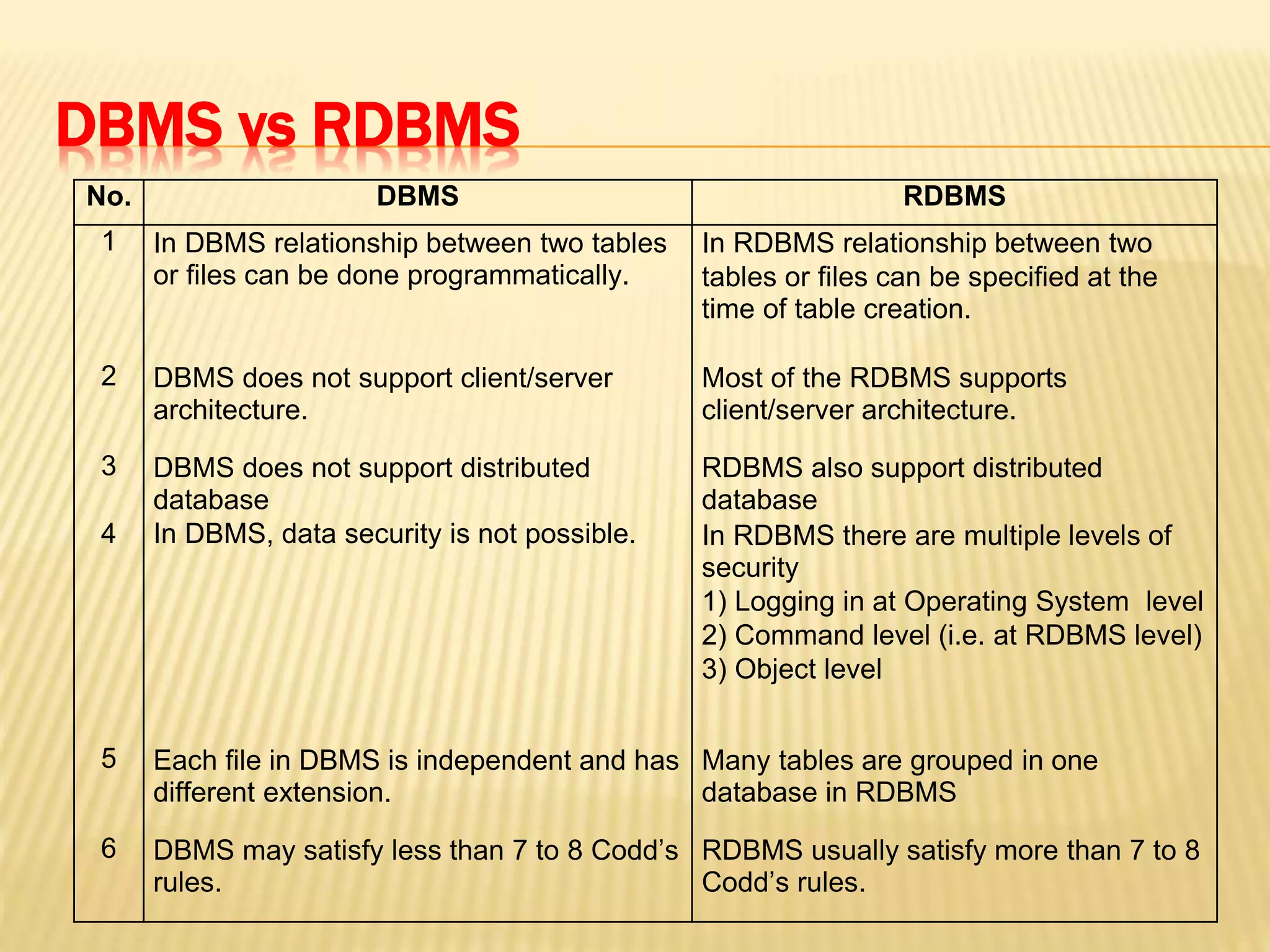
The document discusses database management systems (DBMS) and relational database management systems (RDBMS). It defines them and explains some of their key advantages, including data independence, consistency, control over redundancy, and greater security. It also describes the roles of a database administrator (DBA) and how they design, implement, and maintain the database environment. Finally, it provides brief definitions of data warehousing as a repository for organizational data and data mining as the process of extracting patterns from stored data.