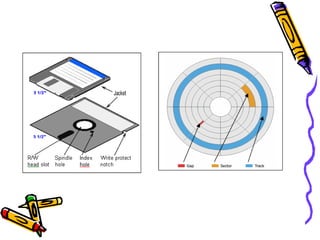
This document discusses different types of computer memory. It describes primary memory, which is directly accessible by the CPU, including RAM and ROM. RAM is volatile and used for active programs and data, while ROM is non-volatile and contains startup instructions. Secondary memory is used for long-term storage and includes floppy disks, hard disks, magnetic tapes, optical disks like CDs and DVDs, and flash memory devices. Cache memory sits between the CPU and main memory for faster access.