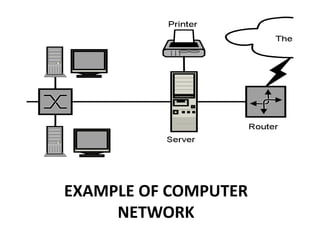
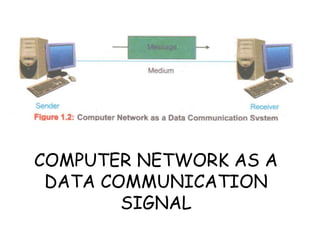
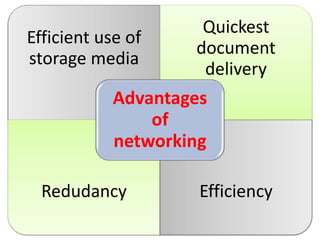
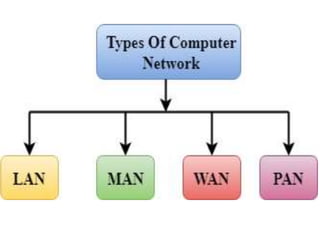
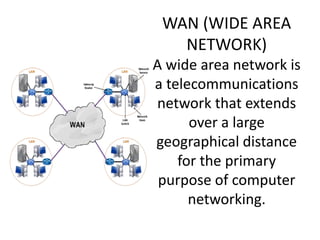
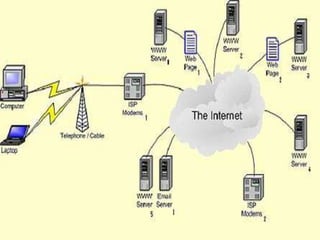
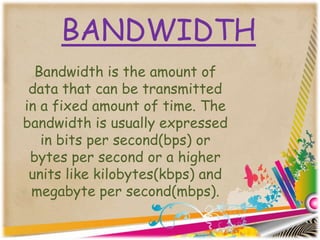
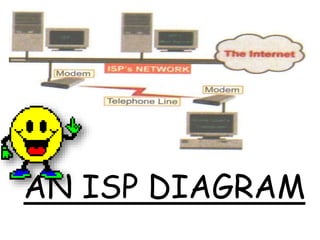
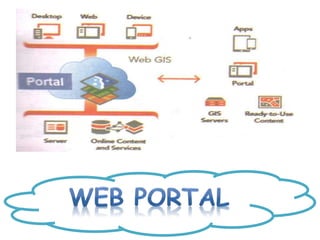
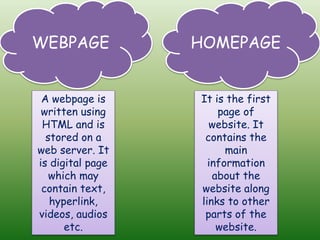
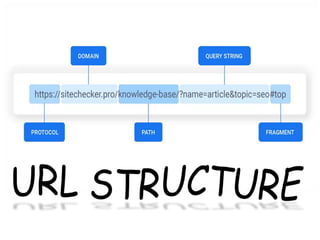
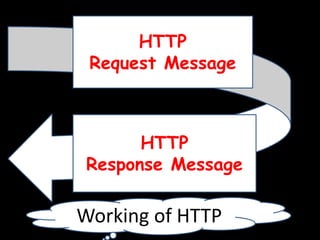
This document provides an overview of computer networking concepts for class 8 students. It defines a computer network and its basic components, including nodes, senders, receivers, and transmission medium. It describes the advantages of networking and different types of networks like LAN, WAN, MAN, and PAN. It also discusses networking media, devices, terminology, and protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, and IMAP/POP. The key topics covered include introduction to networks, networking advantages, media, types of networks, devices, terminology, and protocols.