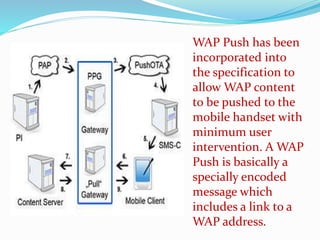
Wireless banking is becoming increasingly important due to customers' need for banking on the go. It allows customers to bank from anywhere at any time through their mobile phones. Mobile banking can be done through SMS or WAP. SMS banking allows customers to access accounts and get information through push or pull messages. WAP banking uses the internet to access banking through a mobile browser. While convenient for customers, wireless banking also poses challenges for banks in areas like security, device compatibility, and reliability.